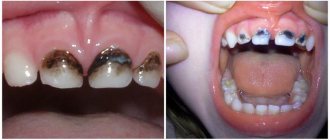
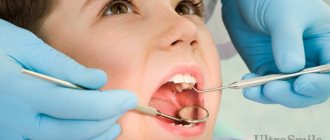
Even young children are susceptible to dental diseases, since the enamel and gums of children are not yet strong enough to resist the effects of negative factors.
However, most parents believe that there is no need to treat children’s baby teeth, since they will fall out sooner or later anyway. This is an erroneous opinion, because the condition of the baby teeth largely determines what kind of molars will grow. Untreated baby teeth can serve as a source of infection. There are many reasons that worsen the condition of the oral cavity and teeth in children: poor hygiene, unlimited consumption of sweets, insufficient intake of vitamins. Against the background of these reasons, immunity decreases and the risk of oral diseases increases.
Main dental diseases in children
The first year of a child’s life can also present surprises to parents in the form of oral diseases. Most often, these are injuries to the oral mucosa, which still has a very delicate structure that can be easily damaged even by a soft pacifier. There is also a danger of developing fungal diseases or the appearance of herpetic stomatitis, sometimes even recurrent.
Dental status of children
The condition of the oral cavity directly affects the entire body:
- pathological changes can lead to malfunctions of internal organs (kidneys, gastrointestinal tract) and the appearance of diseases;
- with an incorrect bite, breathing through the nose is impaired, which leads to dysfunction of organs and organ systems;
- caries and the complications caused by it cause sore throat and other diseases, the causative agents of which are streptococci, which cause carious changes in the teeth.
The body characteristics of young children and their underdeveloped immune system determine that they are at risk for developing diseases. Since the body is a single interconnected whole, the condition of the oral cavity is given the same close attention as other organs. That is why WHO has proposed that dental examinations be carried out according to a specific schedule. If a child has a toothache, an immediate unscheduled visit to a pediatric dentist is necessary for an examination and prescription of a course of treatment.
Caries
With the appearance of the first teeth, the most common disease is caries, which develops much faster at an early age than in adults. If you do not pay attention to it, untreated caries can provoke complications such as: pulpitis, periostitis and periodontitis, and they are serious diseases that require serious treatment. However, caries in children can be treated quickly and almost painlessly, and as we know, any disease is easier to prevent.
To maintain dental health in children, it is important for parents to pay attention to the following points:
- teach your child to maintain oral hygiene;
- monitor your diet, make it balanced, reduce the amount of sweets;
- Monitor the condition of the child’s teeth, contact a specialist at the first symptoms of caries.
Does a child’s baby teeth need to be treated?
Table of contents
- Diseases of baby teeth
- Treatment methods for children's primary teeth
- Anesthesia for the treatment of primary teeth
- Prevention of diseases of primary teeth
- Advantages of contacting MEDSI
The answer to this question is clear. Yes! Baby teeth need to be treated.
You should not think that the milk bite will be replaced by a permanent one, and therefore the diseases do not need to be eliminated.
Lack of proper attention to baby teeth can cause negative changes in the bite, the spread of infection, the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, problems with the pronunciation of individual sounds and with diction in general.
We will understand all aspects of therapy. What diseases do doctors diagnose in children? How is baby teeth treated in children? How to ensure comfortable procedures and how to prevent the development of various pathologies?
Diseases of baby teeth
Caries
This disease is diagnosed most often (in more than 60% of children under 6 years of age). As a rule, caries affects molars. This is due to the relief volumetric surface of these teeth and the baby’s nutritional characteristics. As a result, plaque accumulates quite actively, accompanied by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that destroy tissue. The main problem of effective caries therapy is that it is quite difficult to detect a cavity in the early stages. At the initial stage of development of the disease, a light spot appears on the enamel. This is the reason why parents do not bring their child to the dentist in a timely manner. As a result, the cavity increases, which can provoke the development of dangerous complications and lead to tooth loss.
Periostitis (flux)
This disease is a complication of caries. It occurs when bacteria spread and damage the roots of the tooth and the tissues adjacent to them. The main sign of the pathological condition is swelling of the cheek and the formation of an abscess on the surface of the gum. Pain occurs when damaged tissue is palpated. Periostitis can also provoke a general deterioration in the child’s condition. Treatment of a baby tooth in such a situation is quite difficult. In some cases, removal is recommended.
Periodontitis
This disease is an inflammatory lesion of the periodontium (a complex of tissues formed by the gum, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament and cementum of the tooth root). With this pathological condition, the baby may complain that it hurts to bite solid food. Symptoms of periodontitis include fever and headaches.
