Fluorosis is a disease of tooth enamel associated with prolonged exposure to excessive amounts of fluoride. It can be endemic and occupational in nature - develop in connection with living in a region where drinking water contains a lot of fluoride or be associated with working conditions and the amount of fluoride in the air.
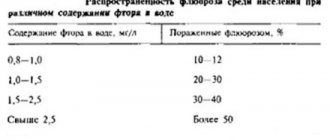
Endemic fluorosis is common in regions where the amount of fluoride in a liter of drinking water exceeds 1.5 mg. The occupational form of the disease is much less common, usually among employees of the aluminum industry.
Causes and mechanisms of development
Fluorine is a microelement that enters the body with water and food and is involved in many physiological processes. It is found in high concentrations in human bone tissue and teeth. The incoming fluoride is not completely absorbed; the main share is fluoride dissolved in water. If a lack of a microelement increases the risk of dental caries, then an excess becomes the cause of the disease.
Fluorosis is most often observed in children during the eruption of permanent teeth. This applies to children, including those who previously lived in regions with high concentrations of fluoride in water. It is enough to live in such a region for up to 3-4 years. Excess fluoride also affects the buds of permanent teeth. In this case, milk teeth are not affected by the disease, since their rudiments are formed in utero, and excess fluoride is retained by the placenta and is not passed on to the baby.
An element concentration of 1.5 mg per liter of water will not lead to the development of fluorosis in adults. Drinking water containing 6 mg of fluoride per liter leads to illness.
Ask a Question
Causes of the disease
The main cause of pathological changes is an excess of fluoride in the body. The optimal concentration of a chemical element is considered to be 1 mg/l; if mineralization indicators are exceeded, there is a high probability of developing fluorosis and structural defects. Fluorine easily undergoes substitution reactions and such transformations are not always benign for the body. The hard tissues of teeth are especially sensitive, and the crystal structure and strength of the protective coating are disrupted. A deficiency of a microelement is no less dangerous than an excess and entails growth retardation, defects and deformations of teeth, and pathologies of the skeletal structure. In addition, among the main reasons for the development of fluorosis are:
- eating plant and animal products with an excess of fluorides;
- irrational use of cleaning pastes and rinses enriched with microelements;
- increased fluorine content in the air (factories producing glass, metals, ceramics, optical and laser devices);
- living for a long time near industrial enterprises.
Children under fifteen years of age are at increased risk, which is explained by insufficiently strong enamel, unstable hormonal levels and lack of adequate oral hygiene.
Classification of fluorosis
By origin, endemic and occupational fluorosis are distinguished. Despite the similar clinical picture, recommendations for undergoing a course of treatment for these two types of disease will differ. An occupational disease causes disease not only of the teeth, but also of the bones - osteoporosis, osteosclerosis. The diseases are accompanied by impaired joint mobility.
As the disease develops, vegetative-vascular disorders and liver pathologies occur, and the risk of cancer—osteosarcoma—increases. It is worth noting that stains on teeth with such fluorosis may be completely absent.
Based on clinical manifestations, researchers distinguish five forms of the disease:
- spotted;
- dashed;
- chalky speckled;
- erosive;
- destructive.
The first two forms are considered a mild form of the disease. Chalky-mottled fluorosis is classified as moderate fluorosis. The last two are severe forms.
One patient may experience several forms of clinical manifestations at once - different symptoms develop on different teeth and groups of teeth. Doctors note that the resulting form of the disease persists for life and does not change even with changes in the concentration of the trace element in drinking water.
Pathogenesis
During normal enamel formation, matrix proteins (ameloblastin and amelogenin) are gradually replaced by growing hydroxyapatite crystals. The space between adjacent enamel prisms is minimized.
When there is an excess of F- ions, they are more quickly incorporated into the crystal lattice than the larger and asymmetric OH- ions. Fluoridated enamel preserves matrix proteins. As a result of incomplete crystal growth, significant spaces remain along the periphery. The penetration of food pigments turns these cavities brown. Porosity of enamel in severe forms of fluorosis contributes to the spread of caries and increases the risk of chipping from mechanical stress.
