It is a rare child who goes to the dentist voluntarily and with pleasure. Desperate to reach an amicable agreement, parents ask a logical question: why bother spending energy and money on treating baby teeth? After all, they will soon fall out. And when the molars appear, the child will grow up and behave more patiently.
The opinion of dentists is clear: it is necessary to treat baby teeth.
The main problem with baby teeth is caries. Under the influence of pathogenic bacteria, the tooth enamel is first destroyed, and then, when a hole is formed, the infection spreads inside the tooth and leads to pulpitis - inflammation of the internal tissue, usually very painful. Then, unfortunately, parents no longer have a choice whether to take their child to the dentist or not. But it shouldn’t come to this. Even if the child does not have any pain, he needs regular dental examinations.
Caries and baby teeth
Caries is the most common childhood chronic disease. According to WHO statistics, 86% of preschool children have it. The American national study National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, updated annually since the 1970s, provides interesting results: the prevalence of caries in primary teeth in children from 2 to 11 years decreased from the 1970s to the mid-1990s, but then the trend changed: the percentage of children with baby teeth affected by caries began to grow - not significantly, but quite noticeably.
The main factors on which the occurrence of caries in children depends:
- heredity
- anatomical features of the teeth, the individual ability of saliva to resist infection and the anatomical features of the teeth;
- amount of carbohydrates in diet;
- diet;
- supply of fluorine to the enamel, protecting it;
- oral hygiene; general condition of the body.
The enamel of baby teeth is less durable than that of primary teeth. Like a child’s body, it is just being formed, and therefore is damaged quickly. There is even the concept of “bottle caries” - it often develops in infants who drink sugar-containing drinks from a bottle for a long time: juice, baby tea, formula or even breast milk. Manufacturers of children's drinks always indicate on the labels that from the age of 8 months a child must be taught to drink from a cup, since drinking from a bottle can damage the enamel. It is especially dangerous to drink sweet drinks from a bottle before bed, day or night: during sleep, less saliva is released, which protects the teeth. The front teeth (incisors) are the first to be affected, since the drink hits them first.
Types of caries
You can learn to distinguish caries on baby teeth by stages from a photo, or by knowing a description of external signs:
- Initial caries of baby teeth is noticeable on the enamel as a matte white spot. It is treated by strengthening the enamel with fluoride compounds, which can be quickly eliminated if detected in a timely manner.
- Surface. The spots are still light, but pain is already possible when eating.
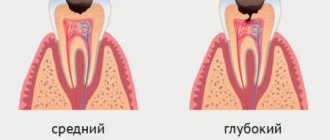
- Average. Carious cavities become deeper - the tooth enamel is already destroyed, pain appears when cold or hot.
- Deep caries. Requires an urgent appointment with a dentist and treatment, since the infection has already reached the dentin and can spread to the pulp. If you ignore caries of baby teeth at this stage, the risk of root infection and the appearance of a baby tooth cyst increases significantly.
Dolotova Marina
Little patients of Aza&Buka rarely encounter deep caries. After all, we, doctors, do everything necessary for this - we make appointments on time, teach how to brush teeth and eat right. And if caries occurs in baby teeth, we treat it as early as possible!
Treatment of caries in children
It is necessary to treat childhood caries, if only because it brings discomfort to the child: the affected teeth become sensitive to hot and cold, and then begin to hurt. In addition, advanced infection can affect the gums and affect the developing molars. If the disease starts, the affected tooth will have to be removed long before it falls out on its own, and this is also undesirable - an incorrect bite may form.
Modern methods of caries treatment help quickly and safely. In general, they come down to isolating the affected part of the tooth, cleaning it and covering it with a protective layer that will prevent caries from spreading again. This could be silvering of teeth, treatment of caries with laser, ozone, according to the ICON system, coating with a remineralizing gel containing fluoride and calcium, or filling, if necessary - the treatment method that is suitable for your child should be entrusted to a qualified dentist.
Regular children's medical examinations are not a whim of dentists, but a necessity
Children's dentists in Moscow recommend bringing your heirs for free medical examinations every 3-4 months to guarantee them a beautiful smile and healthy teeth. If the carious process is not stopped in time:
- a chronic focus of inflammation will appear in the baby’s body, the infection from which can spread to other systems and, in particular, cause severe inflammation of the jaw bone;
- caries that has developed into pulpitis and periodontitis can cause severe pain;
- the rudiments of permanent teeth may suffer or die.