Children are also diagnosed with enamel erosion, pathological abrasion, hypo- and hyperplasia, gingivitis, stomatitis, etc.
Important! Timely treatment of baby teeth allows you to save them. That is why parents need to monitor the condition of the child’s oral cavity and immediately respond to his complaints.
Treatment methods for children's primary teeth
Fluoridation
This method is used to treat the initial stage of caries. Treatment consists of treating the enamel with a special composition containing fluoride. This ensures tissue strengthening, prevents the progression of the carious lesion and the growth of the cavity.
Sealing
This technique is used in advanced cases. The procedure is performed using anesthesia. Thanks to this, the child does not experience significant discomfort. Dentists use modern filling materials that are highly durable and resistant to numerous influences. This allows you to save the baby tooth until the permanent one begins to grow.
Endodontic treatment
Root canal treatment of primary teeth in children is the most difficult. However, experienced dentists perform this too. To treat the roots, a material is used that will dissolve in the future. Thanks to this, the therapy does not in any way affect the order of changing teeth.
Important! The treatment method for caries of primary teeth and other diseases is selected by the doctor. In this case, specialists must first carry out the necessary diagnostics. When selecting methods, the individual characteristics of the child are taken into account, as well as his current condition and identified pathology.
Anesthesia for the treatment of primary teeth
The type of pain relief depends largely on the stage of development of the disease.
In the initial stages, it is enough to use a special spray with an anesthetic. It reduces tissue sensitivity and allows the dentist to calmly perform all procedures without causing discomfort to the child.
Injection anesthesia
carried out for serious problems. It ensures the absence of unpleasant sensations at all stages of treatment of baby teeth. If necessary, the injection area is pre-lubricated with an anesthetic.
In some cases, sedation
. This technology is comfortable and safe. It involves feeding a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen through a mask. This composition allows you to relax the child and relieve anxiety.
General anesthesia
is relevant in the most difficult cases or in case of psychological problems in a child, when it is not possible to persuade him to open his mouth or sit quietly in a chair even for 15–20 minutes.
Important! Don't be afraid of general anesthesia. Safe medications are used to treat children, with a minimum number of contraindications and side effects.
Prevention of diseases of primary teeth
The main measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of various pathological conditions include:
- proper and regular cleaning
- Using a child-appropriate toothbrush
- using high-quality paste
- balanced diet, avoiding a lot of sweets
- mouth rinse after all meals
It is also very important to visit your dentist regularly. Only an experienced doctor is able to promptly notice the slightest tissue changes and the first signs of the development of caries and other diseases.
It is necessary to visit the dentist with your child at least 2 times a year. This will prevent the development of pathologies and their complications, keep baby teeth healthy and ensure proper growth of permanent teeth.
Advantages of contacting MEDSI
- Treatment without discomfort and pain.
Our dentists use modern anesthesia - Experienced doctors.
MEDSI dentists have all the knowledge and skills necessary for the treatment and restoration of baby teeth. They actively use modern technologies and techniques, focus on international standards - Providing a full range of services.
We provide treatment and removal of baby teeth, as well as disease prevention. In clinics it is also possible to perform complex diagnostics - Friendly staff and friendly atmosphere.
All our specialists treat each patient carefully and tactfully. Thanks to this, children are not afraid to visit the clinic - No queues and the ability to make an appointment at a convenient time.
This eliminates the unpleasant wait for procedures
To clarify the conditions for treatment and removal of baby teeth, or to make an appointment, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions. Recording is also possible through the SmartMed application.
Thrush
With thrush, white spots first appear on the palate, tongue, cheeks, and lips on the inside, then they merge, forming a solid white coating. The disease is caused by yeast-like fungi, which, under the influence of unfavorable factors, exhibit their pathogenic effects. It is necessary to consult a doctor to eliminate the cause of the disease.
Dental clinic "Sanident" offers a wide range of dental services to preserve and maintain healthy baby teeth. If necessary, our highly qualified specialists provide consultations and carry out preventive measures to care for the child’s oral cavity. In our practice, we use only high-quality filling materials and find an individual approach to each little patient.
Dental clinic "Sanident" is located at the following addresses:
- Shchelkovo, st. Tsentralnaya, 80 (railway station Voronok);
- Ivanteevka, st. Novoselki, 4 (Ivanteevka railway station).
Periodontitis and periodontal disease in children
Let's start with the fact that periodontal disease is a dystrophic disease. According to our expert, in modern pediatric dentistry this concept is already moving away. As for periodontitis, it actually occurs in children, the reason for this is insufficient oral hygiene.
