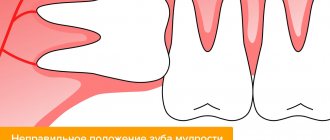
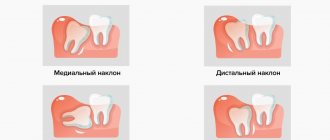
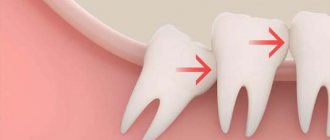
Third molars do not always grow in
This is true. The formation of “eights” does not occur during uterine development, but at the age of 3-5 years. But even if their rudiments are present, eruption does not always occur. The fact is that they begin to grow at the age of 17-25 - at the age when the jaw bone has already completed its formation and the dentition is complete. And there is no room for wisdom teeth.
Often their growth is hampered by the seventh molar. The process of teething occurs individually for each person. Sometimes 1-2 units may grow, while the rest remain hidden by the gum. In some situations, none of the “eights” grows.
But there are also cases (about 8%) when people do not have the rudiments of wisdom teeth at all. In men, the upper molars often do not develop, and in women, the lower molars do not develop. That is why the norm is considered to be 28-32 teeth.
Removable dentures
For centuries, dentists have been solving the problem: if there is no root, how to make a tooth? The first option, which has been around for thousands of years, is removable dentures. They were found during excavations of Egyptian tombs and in the territory of the Mayan Indians, so this is one of the most ancient methods of restoring teeth.
What are its advantages? Firstly, it is fast - making a prosthesis takes from 3 to 7 days, depending on the complexity of the work; secondly, it is inexpensive compared to bridges or implants. Modern materials for removable dentures make it possible to create structures similar to natural teeth, but they still have disadvantages:
- service life even with careful care is about 5–7 years;
- constant risk of prosthesis falling out and the need for additional fixation;
- the prosthesis does not stop bone atrophy;
- does not allow the chewing load to be evenly distributed;
- sometimes causes diction defects;
- there is a risk of allergies to acrylic, nylon, silicone and other materials.
Removable prosthetics are now being used if there are absolute contraindications to the installation of bridges or implants, or as a temporary measure while the patient waits for a permanent prosthesis to be made.
"Eights" have long lost their functionality
In ancient times, people ate raw meat, roots, and they needed massive molars to chew solid food. Over time, people began to consume thermally processed, softer foods, and the urgent need for the most distant units disappeared. However, you should not completely discount them.
Despite the fact that they themselves do not take much part in chewing food, “eights” restrain the loosening of the teeth, which bear the main chewing load. And in old age they can serve as a support for a bridge.
Why can't we leave everything as it is?
When a person loses a tooth in the smile area, he usually tries to restore it - but with chewing teeth that are not visible, the situation is different. Many people think that if one chewing tooth is lost, then nothing bad has happened - the rest are in place, which means they can chew.
Each tooth in our jaw carries an important functional, and not just aesthetic, load. If the tooth is not restored, negative consequences will inevitably occur:
- improper distribution of the chewing load will lead to gradual destruction of the teeth next to the defect - after all, they will have to work for themselves and for the lost tooth;
- bone tissue atrophy will occur due to the fact that there is no load during chewing;
- Bite defects will appear - if a tooth has been missing for years, then its row neighbors gradually begin to shift towards the empty space;
- chewing food will not be of sufficient quality, which over the years will lead to the development of problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- bite defects will negatively affect the functioning of the temporomandibular joint, which will provoke neck pain, headaches, discomfort and pain when opening the mouth or chewing, even insomnia;
- Diction problems will appear.
The eruption of “figure eights” is almost always associated with complications
Difficulties in eruption of third molars are caused not only by lack of space, but also by the fact that they do not have deciduous predecessors. Therefore, they often grow only partially or at an angle. But even the appearance of units growing correctly in most cases causes complications.
Most often found:
- destruction or displacement of adjacent teeth;
- bite problems;
- pericoronitis.
Very often, the eruption of the figure eight is accompanied by a purulent-inflammatory process. This happens because a hood appears over the tooth, and around it there is a pocket in which bacteria, plaque and food debris accumulate. They create favorable conditions for the development of inflammation (pericoronitis).
