Salivary stone disease accounts for 40–60% of all diseases of the salivary glands. Often, patients find out about the presence of a stone in the salivary duct only in the doctor’s office, where they go with complaints of severe pain when swallowing, radiating to the ear or temple, with swelling in the face and neck. A stone located in the duct of the salivary gland interferes with the normal outflow of saliva and can completely block it. For more information about what a salivary stone is, why it occurs and how to treat it, read on.
What are stones in the salivary glands?
Salivary gland stones are pathological biomineral formations that block the ducts of the salivary glands. They can be single or multiple. Such formations are most often found in the submandibular gland and its excretory ducts, less often in the sublingual and parotid glands.
They are formed as a result of the deposition of organic and inorganic components:
- calcium salts;
- epithelial particles;
- sodium;
- mucin;
- magnesium;
- amino acids;
- potassium;
- iron;
- chlorine, etc.
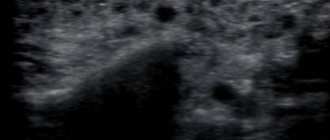
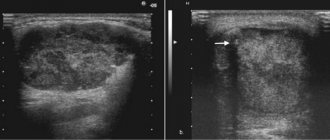
The weight of salivary stone varies from 3–7 to 20–30 g [1, 2]. Round-shaped stones usually form in the parenchyma of the salivary glands, and oblong stones in the excretory ducts. Salivary stones often have a yellowish color, an uneven surface, and varying density.
Proper brushing of teeth to remove plaque
Bass technique has been developed to remove food debris from the gum area. It is performed according to the following algorithm:
- Apply paste to brush
- Rinse your mouth with water
- Position the brush parallel to the teeth
- Slightly tilt the brush approximately 45 degrees.
- Move the device without pressing
- Then move in a circle, trying to get the bristles between the teeth
- Go over the entire jaw 15-20 times
- Move in a circular motion along the side teeth
- Do not ignore your tongue; 80% of pollution accumulates on it.
- Remove plaque from tongue
- There are brushes with a rough or bumpy back wall, specially made for cleaning this organ.
- After the outer part is completed, it is necessary to move on to the back wall of the incisors and molars. To do this, the brush is placed vertically with its bristles.
- It is recommended to carry out the procedure near a mirror to see the correctness of your actions.
As you can see, problems in the oral cavity and teeth occur in most cases due to non-compliance with hygiene rules.
Residues of food and the accumulation of bacteria on them create a plaque that hardens over time and cannot be removed by regular cleaning.
This is not only an aesthetic defect, but also serves as the basis for the development of dangerous diseases.
Brushing your teeth twice a day and regular dental check-ups will help reduce the risk of formations.
Etiology of sialolithiasis
Factors contributing to the development of pathology:
- Mechanical effects on the salivary glands (injuries to teeth and crowns). Inflammation compresses the ducts, where pathological microflora accumulates and pus appears. Over time, the stones increase significantly.
- Abnormal structure of the salivary glands and ducts.
- Disruption of calcium metabolism and, as a result, its deposition in the excretory ducts of the salivary glands.
- Hypovitaminosis, vitamin deficiency.
- Accelerated blood clotting.
- Entry of a foreign object into the gland duct. Bacteria actively multiply around the body, forming stone [2, 3].
The exact reasons for the formation of stones in the salivary gland have not yet been established. Presumably, risk factors are calcium metabolism disorders and vitamin A deficiency. Salivary stone disease most often affects men. Sialolithiasis mainly occurs in people 25–40 years old, and much less often in children.
The formation of salivary stones may be associated with a violation of the outflow of saliva or metabolism, with inflammatory processes in the salivary glands with the participation of microorganisms, poor nutrition, etc. As a rule, they are localized in the submandibular gland and its excretory duct; they are found in the sublingual and parotid glands very rare.
Abdusalamov M. R., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Traumatology of the Maxillofacial Region of the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A. I. Evdokimov [4]
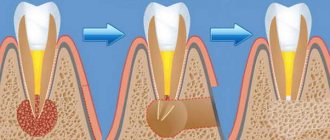
How is tartar formed?
Food particles attach to tooth enamel. Most often from soft and sticky foods, such as flour products.
Under the influence of saliva, a film of glycoproteins is formed; if you do not rinse or brush your teeth, then after 4 hours streptococci bacteria come into play, and actinomycetes join them. After 2 days, streptococci decrease, but the number of anaerobic bacteria increases. After 7 days, spirochetes and motile rods appear.
Remains of food and the bacteria that multiply on them are gradually covered with a film of saliva, smoothed out and hardened. Tartar grows because new layers are added to existing particles.
Fermentation and metabolism processes occur under dental plaque, during which acids are formed. They weaken tooth enamel so that tooth decay can develop over time.
