Sialadenitis is an inflammation of glandular tissue. Most often, the disease affects the parotid glands, a little less often the sublingual and submandibular glands. It can develop in both adults and children. But each age group is characterized by a certain type of inflammation of the salivary gland; they all differ in both symptoms and treatment approach.
The most common pathologies of the salivary glands include:
Sialadenitis is an inflammation that develops when an infection penetrates into the gland or against the background of impaired salivation.
Mumps is an infectious disease caused by paramyxovirus that affects the central nervous system and glandular organs.
Etiology of the disease
The disease most often affects children, but sometimes adults also get it. The latter have a severe course of sialadenitis, especially in men.
Inflammation of the salivary gland occurs for various reasons under the influence of many factors, so the disease is classified as polyetiological. But one condition always precedes the pathological process - the presence of a pathogen, an infectious agent. In most cases, these are either viruses or bacteria.
The most common prerequisites for inflammation of the salivary glands:
any source of infection located in the mouth and ear; carriage of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microorganisms; tuberculosis, syphilis, HIV; metabolic disorders; any immunodeficiency conditions; scarlet fever, rubella, measles and other infectious pathologies; viral diseases such as influenza, cytomegalovirus; mycoses; pneumonia, bronchopneumonia; oncological diseases; benign lymphoreticulosis.
The most common mechanisms of transmission of this infectious disease are: airborne, contact, blood-contact, and single-gene.
Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.
Diseases of the salivary glands: types and symptoms
Different stages and types of inflammation of the salivary glands are characterized by different clinical signs.
Mumps or mumps
This type of viral inflammation of the salivary glands often occurs in children. It begins abruptly: against the backdrop of complete well-being. Occurs with an increase in body temperature to 40 °C.
Usually inflammation affects the parotid salivary glands , which is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling of the cheek and part of the neck on one or both sides (see photo), swelling of the neck, sharp throbbing pain that intensifies during eating, chewing, and opening the mouth.
Sialadenitis
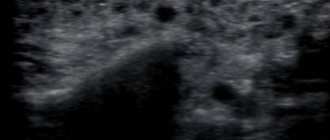
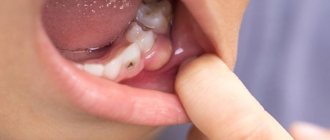
Photo: inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue
Symptoms of the disease differ depending on the location of the infectious lesion:
When the submandibular salivary gland becomes inflamed, the area under the chin swells. There is acute pain when swallowing, especially under the tongue, with pus discharge from the duct. Damage to the submandibular salivary gland is accompanied by lack of appetite, weakness and fever. Inflammation of the submandibular gland can be calculous in nature, that is, it occurs with the formation of stones. In this case, the duct becomes obstructed by a stone and becomes impassable. The cause of the pathological process is excess calcium in the human body. The following symptoms indicate that the gland under the jaw is inflamed: stabbing, paroxysmal pain while eating, when opening the mouth, enlargement of the organ, which is accompanied by swelling of the neck, discharge of pus, and an increase in temperature. Inflammation of the sublingual gland is extremely rare and is more often a complication of an abscess of odontogenic origin. Among the chronic forms, a special type of sialadenitis should be highlighted - dry Sjögren's syndrome. It is directly related to connective tissue pathology and autoimmune reaction. Sialodochitis is a lesion exclusively of the salivary ducts. It occurs more often in older people and is characterized by hypersalivation and the formation of cracks in the corners of the mouth.
Depending on the clinical picture and severity of the disease, the disease is divided into 3 main types: serous, purulent and gangrenous.
Serous sialadenitis
This stage of inflammation is characterized by a slight rise in temperature, dry mouth, swelling and slight thickening in the area of the ear canal and neck. Sometimes there is a slight feeling of fullness and pulsation.
Upon palpation, a person’s salivary glands will produce a small amount of secretion. At this stage, treatment at home is acceptable - this is the most favorable option for the course of sialadenitis.
Purulent sialadenitis
Manifests itself as a complication after serous. Accompanied by increased pain, asthenic syndrome, and autonomic dysfunction. Characterized by insomnia, which occurs against the background of elevated temperature.
When opening the mouth, the patient experiences severe pain, so chewing function is limited. There is hyperemia and severe swelling, spreading to the cheek area and lower jaw area. Regional lymph nodes become enlarged and pus is released into the oral cavity.
Gangrenous sialadenitis
If inflammation passes to this stage, the patients’ well-being deteriorates and they are in an extremely serious condition. There is a high risk of death due to sepsis. Melting and necrosis of tissue occurs, and an inflamed area of destruction is visible above the skin. The enlarged gland becomes an order of magnitude larger.
