Some parents are unreasonably careless about caring for their child’s baby teeth. Indeed, is it worth treating caries of a temporary tooth if you can remove it and wait for the permanent tooth to grow? This statement is fundamentally incorrect; the negative consequences of such removal can be very serious. Dentists pull out baby teeth only in the most extreme cases.
Today we will talk about what premature loss of milk row can lead to, as well as how to take care of your child’s teeth.
Features of the procedure
Tooth extraction is not performed without indications. We perform treatment either planned or emergency. In both cases, a preliminary diagnosis is carried out.
The reason for the procedure may be:
- periodontitis or periodontitis;
- root canal trauma;
- planned orthopedic treatment;
- complex tooth crown injury;
- developmental anomalies;
- neoplasms in the tooth area.
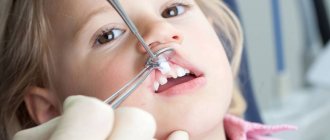
Extraction can be carried out in a simple way, when the crown is simply separated from the gum tissue and the entire tooth is removed, or in a complex way, in which the dentist dissects the gum or periosteum.
What are the indications for the removal of baby teeth?
Common carious lesions are the most common indications for the procedure. However, this is not the only reason. One of the common indications for the removal of primary teeth is their abnormal growth, which increases the risk of malocclusion and problems during the eruption of permanent teeth.
Other indications for the removal of baby teeth are:
- the occurrence of dental diseases that can cause tissue necrosis;
- diagnosis of periodontal fistulas and abscesses, as well as other pathological changes in the gums;
- too late resorption of milk roots, which prevents the eruption of permanent teeth;
- mechanical damage that may occur as a result of a child falling.
An indication may also be the fact that a baby tooth remains in the dental arch for too long, despite the fact that the permanent one has already begun to erupt. A tooth should also be removed when it begins to move and thus makes it difficult for the child to eat and speak. In such a situation, you should not pull it out using old home methods, because this can damage the gums.
Temperature as a sign of pathology
Immediately after a tooth is extracted, the open socket is in no way protected from infection. If the removal was simple, then after a few hours a film forms, blocking the path of pathogenic microorganisms. With complex extraction, the wound turns out to be too open and deep, so it takes much more time for the formation of natural protection. The overall healing period takes from 3 days to 2 weeks.
Extraction (removal) of a tooth in a person causes stress for the body on a psychological and physiological level. An increase in body temperature is a peculiar manifestation of the reaction to the procedure. Additional local symptoms are bleeding from the socket, swelling and redness of the gums. The patient's general health may also deteriorate, accompanied by weakness, dizziness, and sometimes nausea.
Many patients begin to worry whether there may be a fever after tooth extraction, because everyone knows that an increase in body temperature is a sign of an inflammatory process. However, dentists claim that this sign is just an indicator of tissue healing and stress suffered by the body. But only if there are no other symptoms of an unnatural process, the temperature does not rise above 37.5 °C and lasts no more than 3 days.
What if the cause of the elevated temperature is not a cold?
Often, an increase in temperature can be associated with inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity. For example, a cyst could form in a tooth or gum - a cavity filled with fluid. And elevated temperature is nothing more than the body’s reaction to protect itself from the spread of infection.
In an advanced state, the cyst affects neighboring teeth, so if you notice such symptoms, you need to consult a dentist.
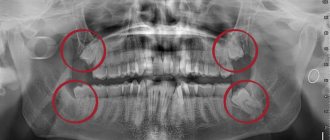
By the way, a dental cyst is diagnosed using an x-ray - this is one of the reasons why it is necessary to undergo regular check-ups with a doctor. Treating the cyst at an early stage will protect you from possible complications, including tooth extraction.
What a high temperature may indicate
Dentists note that the temperature mainly increases after the removal of wisdom teeth, impacted units, or with a concomitant inflammatory process.
When a patient has a temperature of 38 °C or more for several days after wisdom tooth removal, the reason may be the development of:
- granulomas (nodular formations) - pathological formations form on the remains of roots that the doctor did not remove at the extraction stage;
- alveolitis (inflammation of the socket) - the provoking factor is violation of the dentist’s recommendations for wound care, perforation of the walls during surgery, weak immunity or inflammation of the throat;
- osteomyelitis - a process of purulent-necrotic damage to the jaw bone, with a high probability of abscess and gangrene;
- hematomas - occur when blood vessels are damaged during extraction and can provoke a purulent process and the formation of a cyst;
- infections - lack of proper care and antiseptic treatment will lead to rapid penetration of infection into the hole and the development of a pathological process.
After tooth extraction, the temperature may rise due to concomitant sinusitis. It is possible that the dentist may make mistakes, which, in addition to damaging the walls of the socket, may involve leaving foreign bodies (for example, a cotton swab) in the open wound or insufficient treatment of the socket.
How is milk teeth removed for orthodontic reasons?
