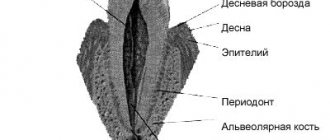
Most people who do not have special knowledge in the field of dentistry believe that periodontitis is an inflammation of the gums. In fact, this is only partly true, since with this disease not only the gums become inflamed, but also the process of destruction of the periodontium begins - the tissues that fix the tooth in the bone. As a result, the tooth loses contact with the gum, and the patient can easily lose the tooth.
In children, periodontitis is diagnosed much less frequently than in adults, and has some differences in the nature of the disease.
Periodontitis in children: a mouth full of worries
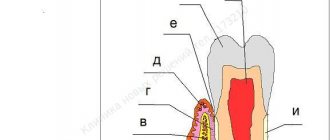
Periodontitis is a disease in which all periodontal tissues become inflamed. Inflammation of the gums occurs, destruction of muscle ligaments, pathological periodontal (so-called periodontal) pockets are formed, the process affects the bone, then teeth begin to loosen and fall out.
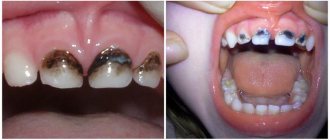
Periodontitis in children is most often detected at the age of 9 - 10 years. And although this is not the most common dental disease, it occurs in only 3 - 5% of children, nothing guarantees that your child will not be affected by this problem.
The peculiarity of the course of periodontitis in children is that the inflammatory process affects functionally immature, growing, constantly remodeling tissues, which sometimes react inadequately even to minor damage.
In addition to the standard division according to prevalence into local and generalized, as well as into chronic and acute - according to the nature of its course, childhood periodontitis is divided into prepubertal and pubertal.
Reasons why periodontitis develops in children
In addition to the above-mentioned causes of the disease, dentists also focus on the following:
- Untimely removal of soft and hard plaque. If a child is not able to clean his teeth independently, then he must undergo a professional hygiene procedure twice a year. It is absolutely painless. It is performed by a dentist using special equipment. Using a device that supplies a pressurized stream of air with small abrasive particles, the doctor treats one tooth after another. This simple measure is the best prevention of gum disease.
- Shortened frenulum of the lip or tongue. If this feature is not detected, the area of the gum adjacent to the frenulum will be under constant tension. As a result, an inflammatory reaction will occur.
- The habit of chewing food with only one side of the jaw. Then plaque will begin to accumulate in large quantities on the opposite side. Over time, it will transform into stones and will irritate the mucous membranes. That is why it is important to teach your baby to chew on both sides of the jaw.
- Severe anomalies in the structure of the jaws and the location of the teeth. Due to an altered bite, individual units may either suffer from overload or not participate in the chewing process at all. Both the first and second options are dangerous due to adverse consequences. Therefore, if a child has obvious disorders, it is necessary to consult with an orthodontist about their elimination. The doctor may prescribe wearing plates, mouthguards or braces.
- Traumatic damage to the gums. Children can damage the soft tissues of the oral cavity when they chew on foreign objects, fall, or hit something. Chronic injuries can also be caused by damaged teeth and inaccurately fixed parts of braces.
- Refusal to eat hard foods. If the baby eats pureed food all the time, then the necessary load is not placed on the chewing apparatus. Then plaque begins to accumulate intensively on the teeth - tartar appears. As it grows, it penetrates under the gums.
It has also been proven that the risk of periodontitis in children increases if they have diabetes or congenital heart disease.
Prepubertal periodontitis
It begins during the eruption of baby teeth or immediately upon its completion. It is characterized by disruption of the connection between the gum and tooth and serious destruction (change in structure) of the bone. Prepubertal periodontitis already at a very early age leads to the loss of a large number of baby teeth, after which the inflammatory process spreads to the rudiments of permanent teeth. The causes of the development of prepubertal periodontitis are most often weakened immunity, as well as the presence in the child’s oral cavity of specific types of microorganisms, the original carriers of which in most cases are the baby’s parents.
Causes of childhood periodontitis
The development of childhood periodontitis may be due to the following factors:
- decreased immunity, which makes the oral mucosa more susceptible to waste products of pathogenic bacteria;
- malocclusion;
- diabetes;
- a seal placed in bad faith;
- violation of daily oral hygiene;
- side effects of medications;
- nutritional errors - excessive consumption of sweets, soda, very cold or very hot foods.
Here the uniform is blue
Local factors
Insufficient level of oral hygiene
The inability to properly brush your teeth with a special children's toothbrush and the reluctance to regularly carry out hygiene procedures lead to the accumulation of microorganisms in the periodontal pockets, and the toxins they release trigger the inflammatory process.
Short frenulum of the tongue or lip
Insufficiently long frenulums provoke atrophy and inflammation of the adjacent gum area due to constant tension on the frenulum fibers. The inflammatory process is localized in the area of the lower central teeth.
Chewing food on one side
The habit of chewing food on one side is fraught with the accumulation of plaque on teeth that are not involved in chewing. It is necessary to explain to the child that food should be chewed on both the left and right sides.
Anomalies and deformations of the dental system
The development of the inflammatory process in periodontal tissues can be caused by both functional overload of certain teeth and insufficient load on them. The reason for this is an incorrect bite or an incomplete set of teeth (the permanent teeth have not yet grown in, and some of the baby teeth have already fallen out).
Gum injuries
This group of factors that provoke the occurrence and development of periodontitis includes chronic trauma to the gums from decayed teeth or parts of braces, as well as filling defects and damage to periodontal tissue by nails, pens, and hair clips.