Symptoms and manifestations
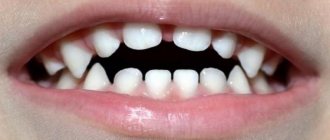
Endemic dental fluorosis manifests itself as white spots or characteristic stripes on the enamel. As the disease progresses, they acquire a yellow or even brown tint. The incisors of the upper jaw are most often affected, but at high concentrations of fluoride, damage to all teeth occurs. Increased abrasion of the enamel is observed, chips and erosions form. Symptoms depend on the form of the disease.
Line
This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of white stripes on the outer surface of the incisors. Sometimes they are pronounced, but more often they are noticeable only when the enamel surface dries. In some cases, the stripes merge into large spots, but the doctor will detect separate stripes in the structure of the spot.
Spotted
With this form, multiple white spots appear that merge with each other. The surface of the stain is shiny and smooth, without roughness. There are no clear boundaries of the stain - it smoothly transitions into healthy areas of the enamel.
Chalky mottled
With this form of enamel fluorosis, a matte tint appears on the entire surface of the hard tissues of the tooth. Clearly defined spots and dots appear on the surface. In some cases, the enamel becomes yellow. In addition, areas of destruction may be observed on the teeth: speckled depressions with a diameter of up to 1.5 mm and a depth of up to 0.2 mm. The bottom of such depressions is pigmented.
This form is characterized by increased abrasion of the enamel, which exposes dentin - the deeper tissues of the tooth, which have a dark brown color. Sensitivity of teeth when dentin is exposed is pronounced.
Erosive
This form is distinguished by the presence of larger areas of enamel destruction - erosions. In the area of such a depression, there is no enamel at all, and increased abrasion is observed on the chewing surfaces of the teeth.
Destructive
In the destructive form of the disease, abrasion and erosion occurs not only of the enamel itself, but also of other hard tooth tissue - dentin. Teeth become brittle, large chips occur, and the shape of the crowns is disrupted. The body strives to prevent the opening of the tooth cavity by forming replacement dentin. This is a severe form of the disease that can develop in regions where drinking water contains at least 10 mg of fluoride per liter of water.
Degrees of development
This disease develops slowly because it is quite complex and serious. According to doctors, it is worth highlighting the following stages of fluorosis development:
- 1st degree. Here small spots appear on the tooth enamel and its surface. But some teeth suffer, not all;
- 2nd degree. It is worth noting the chalky spots here, but pigmented spots also appear that are pronounced. They have a yellow, brown tint;
- 3rd degree. Most of the enamel is affected, and the crown may become deformed. In addition, enamel is soft and can be worn out. In this case, the tooth remains without its protection.
Diagnosis of fluorosis
Typically, diagnosing fluorosis is not difficult for a dentist. The spotted form of the disease may resemble a so-called chalk spot - the initial stage of caries or an area of enamel demineralization. However, in the case of fluorosis, such stains are multiple in nature and affect permanent teeth after they erupt. And initial caries develops singly or on a small number of teeth. A standard examination by a doctor is usually sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis.
One of the diagnostic features is the recommendation to submit drinking water for analysis, this will determine the concentration of fluoride in it. If elevated levels are detected, the doctor will prescribe changing the source of drinking water or purifying it before drinking. If you do not follow this recommendation, a severe form of the disease may develop, accompanied by tooth decay.
Preventive actions
Prevention of fluorosis primarily involves changing the source of drinking water. For children under 1 year of age, it is advisable to avoid artificial feeding if possible, and not to introduce fluoride-containing products into complementary foods. The diet must be enriched with vitamins B, D, and C. The child must consume sufficient amounts of calcium and phosphorus salts - they help remove fluoride from the body and help prevent its excess.
Toothpastes should be chosen that contain calcium glycerophosphate; this is especially important for children’s toothpastes. But do not forget that prevention is effective only before the enamel of children’s molars is fully formed. After this, its effectiveness decreases.
Fluoride is not contained in toothpastes such as Lakalut, Rox-Baby, New Pearl Calcium and others.