If a young patient has crowded teeth, the offending primary teeth should be removed to avoid bite problems during primary replacement.
This dental procedure takes place in four stages:
- Removal of primary posterior incisors at the time of eruption of permanent incisors.
- Extraction of primary canines (this is necessary for the proper growth of permanent incisors).
- Extraction of primary first molars, provided that the first premolars are 1/2 to 2/3 the length of the root.
- Stage four: removal of permanent first premolars before the eruption of permanent canines to make room for them.
When to see a doctor
After wisdom tooth removal, a temperature of 37 °C without accompanying signs of inflammation is considered normal. There is no need to worry about such indicators. The temperature returns to normal within three days. No action needs to be taken.
You should consult a doctor if, after tooth extraction:
- the temperature lasts for 4 days or more;
- body temperature 38 °C or more;
- the pain does not decrease, but becomes more intense;
- there is severe swelling;
- after 2 days the wound bleeds;
- pus is released from the hole.
You can take medications on your own to lower your temperature if the reading is above 38°C. Touching the wound, trying to clean it, or using any traditional methods is not recommended. If you suspect complications after tooth extraction, you should visit your dentist.
Temperature after dental treatment
A slightly elevated temperature after dental treatment is a normal reaction to intervention in the body’s tissues, especially after treatment of complex diseases (pulpitis, periodontitis). Sometimes weakness and drowsiness may appear, which can be relieved with antipyretics, but you should not get carried away with them.
If three days have passed after treatment and the fever does not go away, you should consult a doctor: he will conduct an additional examination and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Specialist help
In a situation where after tooth extraction the temperature remains at 38 °C, it is dentists who provide assistance. You should not waste time visiting a therapist or other specialist. It is advisable to contact the same doctor who performed the operation.
Treatment necessarily begins with diagnostics, which includes examination and x-rays. Once the cause of the patient’s pathological condition is identified, methods for eliminating it are determined.
Treatment methods depend on the factor that provoked the increase in temperature:
- incomplete removal of the tooth root, formation of a cyst or granuloma - cleaning the hole, treating with an antiseptic, prescribing antibiotics;
- damage to soft tissues - cleansing (in case of a purulent process), treatment with an antiseptic solution, suturing and prescribing antibiotic drugs;
- infection of the socket - high-quality cleaning of the socket, installation of drainage, treatment of the wound with an antiseptic, prescription of a course of antibiotics, removal of the drainage, repeated antiseptic treatment;
- osteomyelitis - opening of the gums, cleansing the bone from nicrotic tissue, applying a medicinal application, antiseptic treatment, taking antibiotics, re-diagnosis, removing the application and suturing.
After treatment, body temperature may also rise within normal limits. Rehabilitation will be more difficult and longer.
Dentists advise monitoring body temperature after tooth extraction, especially if it is a complex operation. To reduce the risk of complications, you should strictly follow all doctor's recommendations. If pathological symptoms appear, there is no need to ignore them. Even a preventive visit to the dentist can prevent serious consequences.
What should you consider when removing a baby tooth?
The following are taken into account:
- Anatomical features. The walls of primary teeth are relatively thin, and the roots can go deep at a large angle. Therefore, their removal requires the use of special forceps, which help eliminate the possibility of damage to the tooth walls. Pulling out is done in one motion so that the baby experiences minimal discomfort.
- Pain relief. In most cases, anesthesia is not required, especially if the tooth is already loose. Local anesthesia may be required to remove the nerve. The required dose of the drug is calculated individually for each patient.
- Contraindications to the procedure are diseases that cause bleeding disorders (leukemia, hemophilia), hematomas in the mouth, chicken pox, whooping cough, scarlet fever, influenza, sore throat, etc. Gingivitis and candidiasis can also be a reason to temporarily postpone the procedure.
Filling or silver plating
Silver ions stop the growth and division of pathogenic microorganisms. This means that caries will not develop in the future. But silvering is prescribed only in the initial stages of the disease. When large areas are damaged, it is useless to silver a baby tooth; over time, it will still collapse. A puncture may occur, which certainly will not be pleasant for the baby.
Is it possible to do a filling without a drill?
Today, medicine has made great progress and dentistry is no exception. Our clinic has ultra-modern equipment that does not produce frightening noisy sounds. In addition, filling is currently performed chemically. Its essence is the application of a special gel-like substance, which, after 30 minutes of exposure, is removed along with the damaged tissues. Then filling material is applied to this place.
Anesthesia
In order not to traumatize the psyche of children, dentists use injections extremely rarely. Pain-relieving gels and sprays are mainly used. Injection anesthesia is used only in extreme cases.
Anesthetics are selected in each individual case and are used only when there are no contraindications.