What other problems can arise with baby teeth?
In addition to caries, the child may experience disturbances in the formation of enamel. Moreover, the problem can be not only too thin enamel or insufficient mineralization of teeth, but also excessive formation of enamel (hyperplasia) or even oversaturation of the body with fluoride (fluorosis). At the same time, the enamel changes color and becomes fragile, brittle, and the teeth become deformed. Fluorosis is most often diagnosed in children 3-4 years old.
In order to identify the problem in time and get rid of it, at the first warning signs, for example, darkening of the teeth, the appearance of stripes on them, you need to contact a pediatric dentist. Most diseases of primary teeth are quite treatable; the main thing is not to try to make a diagnosis yourself and not to let the process take its course.
An eternal problem: is it necessary to treat temporary teeth in children?
Some parents do not see the need for such treatment, because they believe that after 6 years, baby teeth will gradually fall out and be replaced by permanent ones. But even one temporary tooth affected by caries and not treated in a timely manner can provoke unpleasant consequences that will create problems in adult life.
However, 5-6 year old children are often brought to see the dentist with “acute pain” and one or even several front teeth that have been destroyed right under the gums. The parents claim that so far they have not caused any problems, and ask the doctor to remove the problematic baby tooth.
Let's figure out why the doctor makes a decision on the need to remove both permanent and temporary teeth, focusing not on the wishes of the grandmother or mother, but solely on the available indications.
Malocclusion of primary teeth
A fairly common problem in primary teeth is malocclusion. Malocclusion can be congenital, genetically determined, but it can also develop due to prolonged sucking of a pacifier, bottle or finger. It also happens that it forms if a child constantly has a stuffy nose and is forced to breathe through his mouth.
As in the case of caries, this problem cannot be neglected. A malocclusion may make it difficult for a child to speak and speech development will be slower. Due to the incorrect positioning of teeth, the enamel wears off and becomes thinner, and caries develops faster. In addition, the primary bite also affects the future bite of the “permanent” teeth, the defects of which will be more difficult and longer to correct.
To correct primary occlusion in children, special soft plates are used (they are also called “vestibular plates”), sometimes with a bead to fix the correct position of the tongue. Removable mouthguards can also be used. For better results, the orthodontist can show the child special exercises that will help correct the bite.
Structure of a temporary tooth
Parents cite the lack of roots and nerves as one of the reasons for not treating baby teeth, although temporary and permanent teeth have a similar structure:
- crown – the visible part of the tooth;
- root – located inside the gum;
- the nervous system, also hidden in the gum.
During the period of change, the roots of baby teeth actually dissolve, which is why the above-mentioned false opinion arose. In fact, a diseased temporary tooth hurts and decays in the same way as a permanent tooth in an adult.
Do children have anesthesia for dental treatment? Is it safe?
If necessary, special anesthesia is used for dental treatment in children.
It's not obligatory. When treating caries at the initial stage, anesthesia may not be necessary. Anesthesia is used with caution when treating children with allergies due to a possible reaction to medications. If you know that your child is allergic to any medications, be sure to notify the dentist about this.
If anesthesia is necessary and there are no contraindications to it, there are special light anesthetic pastes and cocktails for children. But even if the pain is severe and you need to give an anesthetic injection, special needles are used for children - very small and thin. Children tolerate anesthesia well during dental treatment. Very often, it simplifies treatment, and visiting the dentist becomes a comfortable and even fun event for the child.
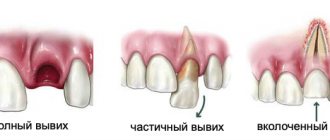
Why pediatric dentistry offers treatment rather than extraction
If the doctor sees that a tooth that should serve the child for another 4–7 years can be saved, he will definitely treat it. A prematurely removed baby tooth can cause problems with bite and pronunciation and lead to the appearance of very serious dental anomalies. So, if the baby “five” is removed before the permanent molar, the “six,” erupts, the child will have to be observed for a long time by an orthodontist and, most likely, wear a plate.
