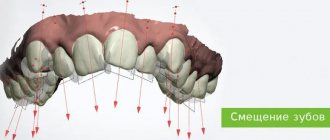
Why is it necessary to replace extracted teeth?
When free space appears in the jawbone, bone tissue gradually begins to decrease, the alveolar ridge thins, and the teeth begin to move, trying to fill the vacant space. Due to the disappearance of lateral support, the “neighbors” of the removed tooth begin to move. The antagonist tooth located on the opposite jaw moves out and “sags”. Due to this, the patient’s bite is disturbed, and the resulting deformations cause new troubles. The more years pass from the moment of removal, the more significant the anomalies will become. Problems can even arise with the temporomandibular joint, which will cause serious pain and disruption of its functionality.
Let's look at a typical example. With a prolonged absence of the “six” and “seven” in the lower row, the last molar tooth of the upper jaw can “sag” so much that it literally rests against the lower gum. In this case, there is no longer any need to talk about conventional dental restoration
Tooth dislocation - symptoms and treatment
Before contacting a doctor, the patient must be given first aid , which consists of the following [4]:
- It is necessary to examine the oral cavity for bleeding, bone fragments or a lost tooth.
- If bleeding is detected, measures must be taken to stop it.
- If the dislocation is complete, then it is necessary to apply a sterile tampon to stop the bleeding. It is made from a gauze bandage, which is folded several times, then applied to the bleeding hole (for 15-30 minutes) and the jaw is closed, thereby providing a hemostatic effect.
- Next, you need to apply cold to the cheek or lips in the projection of the tooth injury. This will help prevent swelling, reduce bleeding, and reduce pain.
- If the injury is impacted, then it is necessary to avoid putting pressure on the tooth or socket, as this can significantly increase the pain.
- If a tooth falls out, it must be saved. To do this, take a clean cloth or gauze moistened with water and wrap it around the tooth. There is no need to treat the surface of the tooth; the dentist will do everything himself.
- Next, ensure urgent delivery of the patient to the dentist.
After an examination, the dentist chooses a treatment strategy for this injury depending on the type of damage, as well as the degree of damage to the tooth and surrounding tissues. The main question is asked: “Is it possible to save a tooth?” Only a dentist can answer this question after a comprehensive diagnosis.
The main criterion is the condition of the bone tissue near the root of the injured tooth. If at least half the length of the tooth root is preserved, it is recommended to save the tooth.
Treatment of incomplete dislocation
If the patient has an incomplete dislocation, treatment begins with conductive anesthesia, after which the doctor carefully reduces (installs in the socket) the tooth. Reposition is carried out correctly if, when closing the jaws, there is no contact of the injured tooth with the antagonist.
It is more difficult to replace the tooth if more than two days have passed since the dislocation, since an organizing blood clot has already formed at the site of injury. In this case, the tooth should be rocked, followed by reposition according to the above method.
But if the patient seeks help after a few weeks and the tooth has already strengthened itself in the wrong position, it can only be placed in the dental arch with the help of orthodontic appliances.
After the treatment, the dislocated tooth is immobilized (immobilized). To do this, the doctor uses an individual mouth guard made directly on the patient. The splint must include at least two healthy teeth on either side of the incomplete dislocation. The splint is applied for at least 5-6 weeks.
Before splinting and during the course of treatment, the electrical excitability (response to electric current) of the neurovascular bundle is checked. A decrease or absence of electrical excitability not only in the first 1-2 weeks after injury does not necessarily indicate irreversible changes. The pulp reaction may return to normal within several months. But if clinical signs of pulp death are detected, it must be removed and the canal treated, otherwise the dead pulp remaining in the canal leads to the development of acute periodontitis or periostitis.
After incomplete dislocation, external resorption (resorption) of the root is possible, which does not progress. In this case, the severity of the resorption process is determined by the degree of displacement of the tooth root during dislocation: the greater the displacement, the larger the surface of the root can be subject to destruction.
Treatment of incomplete dislocation of a baby tooth consists of anti-inflammatory therapy, antiseptic wound treatment and x-ray monitoring after 1, 3 and 6 months.
Treatment of complete dislocation
In case of complete dislocation of a tooth, if no more than two days have passed since the injury, its replantation is carried out (installation of the tooth back into the socket) [8].
But there are cases in which it is not indicated:
- violation of the integrity of the walls of the hole and the developing inflammatory process;
- pronounced destruction of the directly injured tooth.
The earlier replantation is performed, the higher the likelihood of a positive result. Root resorption in this situation is less pronounced and proceeds more slowly.
Replantation is carried out according to the generally accepted method:
- The injured tooth is washed and placed in an isotonic sodium chloride solution with antibiotics until the operation.