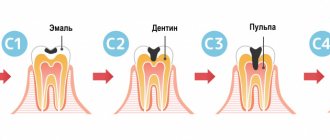
Causes of caries
- artificial feeding;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition (lack of sufficient fluoride in the diet),
- injuries;
- defects, features of the anatomical structure of bone tissue;
- poor oral hygiene;
If the development of the disease is associated with inheritance or poor health, it is necessary to regularly show the child to the pediatric dentist.
The post Filling baby teeth appeared first on.
]]>
A few words about caries prevention
The appearance of caries in babies can be prevented if you pay close attention to the child’s oral care and nutrition.
- It is necessary to develop the correct diet for the baby: up to 3-4 years of age, it is recommended to limit the consumption of sweets as much as possible; it is carbohydrates that provoke the development of caries in children. You should include as much dairy products, herbs, fruits, vegetables, and fish in your daily meals.
- At an early age, it is worth teaching your child to strictly adhere to a diet. You shouldn’t “follow” your beloved baby’s desire to snack on cookies in the middle of the night or drink sweet juice after brushing your teeth in the evening.
- Your baby should be taught to brush his teeth from the moment his first tooth appears. From the age of 1.5 years you can use a brush, and at an early age you can wipe the oral cavity of the crumbs with gauze swabs and special napkins. Also, on the recommendation of the dentist, you can treat the oral cavity with special anti-caries gels. For these purposes, “ASEPTA baby” wet wipes are perfect for cleaning the baby’s mouth, which will give the baby freshness, prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce discomfort during teething.
- It is also important for parents to follow the rules of hygiene - you should not lick your child’s spoon or pacifier, or eat from the same plate with him, because cariogenic bacteria from adults can spread to them.
Now you understand how important it is to cure caries of baby teeth at the first stage of development. Keep an eye on your baby’s health, and the problem of the consequences of removing baby teeth will be unfamiliar to you.
The role of primary teeth in child development
The baby needs milk teeth to chew food, they help him to experience the taste of the world around him, and most importantly, they participate in the development of the entire maxillofacial apparatus. It is the baby teeth that pave the way for the permanent row. The main functions of a time series also include:
- Development of the baby's speech skills;
- Bite formation;
- Participation in the development of facial muscles;
- Development of facial bones.
The formation of baby teeth occurs at 6-7 weeks of fetal life, in the womb. The baby's first tooth begins to erupt at 6-8 months, accompanied by an increase in temperature and very unpleasant sensations.
When is removal appropriate?
Pediatric dentists prescribe baby tooth extraction for children only in advanced cases when the organ can no longer be saved. As a rule, the procedure is prescribed if:
- Most of the crown is damaged by caries;
- The tooth becomes loose and causes discomfort to the baby, but does not fall out;
- The tooth is broken, the sharp part of the crown damages the mucous membrane;
- The permanent tooth cannot erupt in the area of the baby tooth, which causes the baby severe pain and discomfort;
- A fistula forms in the gum;
- Pulpitis and periodontitis develop;
- A cyst, phlegmon and other inflammations form in the gums, requiring surgical treatment;
- The root of the tooth or the surrounding areas become inflamed.
Consequences of early removal of baby teeth
As we have already said, baby teeth play an important role in the development of the maxillofacial apparatus. Early removal of baby teeth can cause consequences such as:
- Violation of aesthetics. Children are not too concerned about the aesthetic problem of missing teeth. However, the older the child gets, the more embarrassed he becomes about his smile. Remember the fairy tale about sold laughter? Like Tim Thaler, the baby will become withdrawn, uncommunicative and aggressive. The issue of premature absence of teeth can disrupt the process of social adaptation of a child, imposing on him a stereotype of aggressive behavior with people.
- Displacement of the maxillofacial apparatus. As Aristotle argued, nature abhors a vacuum. Part of a row of teeth may shift to the place of a prematurely removed baby tooth. When changing, the permanent teeth may move slightly to the side, which will greatly spoil the child’s appearance. Even natural facial features can change.
- Speech development disorder. The front teeth are involved in the formation of sounds. If baby teeth are removed prematurely, the baby begins to “get creative” by uttering certain sounds. Subsequently, such a habit is difficult to change.
Milk teeth, like permanent teeth, have roots. Let's consider the consequences of premature removal of specific baby teeth:
- Loss of primary canines. Unexpected elimination of the upper primary canines can cause malocclusion and speech distortion. Removal of the lower fangs causes the child to chew food inadequately and develop gastrointestinal diseases. Losing canine teeth can also lead to a shift in cosmetic focus.
- Removing primary chewing teeth also reduces the baby's chewing activity. As a result, the load on the front teeth increases, and the milk rows begin to wear off. Consequences - the child, worried, refuses solid food. As a result, due to lack of stimulation, the development of the temporomandibular joint may be impaired. Permanent teeth have less space, the rows may develop crowded, the teeth “climb” on top of each other or grow into a second row.
- Removal of primary incisors can cause the canines to shift towards the socket. Sometimes babies suffer from the rotation and tilting of the remaining teeth.