It is clear what the first experience of visiting a dentist will be like for a child who, at the request of his mother, will have a tooth removed. It is not difficult to assume that a frightened child will most likely become a difficult patient who cannot be lured into the dental clinic by any persuasion. He will certainly have serious dental problems in the future.
At what age should a child be taken to the dentist?
It is recommended that the first visit to the dentist be made when the child is one year old. By this age, not all baby teeth will have erupted, but the doctor will already be able to assess whether the teething process is proceeding correctly, give hygiene recommendations and select dental care products.
And at the age of two years, when all the teeth have already erupted, it is necessary to visit a pediatric orthodontist separately so that he can see whether the bite is formed correctly.
Regular visits to these two specialists will ensure that you begin treatment for your baby teeth on time and avoid more serious dental problems in the future.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT PRICES
“Why treat baby teeth?” Pediatric dentist Yulia Selyutina answers
We asked pediatric dentist, founder of the dental center Yulia Selyutina (@stomatolog_selyutina) to dispel this myth, and also tell us what stages caries of baby teeth goes through and what actions can be used to prevent its occurrence.
Photo courtesy of Yulia Selyutina
Why treat baby teeth and what will happen if they are not treated?
Every day at appointments I hear a standard question from the parents of my young patients: “Why treat baby teeth? They’ll fall out anyway.” Let's figure it out together: the most common cause of problems with teeth, including milk teeth, is caries. This pathology and its complication is an infectious process that requires timely and high-quality treatment. It doesn’t matter whether the tooth is baby or permanent.
An untreated tooth is a source of chronic infection in your child’s mouth.
Think about it and decide whether to ignore it. In a baby tooth, like in a permanent tooth, there is a “nerve” (dental pulp). When caries is not treated in time, the depth of the carious cavity reaches the “nerve” and the tooth may begin to hurt.
Unpleasant sensations can manifest themselves in different forms: from mild sensitivity, for example, while eating, to paroxysmal pain at night, which will be difficult to calm at home. To prevent tooth pain, the tooth pulp has to be removed.
However, often the destruction of baby teeth is asymptomatic. You need to know about this, remember and not be surprised if suddenly, having come for a professional examination to a specialist, he states pulpitis, but the child had no complaints. Such “asymptomatic” pulpitis occurs quite often.
How does caries appear?
The causative agent of caries is streptococcus bacteria. Normally, they are present in the mouth of every person.
Bacteria actively attach to the surface of the teeth and multiply under such favorable conditions as:
the presence of dental plaque (due to poor home hygiene);
frequent consumption of soft carbohydrate foods and lack of raw vegetables in the diet;
hypovitaminosis;
deficiency of minerals (fluorine, phosphorus and calcium) in drinking water;
reduced immunity;
presence of gastrointestinal diseases.
Streptococci absorb carbohydrates and produce acid during their life processes. As a result, a person's saliva becomes more acidic and leaches minerals from the enamel, making it less durable. The situation can get worse when a piece of food gets stuck in a small area of the tooth.
Bacteria actively process it, and the acid becomes so caustic that the enamel softens and carious bacteria penetrate into the deeper layers of the tooth (dentin). They begin to process dentin collagen and continue to secrete acid. Gradually, a cavity is formed filled with bacteria and dead tooth matter. If this process is not intervened in time, the tooth may be lost altogether.
What stages of development does caries go through?
Caries in the spot stage
A white matte spot appears on the tooth. In most cases, in children, such stains appear on the frontal group of teeth and have an oblong shape. Then the spot darkens and becomes rough.
It can be stabilized and further deterioration prevented by:
manic home care;
applications with remineralizing agents;
regular courses of deep fluoridation in the dentist’s office;
nutritional control (sweet snacks, meals after evening brushing and at night are excluded).
Superficial caries
The top layer of tooth enamel is destroyed, but the dentin (hard tooth tissue under the enamel) is not yet affected. There is an increase in tooth sensitivity. To restore a tooth, the affected tissue is removed and a filling made of light-curing material is placed. Anesthesia may not be used, since the enamel does not have nerve endings and is not sensitive.
Average caries
Bacteria penetrate deep into the enamel and affect the upper layers of dentin. A carious cavity appears. Dentin is less dense than enamel, so tooth decay accelerates. Acute and prolonged pain occurs when eating sweet, sour, too hot or cold foods.