- If no more than 10 hours have passed since the dislocation, the tooth can be replanted without undergoing endodontic treatment (root canal treatment). In this case, endodontic treatment of the tooth is carried out 2-3 weeks after replantation, when the healing of the tooth becomes obvious.
- If more than 10 hours have passed since the dislocation, the pulp is completely removed, and the canal is sealed after mechanical and medicinal treatment. After replantation, the tooth is removed from the bite and strengthened by splinting with a plastic splint-guard. It is removed only after 3-4 weeks.
- After replantation, it is necessary to carry out X-ray monitoring for one to twelve months. This allows us to judge the condition of the tooth root, periodontium and bone.
It should be noted that the most favorable results were obtained when replantation was performed 20-30 minutes after dislocation.
Treatment for complete dislocation of a baby tooth consists of anti-inflammatory therapy and antiseptic treatment of the socket. Replantation of a temporary tooth is not performed.
Treatment of impacted dislocation presents certain difficulties.
You can follow a wait-and-see approach aimed at self-extension of the injured tooth. Most often, this technique is used for impacted dislocations of temporary incisors: in this case, tooth advancement is facilitated by the further formation of the tooth root, if the tooth growth zone is preserved.
The first signs of spontaneous tooth protrusion can be seen a week to a week and a half after dislocation, but sometimes the time period increases to four to six weeks.
If signs of an acute inflammatory process appear, it is necessary to treat the tooth endodontically. Root resorption in the case of impacted dislocation is also possible, but it is less voluminous than with replantation.
The likelihood of spontaneous tooth protrusion decreases with strong impaction, a large inflammatory process, or the presence of infection at the top of the tooth.
Reposition of the impacted injury with fixation for 4-6 weeks should be carried out no later than three days after the dislocation. This manipulation is accompanied by loss of the marginal portion of the alveolus and subsequent resorption of the tooth root. Complete treatment of tooth root canals is carried out after strengthening the tooth in the socket [6].
You can also use orthodontic appliances to move the tooth. This is advisable when the tooth is driven shallowly into the socket, when part of the tooth crown makes it technically possible to fix the orthodontic structure on it. To prevent the development of ankylosis (immobility), orthodontic tooth advancement must begin immediately after the injury. This tactic reduces the degree of root resorption.
It should be noted that hardware orthodontic treatment in children begins no earlier than 3-4 weeks after injury.
When treating an impacted dislocation, it is sometimes permissible to remove a tooth and then replant it. It is worth remembering one rule: the earlier a tooth is replanted in case of dislocation, the later complications arise in the form of root resorption.
Indications for removal of an impacted tooth without its replantation are severe ankylosis and significant trauma to the alveoli (wall fracture) [5][7].
How can you solve the problem?
A layman will immediately name two obvious solutions:
- remove protruded tooth;
- file down its coronal part.
Removing a tooth without pain can only be justified by its severe destruction, and even accompanied by the patient’s complete reluctance to seriously engage in dental treatment.
Filing the crown does not seem rational either. After all, for this you will have to remove the nerve of the tooth, since it will have to be “shortened” by more than half, and then covered with an artificial crown. It is difficult to call the formed “formation” a full-fledged tooth. “Grinding” is not required only when the molar is slightly advanced, when you can limit yourself to grinding its cusps to the existing bite height.
The best option is orthodontic treatment, since it is the orthodontist who deals with problems of tooth displacement. Modern technologies make it possible to return a “failed” upper molar to its place.
Gap between teeth - diastema
Diastema is a fairly common phenomenon. In adults, you can often notice a gap, expressed to a greater or lesser extent. Statistics show that literally every second baby is at risk of developing a gap between the front teeth.
If the gap between the upper or lower front teeth is more than 1 mm and varies in width up to 10 mm (most often the limit is 2–6 mm), we can confidently speak of a diastema. The spaces between other teeth have another name - trema.
Due to the formation of a gap, all sorts of inconveniences arise in the implementation of everyday and vital functions. Diastema complicates the normal process of eating and affects diction, so if there is a sufficiently pronounced gap, the child speaks poorly. In addition, the gap is an additional stimulus for the occurrence of caries and periodontitis.
There is a classification of diastemas, including false ones: this involves the presence of a gap between the baby teeth, which naturally disappears during the change of teeth to molars.
If a gap occurs after the appearance of permanent teeth, measures should be taken to eliminate it as soon as possible. And although dentists eliminate diastema even in adulthood, it is most comfortable to carry out treatment in childhood.
What kind of gap could there be? The main division assumes the existence of symmetrical and asymmetrical diastemas. In the first case, the upper or lower incisors are at an equal distance from each other. In the second, only one tooth has an incorrect position, while the second remains in its rightful place.