“Due to the fact that children do not cope well with brushing their teeth, plaque forms on them, which gradually turns into tartar - so to speak, a single conglomerate that is not possible to clean off on your own,” says Victoria Arutyunova.
If you regularly visit the dentist and carry out professional oral hygiene on time, the problem can be identified at an early stage and first prevent gingivitis, and then, as a consequence, periodontitis, which is an inflammatory disease. First, the stone appears above the gum, then it begins to multiply and goes under the gum. As soon as this happens, under the influence of infectious agents, inflammation begins in the soft tissues, they sag, expose the roots, and periodontitis appears.
The main method of control is to visit the dentist in a timely manner for professional hygiene. If the oral cavity is in poor condition, then visits to the dentist become more frequent. Then, instead of seeing each other once every six months, the doctor and patient meet once every three months to monitor the process and correct the current situation. If children have bad habits such as thumb sucking or reluctance to give up pacifiers, this provokes receding gums.
flickr.com/
Forms of enamel hypoplasia
Clinically, the following forms of enamel hypoplasia are distinguished: spotted, cup-shaped (erosive), grooved (wavy) forms, thinning or aplasia of the enamel.
The spotted form is spots and stripes, most often white or yellow, with clear or fuzzy contours. Their surface can be smooth and shiny or rough and dull. Shiny smooth enamel means demineralization of its subsurface layer, dull and rough – changes in the surface layer at the end of the enamel formation process.
Cup-shaped, grooved forms, thinning, aplasia of enamel are manifested by areas of hypoplasia through which dentin is visible, grooves, aplasia (complete absence) of enamel. The edges, walls and bottom of the defects are sometimes yellow-brown pigmented and smooth.
Separately, it is necessary to mention molar-incisal hypomineralization. Its characteristic feature is damage to one to four permanent molars, often combined with damage to the incisors. Clinically, these are cloudy spots of white, yellow or brown color, sometimes covering the entire crown of the tooth. Children may be bothered by teeth chipping and sensitivity. Because of this, they may refuse to brush their teeth, which soon leads to the development of caries. Parents may be concerned about the unaesthetic appearance of their teeth.
Teeth of Hutchinson, Fournier and Pflueger
Also manifestations of systemic enamel hypoplasia are the teeth of Hutchinson, Fournier and Pfluger. They are characterized by a change in tooth shape. The main reason is late congenital syphilis.
Local enamel hypoplasia
Local enamel hypoplasia (Turner's tooth) is a violation of the development of enamel (sometimes dentin) of individual permanent teeth. As a result, the tooth changes color: it becomes white or yellow-brown, and areas of hypoplasia appear on it. Turner's tooth is directly related to the periapical inflammatory process of the primary tooth.
Focal enamel hypoplasia
With focal enamel hypoplasia (regional odontodysplasia), underdevelopment of all dental tissues is observed. Typically, the process involves several teeth located nearby. These temporary, and subsequently permanent, teeth are characterized by late development and eruption. After eruption, the teeth are yellowish, with a rough surface. The characteristic name for such teeth is “ghost teeth,” which is also due to their special appearance on an x-ray. The enamel and dentin are thin, their density is reduced, the pulp chamber is large, the roots are wide and short, with open apexes.
What does dental health depend on?
The enamel on baby teeth is not yet strong and strong enough, so it is susceptible to any mechanical stress. Unfortunately, many adults believe that it is not necessary to treat baby teeth, because they will very soon be replaced by permanent ones. However, such a judgment is fundamentally wrong! The health of molars is directly related to the condition of their predecessors.
The fragility of the enamel may be due to a hereditary factor: perhaps one of your relatives has very fragile teeth that are prone to destruction. Also, factors such as unfavorable environmental conditions in the region of residence, poor-quality tap water, mental health problems and much more can lead to the depletion of a child’s tooth enamel.
An important factor can be a woman’s careless attitude towards her health during pregnancy. In particular, this applies to drinking alcohol and smoking. This negatively affects not only the development of the baby’s bones and teeth, but also his overall health. Also, the cause of tooth decay can be liver pathologies, problems with the thyroid gland, gastrointestinal diseases, etc.
How gum and dental diseases manifest themselves
Regardless of the nature and complexity, dental diseases must be treated. People who visit the dentist at least twice a year protect themselves from the development of dental pathologies and dental diseases with regular visits to the doctor. Timely consultation with a doctor allows not only to carry out gentle treatment and prevent the development of the disease, but also to completely eliminate the consequences of the disease. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to the development of complications, the appearance of concomitant diseases, damage to healthy teeth, tooth loss and disruption of chewing functions.
The following symptoms are reasons to consult a doctor:
- change in tooth color;
- The appearance of painful and uncomfortable sensations in the tooth or surrounding tissues;
- Sharp reaction of teeth to cold and hot foods;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth;
- Bad breath;
- Presence of tartar and abundant plaque.