If the pain is associated with damage to the frenulum
The hyoid frenulum is a mucous membrane that connects the tongue to the base of the mouth. Inflammation can be caused by:
- Diseases occurring in the oral cavity - stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- Using incorrect hygiene products: toothpaste, toothbrush, mouthwash;
- Allergies caused by taking medications.
Inflammation of the frenulum under the tongue can also occur as a result of injury to it during brushing teeth, eating (too hot or cold foods), talking loudly, sharply biting the tongue, or careless handling of cutlery.
The reason why it hurts under the tongue may also be a physiological feature. In cases where the frenulum is short from birth, the likelihood of damage increases significantly, and discomfort can occur even while eating.
What can you do
A visit to the dentist cannot be avoided if the frenulum under the tongue hurts. The doctor will examine the damage and prescribe treatment. At home, especially if you can’t immediately visit a specialist, in order to relieve pain, you can rinse your mouth:
- Soda solution (a teaspoon per glass of chilled boiling water);
- Chamomile or sage decoction;
- Preparations: Stomatofit, Rotokan, Chorophyllipt.
Also, if the frenulum under the tongue is inflamed, it is recommended to treat the affected area with Iodinol or place a cotton swab dipped in sea buckthorn oil at the damaged area. Such measures can only be used in cases where you know for sure that the cause of the pain under the tongue is an inflamed frenulum.
What you can do at home
Treatment of inflammation of the salivary glands at home is acceptable, but only at the very initial stages of the disease or in combination with traditional methods of therapy. To avoid complications, you must consult a doctor .
To speed up recovery, you can drink and rinse your mouth with decoctions based on the following herbs:
chamomile; mint; raspberries; needles; eucalyptus; feverweed; sage; elder.
An excellent folk remedy for reducing pain and inflammation is aromatherapy with essential oils of fir, pine needles, eucalyptus and many other oils.
Causes of pain under the tongue
- Allergic reactions cause tissue swelling and pain.
- Harmful microorganisms that appear in the mouth during a sore throat cause acute inflammation. Often, it affects the floor of the mouth.
- Mechanical injuries from a bruise or a fall damage blood vessels, nerves, and soft tissues. Vessels may rupture, which will lead to the accumulation of blood between the muscle fibers.
- Some untreated diseases lead to phlegmon, inflammation with pus inside. In most cases, phlegmon appears under the tongue.
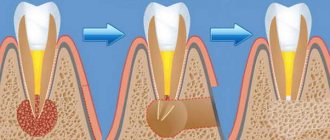
- Ordinary caries, if left untreated, causes inflammation that reaches the sublingual area.
- There are many ducts in the salivary gland, and if an infection gets into it, then through these ducts it can easily enter the gland tissue.
- Injury to the frenulum of the tongue. In people with a congenital short frenulum, injuries occur more often. Even a normal conversation can cause a breakup. However, people with a normal frenulum size also suffer. Inflammatory diseases and allergic reactions often lead to injury, leading to swelling of the tongue and the appearance of ulcers. But also improper oral hygiene leads to damage to the frenulum - the so-called dangerous brushing.
Some people have asymmetry of the hyoid bone from birth, and sometimes this anomaly is formed due to injury. Asymmetry prevents the organs of the floor of the mouth from functioning properly.
Prevention
Preventing inflammation of the salivary gland is easier than treating it. To do this you need to follow only 4 rules:
sanitize the oral cavity, cure carious teeth, pharyngitis, tonsillitis; remove foci of infection, especially those located near the ear canal and throat; stimulate and strengthen the immune system; protect your body from stress and be less nervous. The acute process ends either with transition to chronicity or with recovery. Chronic sialadenitis is often complicated by atrophy, sclerosis and is difficult to treat. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and not self-medicate.
Treatment
Having established the causes of inflammation of the tongue, the specialist prescribes treatment. In case of inflammation of the salivary glands, the purulent contents are initially removed, then antibacterial agents are injected into the ducts, and the patient is also prescribed antibiotics or sulfonamide drugs orally.
As a rule, therapy is accompanied by rinsing (in each case the doctor selects the optimal solution) and physiotherapy: UHF, Sollux and others. For fever and general malaise, paracetamol or ibuprofen is prescribed.
Surgical treatment methods are used extremely rarely. The operation is performed if there are stones in the duct and they cannot be removed in any other way.
If you experience unpleasant symptoms or discover inflammation or swelling under your tongue, do not look for what it might be. Go to a qualified dentist, he will examine the oral cavity, make a diagnosis, and prescribe adequate therapy. Perhaps pain in the sublingual space is a symptom of another serious disease and consultation with an appropriate specialist will be required.
Monitor the condition of your teeth and mucous membranes, visit the dentist regularly, promptly treat inflammation of the ENT organs and ARVI - such preventive measures will minimize the possibility of inflammation and pain.
Tests and diagnosis of sialadenitis
Diagnosis of sialadenitis is carried out using clinical, instrumental and laboratory methods.