Tartar can also cause bad breath.
Plaque can eventually turn into tartar through mineralization—minerals from saliva are deposited in plaque and make it very hard.
This is how complications arise; as a result of a neglected condition, you can lose a healthy tooth, but ringed with plaque.
The rate of mineralization varies from person to person. It all depends on the following factors:
- the amount of saliva produced;
- its composition and activity of secretions;
- quality of oral hygiene;
- nutritional characteristics;
- violation of salt exchange in the body;
- wearing dental structures (prostheses);
The predominance of solid foods (raw vegetables) significantly reduces the development of plaque. The products act as a cleaning agent, helping to remove dirt from the enamel. Chewing for a long time releases more saliva, which has an antibacterial effect.
Symptoms of a stone in the salivary gland
The onset of the disease occurs unnoticed (from several months to several years). Upon examination, the patient does not show any abnormalities. The first symptoms of the disease appear when the flow of saliva is disrupted during food intake, especially sour or spicy food.
Patients note the periodic appearance of swelling in the area of the salivary gland. Increased pain during eating is associated with difficulty in the outflow of saliva due to the presence of a stone in the duct. After eating, pain and swelling in the gland area gradually decrease.
The following symptoms are observed:
- increased body temperature;
- dry mouth, secretion of a small amount of saliva;
- a feeling of fullness in the part of the oral cavity where the stone has formed;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- frequent pain when eating;
- swelling and redness on the face;
- discomfort when chewing and swallowing.
Over time, changes in the gland increase: the disease passes into a clinically pronounced and late stage, when clinical signs of chronic sialadenitis are visible. The submandibular salivary gland enlarges, becomes dense and painful.
Side effects from scaling
These effects can appear after professional removal and when using folk remedies.
- Uncomfortable sensitivity from ultrasound: Some patients are sensitive to pain from ultrasound because the dental nerve or gums may be irritated. In addition, some people are bothered by accompanying sounds.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Once plaque is removed, teeth may be more sensitive to stimuli such as cold or heat. This is because tartar protects the tooth from these irritants. After removal, he first needs to get used to the intensity of the stimuli.
- Loose teeth: If you begin to notice loose teeth after tartar removal, especially the incisors, this may be a sign of periodontitis, which was previously unrecognized because the tartar was holding the teeth together. Depending on the severity of periodontitis, the dentist treats the bacterial infection of the periodontium with medications.
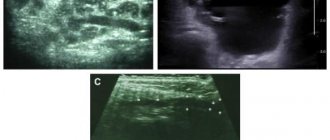
Diagnostics
If you suspect sialolithiasis, you should consult a dentist.
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- X-ray examination is currently the main diagnostic method. To identify a stone in the duct, an X-ray of the facial skeleton is taken in a direct projection. If the stone is localized in the anterior part of the duct, an x-ray of the floor of the mouth is shown; if it is located in the posterior part of the duct or in the submandibular gland, an x-ray of the lower jaw in a lateral projection is shown.
- Ultrasound - a study is carried out if there is a discrepancy between clinical manifestations and radiographic data to clarify the diagnosis.
The indicated diagnostic techniques are usually sufficient to establish a diagnosis and determine the location of the stone. There are other methods for studying the salivary glands, which are used less often in practice - CT and MRI. Their diagnostic value for calculus detection is close to 100%, since it allows one to determine the spatial location of the salivary stone.
Types of Tartar
Fossils on enamel come in different types depending on location. So they distinguish:
- supragingival stones – formed on the first molars (lateral) and front or lower teeth;
- subgingival - hard areas that penetrate soft tissue;
- stone bridge – covering the main and adjacent teeth.
Treatment of stones in the salivary gland
In order to remove stone from the salivary gland duct, use:
- conservative therapy;
- surgical treatment.
First of all, the following are assigned:
- antibiotics;
- drugs that stimulate saliva production;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
Re-inflammation often occurs and the process can become chronic. In such cases, the only treatment method that eliminates the root cause of inflammation is surgery.
Removal of a stone in the salivary gland from the duct is carried out under general anesthesia. The stone itself and the capsule surrounding it are excised. This surgical intervention is called sublingual extirpation and lasts 40–60 minutes. The main risk when performing surgery on the salivary glands is due to the fact that the facial, lingual and hypoglossal nerves pass in close proximity to them.
There is a less invasive method - sialoendoscopy. It allows one to penetrate the ducts of the salivary glands through the thinnest endoscopes without dissecting tissue and visualize the salivary system at high magnification. The endoscope is inserted into the opening of the gland duct in the mouth. Next, using micro-instruments, the surgeon examines the ducts, removes the stone, injects medicinal substances into the gland and performs other necessary manipulations.