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia
Several methods are used to treat enamel hypoplasia. The choice of each depends on the violation of aesthetics, type, depth, area of the defect, degree of enamel mineralization, motivation of the child and parents, and technical capabilities.
The essence of the conservative method is to increase the mineralization of hard tooth tissues. This is both endogenous and exogenous use of vitamins, preparations containing fluorine, calcium, phosphorus. It can be used both independently and as an initial step before other methods.
Microabrasion and/or bleaching is carried out after the mineralization of the tooth is completed. The technique consists of etching the enamel, followed by grinding it with a minimally abrasive bur and polishing it with a rubber cup. This method is effective if the defect is in the surface layer of the enamel or when it is clouded.
The surgical method is preparation and then filling. It is also carried out either after conservative therapy or after mineralization of the tooth is completed. Used for the deepest defects in the enamel. Options include filling with GIC (followed by replacement with composite), composite materials, veneers, laminates and crowns.
Another treatment tactic for focal hypoplasia. The optimal approaches to restoring teeth in this case are covering the teeth with crowns soon after eruption or removing them with prosthetics.
Prevention of enamel hypoplasia
The main directions of prevention of enamel hypoplasia:
- Prevention of diseases in a pregnant woman, her balanced diet;
- Prevention and treatment of somatic diseases in young children;
- Sanitary and educational activities of a dentist in a antenatal clinic, a children's clinic;
- Treatment or removal of temporary teeth with complicated caries;
- Prevention of trauma to temporary teeth;
- Atraumatic removal of a temporary tooth.
The article was written by Titenkova O.V. especially for the OHI-S.COM website. Please, when copying material, do not forget to provide a link to the current page.
Classifications of enamel hypoplasia
The most common classification of enamel hypoplasia is the classification of M.I. Groshikov. It is based on different etiologies and the number of teeth affected. Based on this, methods of treatment and prevention of various forms of hypoplasia differ.
Systemic enamel hypoplasia
Systemic enamel hypoplasia is a disorder in the structure of all teeth, but more often in groups associated with close periods of formation and eruption.
Such diseases in the ICD-C (1995) as prenatal enamel hypoplasia, neonatal enamel hypoplasia, enamel hypoplasia, non-endemic mottling are nothing more than “systemic enamel hypoplasia” according to M.I. Groshikov.
Features of the clinical manifestation of defects in systemic enamel hypoplasia:
- appearance from the moment of eruption;
- symmetrical, of the same size on teeth of the same name;
- localized parallel to the chewing surface or cutting edge, most often on the tubercles or vestibular surface.
There is also a relationship between the defect and the action of the damaging factor:
- The type of defect (qualitative or quantitative change in enamel) depends on the intensity of the factor;
- Localization of the defect - depending on the time of its exposure;
- The width of the defect depends on the duration;
- The number of defects indicates the frequency of action of the damaging factor.
Do I need to treat rotten teeth?
Of course, it is necessary to treat any damage to baby teeth. The loss of one or more milk units can affect the correct formation of the bite in later life. In addition, the destruction of hard tissues inevitably leads to inflammatory processes in the surrounding soft tissues. If you do not deal with the problem in a timely manner, then there is a high risk of developing an abscess, meningitis, sepsis, etc.
Quite often, dental caries does not manifest itself in any way until the child’s immune system is weakened due to illness or a common cold. The consequences can be quite serious: sinusitis, pain in the ears (otitis and other problems), digestive problems, intestinal disorders and stool disorders, as well as severe stomach pain.
In addition, rotten teeth look very unsightly even in a child. Older children may begin to feel complex about their appearance; they will develop self-doubt and tightness. That is why it is very important to periodically check the condition of your baby’s teeth, because it is much easier to eliminate the problem at an early stage.
previous post
The difference between paid and free anesthesia
next entry
Why are caries so common in children now, even the smallest? What is the reason?
I think that a lot depends on the nature of nutrition, on the quality of food and products. Poor hygiene also contributes to the increase in morbidity. Very often I hear at receptions that parents, due to their busyness, do not control the brushing of their child’s teeth, and children aged 3-4 years do it independently and are fully responsible for oral hygiene. It is not right.
I strongly recommend that parents up to 6 - 7 years old help and brush their child’s teeth, because at the age of 5.5 - 6 years, the change of milk teeth to permanent ones begins, at this time six teeth erupt (few people know about this, but these teeth are not milk teeth, they are immediately permanent). It’s very disappointing when children come for an examination and I find permanent teeth already affected by caries, and this at such a young age.