Treatment: tissues affected by caries are removed, the cavity is processed, and a filling is placed.
Deep caries
Reaches the deep layers of dentin in close proximity to the pulp (neurovascular bundle). The carious cavity is getting larger. The tooth reacts sharply to external irritation (thermal, chemical, mechanical). Without treatment, this stage risks quickly developing into pulpitis.
Treatment: the affected area of the tooth is removed, the cavity is treated and a filling is placed. If there is significant tissue loss, the doctor may place a crown on the tooth.
Photo courtesy of Yulia Selyutina
How can you avoid caries in baby teeth?
Caries is a multifactorial disease. And the best way to avoid it is prevention.
Here are some of my recommendations:
Thorough home care: the child should brush his teeth twice a day for three minutes with “sweeping” movements from gum to tooth. Always recheck and clean contaminated areas where the baby could not cope on his own.
Make applications with remineralizing agents.
Regularly undergo professional examinations and fluoridation courses from your doctor.
Improve your child’s nutrition - this is also very important (minimize snacks, monitor the quality of food, do not eat at night and after evening cleansing).
If you still couldn’t avoid caries, then remember: timely treated baby teeth are the key to healthy permanent teeth. A permanent tooth develops above the baby tooth in the jaw. If a baby tooth is left untreated, eventually all the bacteria will grow beyond it and threaten the health and proper development of the permanent tooth.
Read more on the topic
My child is afraid of the dentist. What to do?
A dental drama in 20 parts: a complete guide to teething from pediatricians
I'm a dentist! 10 scary questions for a dentist
/
/
What to do if a child does not allow or is afraid to have his teeth treated?
Many children experience panic, so it is very important to intelligently approach the question of how to properly persuade a small child to have their teeth treated. To make the process painless and, perhaps, even positive, adhere to the following rules:
- Meet the doctor.
This should be done not at the moment when the tooth is already sick, but in advance - during a preventive examination.
- Motivation.
The child does not know why this is needed and what awaits him in general, so you should tell him about the importance of the procedure or, for example, show him in a playful way on his favorite toy.
- Elimination of physical force.
If a child resists, is capricious and protests, he should not be forced into the dental chair. This will not only traumatize the psyche, but will also completely discourage you from visiting dentists. Here it is better to act carefully - persuade, talk about the great benefits of treatment, or offer a new toy as a present.
- Timing.
If treatment is required, you should see a doctor without delay, but you should also consider the child’s needs. If he is used to, for example, sleeping at a certain time, you should not go to the doctor at that very moment. This is fraught with bad mood and whims. First, let your child sleep, and only after that get ready for the dentist. The same goes for eating, playing and other hobbies.
- Do not lie.
Many parents say that the doctor will only look and do nothing. This is a very big mistake, because the child expects one thing, but in the end it turns out something completely different. It will be better if you tell him the truth in a positive way.
Another good way to motivate your child is by example. If you regularly visit a doctor for preventive purposes and talk about the benefits of procedures, then your child will follow your example.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
What type of anesthesia will be used during treatment depends on the degree of advanced disease. Most often, doctors use a spray that makes the gum tissue insensitive.
If the problem is serious, injectable painkillers are used. But so that the little patient does not feel pain during the injection, the doctor first lubricates the area where the needle is inserted with an anesthetic. This approach to pain relief makes even complex dental procedures not at all scary and as comfortable as possible for the little fidget.
General anesthesia in pediatric dentistry is used only for the most severe illnesses or if it is not possible to persuade the patient to open his mouth and sit quietly in a chair. Parents should not be alarmed if the doctor recommends general anesthesia. It involves the use of a modern, safe drug with a minimum number of side effects.
How to identify milk caries?
It is quite simple to identify caries in young and older children. White or brown spots appear on the teeth, a painful reaction to hot and cold is observed, and the child may develop bad breath. When these first symptoms of caries appear, it is already worth sounding the alarm, since the carious process is developing very rapidly. It is characterized by almost instantaneous damage to several teeth, and if measures are not taken, the entire dentition may be affected. Of course, it is often difficult for a child to articulate that his baby tooth hurts. He may refuse to eat or chew on only one side. This should also alert parents and encourage them to take their child to pediatric dentistry.