Often, when the eighth tooth appears, severe pain is felt, which occurs due to oppression of the roots of neighboring units.
About fibrin and fibrin plaque
Fibrin
- a high-molecular, non-globular protein formed from fibrinogen, synthesized in the liver, in the blood plasma under the action of the enzyme thrombin; has the form of smooth or cross-striated fibers, the clots of which form the basis of a blood clot during blood clotting. Thus, fibrin promotes rapid wound healing by forming fibrin plaque.
Fibrin plaque
- a natural phenomenon that occurs in the oral cavity in the area of surgical intervention (at the site where a tooth was removed, stitches were applied, etc.). It occurs on the 3-4th day after surgery in the oral cavity. And this is one of the normal and inevitable stages of healing of a hole covered with a blood clot. This is followed by tissue restructuring, covering the wound with protective epithelium and restoration of normal mucosa.
Patients often confuse fibrin plaque with pus, causing them to worry and call their dentists.
Why does fibrin plaque occur?
Healing of a wound in the oral cavity occurs in a moist environment. If you have a cut on your skin, once the bleeding stops, the wound will be covered with a scab. We all know from childhood that this crust cannot be torn off. A blood clot covered with fibrin plaque is essentially the same “crust”, only in the mouth. And you can't touch her either! Otherwise, the healing process will take longer and the result will be less favorable.
There is no need to rinse out fibrin plaque!
After tooth extraction, tooth transplantation or dental implantation, intensive mouth rinsing is contraindicated, otherwise you may rinse out blood clots and fibrin plaque. As a result, painful sensations will appear, and the wound healing process will be worse.
Therefore there is no need to rinse
, and especially antiseptic and refreshing rinses, which often contain alcohol. However, the mouth can be washed. Make a kind of bath to wash away food residues. For this, a solution of chamomile or even simple black tea is suitable, which you just need to take into your mouth, hold for a while on the injured area and carefully spit out.
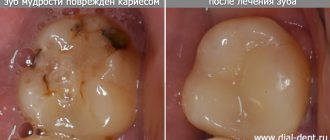
Eighth teeth are more likely than others to suffer from caries and other diseases.
This is due to their remote location and the inability to thoroughly clean them. Which leads to a large accumulation of bacteria and the development of caries, gingivitis, and periodontitis. Treatment in such situations is possible, but filling is often complicated by twisted roots and canals. Also, many people cannot open their mouths wide enough or some have a pronounced gag reflex - this significantly complicates the dentist’s work. Due to objective reasons, the “eights” are treated poorly.
Therefore, if the patient wants to keep the unit, a consultation with a dentist is required, who can professionally assess the situation and make the right decision.
What determines the symptoms of teething?
At what age do wisdom teeth erupt and what symptoms of this process depend on the individual characteristics and position in the jaw bone. The more abnormal the position, the more problematic it is. Impacted teeth (unerupted) cause particular inconvenience. They can grow at the wrong angle, put pressure on the “sevens”, and cause inflammation and bleeding of the gums. With such symptoms, the development of infection makes the situation worse. An unpleasant odor, shooting pain, and redness of the gums indicate active inflammation with the formation of pus. The situation is dangerous in terms of location, proximity to the brain and the possible development of complications.
Wisdom teeth need to be removed early
There is still debate in the dental community about the need to remove third molars in advance, even if they do not bother you. However, most experts are still inclined to believe that this is not worth doing. Scientists do not have sufficient evidence that preventive removal can preserve oral health in the future.
Indications for tooth extraction are:
- its incorrect location;
- lack of space for teething;
- destruction of the adjacent seventh molar;
- deep caries (pulpitis, periodontitis);
- crowding of units;
- inflammation of the hood.
In these cases, there is no point in fighting for the G8. And, if it is not possible to save the molar, you should think about choosing a dentistry where experienced professionals will remove the tooth.
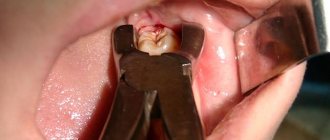
Removing "eights" is always difficult
If the unit is located correctly and does not have serious pathologies, it will not be difficult to remove it. To carry out the removal without the risk of complications, before the procedure the patient is prescribed an X-ray of the tooth.