The essence of clinical methods is the collection of complaints and anamnesis. The doctor also examines the patient.
Laboratory methods - a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test are performed. A study of saliva is also carried out, in which, during the inflammatory process, leukocytes and an admixture of pus are found.
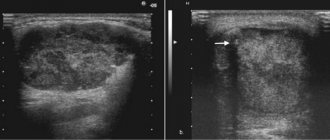
Hardware methods - diagnosis of diseases of the salivary glands involves, first of all, sialography with contrast, that is, x-rays of the gland. With the help of such a study, stones, narrowing of the lumen of the excretory duct, as well as other obstacles to the normal secretion of saliva are determined.
CT, MRI - it is advisable to carry out if the presence of stones is suspected.
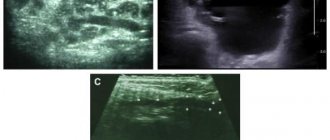
Ultrasound - allows you to determine the structure of the gland and the characteristics of the inflammatory process.
Thermosialography – the temperature of the gland is measured.
Salivary gland biopsy - performed under ultrasound guidance.
Sialendoscopy.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Classification
Taking into account the peculiarities of the process, acute and chronic sialadenitis are distinguished.
According to nosological independence, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Primary is an independent disease.
- Secondary – a complication in the development of other diseases ( flu , sore throat , etc.).
Taking into account the causes of the development of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- Traumatic – a consequence of injuries and the influence of external factors.
- Radiation – a consequence of irradiation.
- Toxic – a consequence of chemical influence.
- Infectious – develops after infection.
- Allergic.
- Autoimmune.
- Obstructive - a consequence of blockage of the excretory duct by a foreign body or cicatricial narrowing of the duct.
According to the location of the lesion there are:
- Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland - the inflammatory process of the sublingual gland is also called sublingual gland.
- Inflammation of the parotid salivary gland - in this case, the cheeks swell and there are signs of general intoxication. Sialadenitis of the parotid gland is also called mumps .
- Sialadenitis of the submandibular salivary gland is an inflammatory process of the submandibular salivary gland. When this gland is damaged, calculous sialadenitis , which is characterized by the development of stones in the ducts of the salivary glands or in their parenchyma.
Taking into account the condition of the parenchyma, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- interstitial sialadenitis - only stromal damage occurs.
- parenchymal sialadenitis - in addition to the stroma, the parenchyma is also affected.
Depending on the nature of the inflammatory process, the following forms of sialadenitis are distinguished:
- Purulent.
- Serous.
- Hemorrhagic.
- Connective tissue.
- Destructive.
- Granulomatous.
- Fibroplastic.
- Sialadenitis without deformation of the gland.
- Sialadenitis with scarring of the gland.
There are also epidemic and non-epidemic sialadenitis.
- The epidemic form of the disease develops against the background of viral diseases and infections.
- Non-epidemic form - diagnosed if there is a blockage of the salivary gland. Such blockage can develop as a result of injuries, salivary stones, or foreign bodies entering the ducts.
Diet
Diet to boost immunity
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 3 weeks
- Terms: 1-3 months or more
- Cost of products: 1600-1800 rubles. in Week
During the treatment period, it is recommended to eat properly to strengthen the immune system. Sometimes doctors advise sticking to the so-called salivary diet. However, if a patient is diagnosed with calculous sialadenitis, then in this case it is necessary to carry out mechanical removal of stones, since nutritional correction will not help cure the calculous type of disease.
The salivary diet involves introducing the following products into the menu:
- Sauerkraut, sour berry fruit drinks, lemon juice, pickles.
- Citrus.
- Sour lollipops.
- Fresh vegetables.
- Juices from cabbage, carrots.
- Rose hip decoction.
You need to exclude from your diet foods that contribute to the formation of stones:
- Cheeses, cottage cheese.
- Tofu.
- Almonds, sesame.
- Fish.
- Milk.
Causes
There are a number of factors that provoke the development of sialadenitis:
- Wrong approach to oral hygiene.
- Diseases in which the composition and viscosity of saliva changes.
- Postponed surgeries.
- Infectious diseases - influenza, encephalitis , herpes , ARVI , etc.
- Oral diseases – caries , pulpitis , periodontitis , etc.
- Dry mouth.
- Treatment with chemotherapy , radiation therapy .
- Diabetes.
- Disorders of mineral metabolism leading to stone formation.
The epidemic type of the disease develops as a result of infectious processes. Most often, this condition develops with mumps (mumps) . This virus is transmitted from infected people through airborne droplets.
The non-epidemic form of the disease is usually associated with blockage of the glands. This happens with injuries or exposure to foreign bodies. Also the cause of the development of this form of the disease is the so-called salivary stone disease ( sialolithiasis ). If a person develops sialolithiasis of the submandibular salivary gland, the resulting stones may block the ducts.