Also, the spaces between the teeth can be conditionally divided according to the direction of growth of the incisors. The gap can be caused by the divergence of the incisors in different directions with parallel roots (lateral deviation of the crowns) or by a divergence starting from the roots (corpus lateral displacement).
In addition, a so-called medial tilt is possible, when teeth grow with rotation around their axis or have a clear direction to the side.
Mini-implants - as a basis for orthodontic treatment
The procedure for installing mini-implants is carried out under local anesthesia and does not require any incisions or sutures. A puncture is simply made in the tissue through which the surgeon implants a titanium implant. But simple and low-traumatic manipulations should be performed by a highly qualified specialist who can take into account the peculiarities of the location of the dental roots so as not to injure the tooth.
- In this example, small orthodontic dental implants will be installed next to the lowered upper “seven” - one each on the vestibular (external) and lingual (internal) sides.
- The orthodontist will glue special hooks to the molar on both sides, which will be connected to the heads of the implants using elastics. This way, the doctor will create a constant force, supported by the implants, pulling the sagging tooth back into the jaw bone.
- As with treatment with braces, stretchable elastic bands will need to be replaced periodically, for which you will have to visit the clinic. At the same time, the orthodontist will monitor the process, correcting the movement of the problem tooth.
As a result, a place for prosthetics will be obtained without removing, depulping or grinding the molar.
Cost of correcting diastema
It is easy to guess that the cost of correcting a diastema depends on the chosen method and the need to use certain materials. The severity of the defect also matters.
In general, the most affordable way to achieve a beautiful smile is cosmetic correction or surgical plastic surgery. Artistic restoration, braces and other methods of correcting the position of teeth will be more expensive, but the cost of these methods remains affordable for most patients. When it comes to mouthguards, their production will be the most expensive.
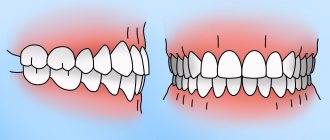
What causes malocclusion to form?
Defects appear for various reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. In most cases, mesial and distal bites are inherited. Therefore, parents who have this problem should take their child to an orthodontist in early childhood.
- Anomalies of fetal development. A child’s teeth are formed while still in the womb. During a complicated pregnancy or the influence of negative factors on its course, anomalies of the dental system can form.
- Birth injury. Mesial bite in some cases is a consequence of dislocation of the baby’s lower jaw during childbirth.
- Bad habits. Constant thumb or pacifier sucking, improper latching of the nipple, incorrect sucking during artificial feeding - all this provokes the development of malocclusion pathologies.
- Inferiority of the dentition. You can resort to removing baby teeth if there is less than a year left before the change. Otherwise, the dentition becomes asymmetrical, the midline shifts, and the chewing movements of the jaw are blocked. The formation of a permanent bite ends at approximately 15 years of age. For adults, after tooth loss, it is important to undergo prosthetics in a timely manner.
- Displacement of the jaws as a result of hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, which can be observed due to stress.
Jaw injuries, as well as improper prosthetics, can provoke the development of malocclusions.
Causes of dislocations
Dislocation always occurs under the influence of a directed force, the source of which is:
- a blow to the tooth during a game, a fall, a fight, an accident, an industrial accident;
- the load acting on the tooth when chewing bones, unshelled nuts, or opening beer bottles with the teeth;
- incorrect tooth extraction technique;
- pressure on a moving tooth when biting hard food.
When dislocation occurs, the position of the tooth root in relation to the walls of the socket changes, periodontal fibers are completely or partially torn, and the neurovascular bundle is damaged; often a dislocation is combined with a fracture of the tooth crown or maxillofacial injuries. Based on the nature of tooth displacement, incomplete, complete and impacted dislocations are distinguished.
What will be the consequences if the gap between the teeth is not corrected?
Will the child face consequences if the gap between the teeth is not corrected? It is impossible to answer unequivocally. During the consultation, the dentist will assess the degree of development of the diastema and correlate this with a number of other factors. However, it is impossible to accurately predict the consequences. The gap may not manifest itself in any way throughout life, but serious consequences cannot be ruled out. The diastema can expand and cause problems with bite and diction. If your child is already burring, then it makes sense to work on eliminating the diastema instead of trying to solve the diction problem with a speech therapist.
With age, the load on teeth increases, especially if they are incorrectly positioned in a row. This easily leads to caries and can cause periodontitis. An incorrect bite often results in teeth that are loose, painful, worn down, and at risk for infection and inflammation.
Therefore, in order to protect your child from frequent visits to the clinic in the future, take care of the position of his teeth today.