However, most often the third molar grows incorrectly, partially erupts or becomes intertwined with neighboring roots. In this case, the intervention will be carried out in a complex way. The final decision on the choice of method is made by the doctor after examination and obtaining the results of an x-ray of the tooth.
When using a complex method, manipulations are performed in the following sequence:
- The gum is cut and peeled away from the bone.
- To access the roots, a hole is drilled into the bone.
- The unit is extracted (in whole or in parts).
- The wound is treated and stitches are applied.
The procedure can take from 20 minutes to 2 hours. Everything is individual and only an experienced doctor can professionally perform the removal. Therefore, you should be careful when choosing a clinic and specialist.
After surgery, it is recommended to eat soft foods and refrain from physical activity for several days. Antibacterial therapy may be prescribed for prophylactic purposes. Pain and swelling persist for 3-4 days and then gradually disappear.
Visiting the dentist immediately after the figure eight begins to erupt will save you from many serious complications.
Complex dentistry "Sanident" invites all residents of Ivanteevka and Shchelkovo to use the services of experienced dentists who can cope with any dental disease.
Reasons for delaying the replacement of baby teeth
When will permanent teeth erupt and baby teeth fall out?
Reasons for delayed replacement of baby teeth.
The question often arises about when permanent teeth will erupt and baby teeth will fall out. The reason for the slow change is general and local factors.
Common factors include body conditions:
- Chromosomal abnormalities - Down and Turner syndromes
- Nutritional deficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- Gingival fibromatosis and drug-induced gingival hypertrophy
- Cranioclavical dysplasia
Local factors for delayed teething:
- Additional temporary or permanent tooth in the bud
- Changed position of teeth (their rudiments), out of place
- Dental crowding
- Thickening of the gums due to early removal of a temporary tooth
- Trauma or infection of primary teeth
- Immobility (ankylosis) of primary teeth
The timing of teething varies individually: -/+ 6 months for temporary teeth and a year for permanent teeth. Delayed eruption of primary teeth does not require treatment. What to expect in case of primary teeth:
- in premature infants
- children with low birth weight.
If the eruption of permanent teeth is delayed, the child should be examined for the presence of a supernumerary (extra) tooth. Such teeth, as a rule, do not have a full-fledged structure at the macro and micro levels, cannot perform their function and interfere with neighboring teeth. An additional tooth is removed from the dentition.
Crowding of the dentition can be suspected upon examination at 3.5-4 years. If at this age the baby teeth are straight, but there are no gaps between them, you need to consult an orthodontist.
The changed position of the rudiments can most often only be detected by a doctor from an examination image. In this case, individual treatment is selected after diagnosis.
Due to the early removal of a temporary tooth, bone tissue and dense gums form at the site of the hole. The path of the permanent tooth germ is complicated by the thickness of the bone and gums, which leads to slow eruption.
Trauma and infection on the roots of primary teeth can lead to cystic changes in the buds of permanent teeth. In this case, the prognosis for the eruption of such teeth is unfavorable.
Prevention is dental treatment, regular examinations after injury every 3 months.
The last one is the most mysterious reason that raises questions.
The fixed tooth “by eye” is located lower in height than the other teeth. It appears to be embedded in the dentition as a result of predominant jaw growth and eruption of adjacent teeth. Sometimes such a tooth ends up under the gum.
Such teeth are called fixed, submerged or ankylosed because they are tightly connected to the bone. Because of this feature, they most often do not fall out and have to be removed.
Such sunken teeth:
- Occurs equally in girls and boys
- Often combined with the absence of permanent tooth buds
- Scientists have noticed a genetic predisposition
- Occurs together with other anomalies of the teeth, for example, canines and first molars.
The tactics for managing such cases depend on several factors:
- Presence of permanent tooth buds
- Degree of immersion of a baby tooth under the gum
- Resorption of the roots of a temporary tooth
Examinations by a pediatric dentist or orthodontist will help identify this dental condition. Diagnosis (panoramic image) at 6-7 years will allow you to track the dynamics and draw up an action plan to correct the situation.