Methods for removing tartar
- Physical method. Consists of mechanical destruction of deposits using a dental instrument with a thin tip. Modern medicine uses the Air flow system. Fine particles of soda are applied under high pressure, causing a stream of air containing the powder to knock the fossils off the tooth. A subsequent stream of water washes away the separated particles.
- Chemical method. Allows you to remove formations with the help of compounds that dissolve the basis of tartar - deposits of mineral salts. A composition is applied to the teeth that softens plaque, but does not cause significant harm to the enamel. Then the impurities are removed.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasonic waves do not injure teeth and gums. Contraindicated in patients using a pacemaker.
- Laser. The laser method can be used specifically in dentistry for various procedures. It is one of the most effective and expensive procedures. The laser beam is very thin and can be used precisely. This way, only truly unwanted tissue is destroyed. Healthy tissues are preserved. Local anesthesia is often not required. Laser treatment does not cause noise or vibration like drilling. The virtually painless treatment is especially suitable for anxious patients.
Prevention of salivary stone formation
It is worth taking note of a few rules to prevent the occurrence of salivary stones:
- Avoid disruption of mineral and vitamin metabolism.
- Give up bad habits, which will have a beneficial effect on other body systems.
- Protect yourself from maxillofacial injuries.
- Carefully follow the rules of oral hygiene: brush your teeth 2 times a day, follow the dentist’s individual recommendations. Perhaps you need a toothpaste with a certain composition, mouth rinses, or dental floss.
- Choose the right toothbrush (medium-hard bristles with artificial bristles).
- Visit the dentist regularly to monitor the condition of the oral cavity, timely detection of lesions and effective treatment.
Sialolithiasis is a fairly common pathology, for the treatment of which conservative and surgical methods are used. With timely detection of the disease and subsequent proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. This will also prevent complications and speed up the healing process.
List of sources:
- Gamataev I. I. Study of human salivary stones. New challenges of modern medicine, 2013 // URL: https://moluch.ru/conf/med/archive/86/3883/ (access date: 11/04/2020).
- Dmitrienko E. V., Shashkevich V. A. Algorithm for the diagnosis and treatment of salivary stone disease. Journal "Bulletin of the Smolensk State Medical Academy", 2010 // URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/algoritm-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya-slyunnokamennoy-bolezni (access date: 11/04/2020).
- Kartashov R. Sialolithiasis: the stumbling block is in the salivary gland. European Medical Center // URL: https://www.emcmos.ru/disease/sialolitiaz-kamen-pretknoveniya-v-slyunnoy-zheleze/ (access date: 12/13/2020).
- Gamataev I. I. Study of human salivary stones. Intl. scientific Conf., 2013 // URL: https://moluch.ru/conf/med/archive/86/3883/ (date of access: December 26, 2020).
How is surgery and rehabilitation carried out at our Center?
When seeking a consultation at the Center for Maxillofacial Surgery and Implantology, an experienced doctor will conduct an examination, prescribe an X-ray, ultrasound and sialography. Surgical methods of treating salivary stone disease involve removing the stone using the most modern techniques using ultra-thin endoscopes. This is not only the most progressive, but also the least traumatic and at the same time the most effective technique. The endoscopes used in our Center are so small that they allow us to remove the stone and cure the disease without removing the gland (as was previously used in medicine) and without making external incisions, but performing all manipulations through the natural pathways of the salivary ducts. This significantly reduces the postoperative recovery period - to 1 day - increases the safety of the procedure, and reduces to zero any risk from the intervention.
Treatment of salivary stone disease at the Center for Maxillofacial Surgery and Implantology can be carried out in just one visit and then forget about this problem forever. Surgery is performed in the comfortable conditions of our own hospital, which includes operating rooms equipped with high-precision medical and anesthesiological equipment. The team of doctors has extensive experience and the highest qualifications: surgeons and anesthesiologists with extensive practical experience, including in the field of removal of benign cervical formations and tumors, work here. In addition, the Center for Maxillofacial Surgery and Implantology has comfortable wards where you can undergo rehabilitation after surgery, under constant, attentive and sensitive medical supervision. Care is provided by responsible and highly qualified personnel who will help make the recovery period as fast, comfortable and painless as possible.
Prices for tartar removal in Moscow
| Removal of dental plaque (1 tooth) | 150 rub. |
| Ultrasonic cleaning (1 jaw) | 2000 rub. |
| Comprehensive professional preventive oral hygiene (including ultrasonic cleaning, Air Flow, polishing and fluoridation) | 5500 rub. |
| Polishing 1 tooth with abrasive paste | 500 rub. |
| Local enrichment of the 1st tooth with fluoride | 300 rub. |
| Fluoridation (1 jaw) | 2000 rub. |
| Air-flow (1 tooth) | 250 rub. |
| Air-flow (1 jaw) | 2000 rub. |