Features of treatment
If you have enamel fluorosis, your doctor will recommend using fluoride-free toothpastes and mouth rinses. This recommendation applies to all cases and forms of the disease.
Removal of affected areas of enamel and filling are not used, since the likelihood of the filling falling out and further tooth destruction is very high. The doctor may prescribe phosphorus and calcium supplements to further strengthen hard tissues.
Mild forms of the disease are subject to cosmetic correction. Chemical, photo-whitening or laser teeth whitening can be used. After this, remineralizing therapy is necessarily performed: the doctor will apply preparations based on phosphorus and calcium compounds to the enamel using electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis or application. Sometimes it is advisable to use mouthguards with a special composition inside - this procedure can be carried out both at home and in a dental office. The course of remineralizing therapy for this disease consists of 10-20 procedures, depending on the degree of tissue damage.
Chalky-mottled, erosive and destructive forms do not allow effective whitening. In this case, dental restoration can help achieve a cosmetic effect - installing lumineers or veneers. In severe cases, treatment of fluorosis is carried out by restoring teeth with artificial crowns made of metal-ceramics or ceramics.
Orthopedic treatment can not only eliminate a cosmetic defect, but also prevent further tooth decay, as well as cope with increased sensitivity.
Dental restoration for fluorosis
Often the disease goes undetected. The price for this is tooth decay. The pathogenesis of the disease involves constant progression. In advanced stages, you can get rid of the consequences of the disease through restoration.
Depending on the degree of tooth damage, various options for restoration work are used. Most often, this is the application of light-curing polymers to the surface of the tooth, which then perform the function of tooth enamel. The color of the polymer mass is selected separately for each patient, depending on the shade of the dentition.
In some other cases, when the enamel is severely damaged, veneers or crowns are used.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis is favorable if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner and follows all instructions. Even severe forms of the disease leave room for restoring the aesthetics of a smile using modern methods. But the sooner you contact a specialist, the less effort treatment of dental fluorosis will require.
The main direction of prevention is to reduce the amount of fluoride entering the body. When living in a region with a high concentration of trace elements in drinking water, it is important to find another source - consume purified water or purchase water brought from another region. You should also limit the consumption of fluoride-containing products: sea fish, spinach, butter, seaweed, etc.
It is important to stop using toothpastes, gels and rinses with fluoride. Please note that most children's toothpastes do not contain fluoride or aggressive abrasive particles.
The dentists at the STOMA clinic know how to treat fluorosis of all forms. We have ample opportunities for professional whitening and high-quality teeth restoration. You can make an appointment for an examination and consultation with a doctor by phone or through a special form on the website.
FAQ
How to treat fluorosis in children?
If your child has fluorosis, treatment options are much the same as for adults. Yellow stains on children's teeth and other manifestations of the disease are eliminated using whitening procedures. Be sure to eliminate the source of increased fluoride.
In addition, children do not undergo restoration, as well as prosthetics and installation of veneers. If we are talking about baby teeth, then such events are pointless, because permanent teeth will replace them.
Fluorosis in children: photo
What happens if fluorosis is not treated?
Pigmentation on teeth is far from the only trouble with fluorosis. If the disease is not treated, it progresses, until the complete loss of the tooth. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is extremely important to consult a doctor and undergo treatment.
Is it possible to whiten teeth with fluorosis?
This procedure can be carried out in the initial stages of the disease, when no more than 25% of the enamel is affected. Whitening is carried out to restore the previous aesthetics. It must be remembered that without eliminating the cause of the disease, such an event is meaningless. This way you will only temporarily regain the lost whiteness of the enamel, because if you continue to take fluoride in large quantities (with water, food or medicine), the disease will not go away.
How to avoid dental fluorosis?
To ensure that bones and teeth do not experience problems associated with an excess of fluoride, it is important to monitor the composition of drinking water. In regions where water has high levels of fluoride, people should be informed about this. Don’t be lazy – take an interest in this question. If you buy drinking water, ask for certificates certified by experts that indicate the chemical composition. Normally, 1 liter of drinking water contains from 0.5 to 1 milligram of fluoride.