Nutritional nature
Too soft food does not contribute to a sufficient load on the child’s chewing apparatus and self-cleaning of the teeth, which results in the accumulation of plaque at their base, and as a result, the appearance of tartar in children.
Medical Internet conferences
The need for orthodontic treatment has increased significantly in recent years. But at the same time, the number of dental diseases that are directly related to the presence of structures in the oral cavity is growing [3]. This is explained by the fact that orthodontic appliances are not indifferent to the human body and, when exposed to the oral mucosa, change the activity of salivary enzymes, causing dental diseases. These complications of orthodontic treatment lead to changes in homeostasis: the destruction of normal microflora or a disproportionate change in the number of components of the oral microbiocenosis, which ultimately leads to the development of dysbiosis and the occurrence of both inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues and processes of demineralization of hard dental tissues [2, 7, 10, 12, 13].
The main etiological factor causing inflammation in periodontal tissues, as well as dental caries, is dental plaque. In patients undergoing orthodontic treatment, the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity increases due to the fact that around the elements of the orthodontic structure, in the spaces between the teeth and in the cervical areas, due to difficulty in hygiene, food residues accumulate in which microorganisms multiply, producing acids in the process of their vital activity, leading to a decrease in the pH of the oral fluid, increased enamel permeability and demineralization [5, 9, 11, 14–16].
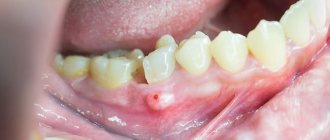
Plaque contributes to the development of not only caries, but also periodontal disease. Pathological processes in the periodontium begin with gingivitis, which is manifested by redness and bleeding. Bleeding gums during orthodontic treatment occurs quite often when brushing teeth, as well as while eating solid foods. If left untreated, gingivitis progresses to periodontitis. With periodontitis, tooth mobility appears, pathological periodontal pockets form, and patients may be bothered by bad breath.
To avoid complications during orthodontic treatment, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene and a balanced diet. It is very important to teach the patient the rules of hygiene and monitor its implementation even before installing the device. It should be explained to the patient that toothpaste and toothbrush alone will not be enough to maintain the oral cavity in good condition. It is necessary to use a soft toothbrush and a special paste to clean the surface of the removable appliance from plaque, a gel or mouthwash for daily use that dissolves dirt and destroys bacteria that accumulate on the appliance. Once a week you need to soak the device in cleaning concentrate for more thorough care. An integral part is the use of the following additional hygiene products: brushes - for cleaning interdental spaces and removable orthodontic appliances; floss - will clean the interdental spaces and gum pockets; irrigator - for thorough cleaning of dental spaces, cleansing the surface of teeth from newly formed plaque and improving blood circulation in soft tissues; plaque indicator tablets – allow you to evaluate the quality of hygiene.
During meals, it is necessary to remove the orthodontic device and put it on after carrying out hygienic measures [1, 6].
It is well known that after tooth eruption, active mineralization of the enamel occurs within 2–3 years. Therefore, it is advisable to carry out local preventive measures during this period. One of the most effective modern methods of preventing dental caries, stimulating the process of “maturation” of enamel, is fissure sealing. For this purpose, special materials are used - sealants. Most sealants contain silanes - fluorine-containing substances that split off fluoride ions over a long period of time, which diffuse into the layers of hard tooth tissue adjacent to the sealants, stimulating their mineralization. The use of sealants leads to stabilization of the carious process for 1–9 years.
The next important point is diet correction. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates (chocolate, sweets, flour products), and, on the contrary, increase the consumption of foods containing easily digestible Ca2+ (milk, low-fat cottage cheese) in order to increase the mineralizing function of saliva. At the same time, it is useful to consume foods that help shift the pH to the slightly alkaline side, for example, cheese [4, 8, 16].
Such an integrated approach to prevention will help improve the hygienic state of the oral cavity and reduce the incidence of dental caries and periodontal diseases in patients during orthodontic treatment.
Treatment of periodontitis in children: the work of professionals
Non-surgical methods for treating the inflammatory process of periodontal tissue are the same as in adults.
This includes professional oral hygiene and various physiotherapeutic procedures. Surgical interventions, such as lip frenulum correction, may also be required. In any case, before prescribing certain procedures, a child must visit pediatric dentistry for consultation with three specialists - a therapist, a surgeon and an orthodontist. They will determine the true causes of periodontitis and develop an individual treatment plan. It is also important to exclude systemic diseases that can provoke periodontitis. Their treatment must be carried out with the participation of a specialist of the appropriate profile.
Causes of gum inflammation in children
- Skipping or poor quality teeth brushing;
- Sucking dirty objects;
- Errors when installing seals;
- Pathologies of the dentition;
- Carious cavities with sharp edges;
- Bite correction;
- Breathing through the mouth;
- Abnormal structure of the oral cavity organs (attachment of the frenulum of the tongue and lips);
- Problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza);
- Hormonal abnormalities;
- Hereditary anomalies.
Diagnosis of gum disease in children
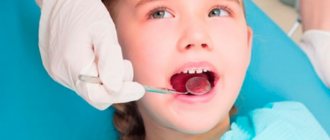
A routine oral examination should be performed by a pediatric dentist every six months. And as necessary, if a small patient exhibits any deviations in the development of teeth or symptoms of disease of the oral mucosa. Since it is advisable to diagnose the inflammatory process at the earliest stage.
If redness, swelling and bleeding are detected, the cause of which is an excessive amount of soft plaque or food debris on the teeth, the dentist will make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, a clinic specialist can take biomaterial from the inflamed areas of the gums for clinical tests. Based on the results of the analysis, the specialist prescribes a treatment plan and the date of the next appointment to ensure the final recovery of the little patient.