Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Periodontal disease is one of the most dangerous and insidious dental diseases, which can lead to the complete loss of not only single teeth, but also entire dentitions. Periodontal disease practically does not affect the teeth themselves, however, under its influence, periodontal tissue is destroyed - that part of the gum and jaw that is in direct contact with the root of the tooth and ensures its fixation. Not only the soft tissue of the gums weakens and collapses, but also the bone tissue, as a result of which the teeth become loose and there is a threat of their complete loss.
Degenerative processes in gum tissue that occur during periodontal disease develop under the influence of a number of factors, none of which researchers single out as the main and only one. Patients suffering from periodontal disease almost always exhibit certain trophic and circulatory disorders in the gum tissue, in particular of an atherosclerotic nature. However, such disorders can arise as a consequence of a wide variety of pathologies. Among the reasons that can provoke the occurrence of periodontal disease, experts name various dysfunctions of the endocrine and digestive systems, vascular diseases, neurological diseases and occlusion pathologies, single or regularly recurring injuries. Bad habits (alcohol and tobacco consumption), poor nutrition, which causes a lack of vitamins and minerals, and a persistent decrease in immunity, leading to increased activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms in the oral cavity, play a role in this process.
Unfortunately, today there is not a single drug that could completely restore destroyed tissue and reverse the process of development of periodontal disease. However, the use of a complex of physiotherapy and medications makes it possible to stop the progression of the disease, stabilize the patient’s condition and help the body regenerate damaged periodontal tissue. The leading role in achieving this result belongs to medications. You will learn about how to treat periodontal disease with medication from our material.
Content:
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Why do you need an orthodontic consultation?
- Treatment
- Other recovery methods
Dentistry is one of the branches of official medicine, whose services in Russia are traditionally resorted to in extreme cases. In theory, everyone knows about the need for regular examinations and professional cleaning twice a year, but in practice they turn to a doctor when severe pain bothers them. One of the serious dental problems is receding gums with exposed teeth. Home methods and antibiotics will not help; only in severe forms with an inflammatory process, lincomycin is used for periodontitis.
Indications for antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are not always used in the treatment of periodontal disease in dentistry. The dentist prescribes antibiotic therapy to the patient if there are indications:
- Inflammation of the gums, complicated by a bacterial infection.
- Dystrophic damage to bone structures.
- The appearance of periodontal pockets.
- Abscesses in the oral cavity.
Uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents leads to:
- disruption of intestinal microflora;
- reduction of the body's defenses;
- development of fungal diseases in the oral cavity.
Before prescribing antibiotics, the dentist prescribes a number of examinations to the patient:
- X-ray;
- allergy tests;
- determination of sensitivity to antibiotics.
The last type of research allows us to identify the type of periodontal disease causative agent. Treatment of periodontal disease with antibiotics is not considered the only way to combat the problem. The fight against pathology is complemented by the following:
- vitamins;
- steroid hormones;
- antifungal drugs;
- antihistamines;
- preolytic enzymes.
Causes
In the age of the Internet, any ordinary person can find answers to all questions. Unfortunately, the professionalism of some dentists is also based on knowledge gleaned from the World Wide Web. Confusion in concepts arises, and as a result, incorrect treatment is prescribed, which aggravates the pathology, but does not eliminate it.
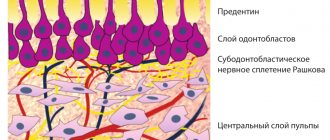
Periodontium is a set of tissues around the tooth responsible for its retention in the alveolus : gums, cementum, periodontium, periosteum and alveolar processes. When the functions of this complex are impaired, the dental units become loose and fall out; it is this pathology that is called periodontal disease.
The inflammatory process is periodontitis; it does not always accompany bone dystrophy, which has a chronic course and varies in severity.
Most often, receding gums develop in chronic pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2;
- malignant neoplasms and liver pathologies;
- atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease;
- endocrine disorders, increased stomach acidity;
- kidney damage, deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- psychical deviations.
The risk of developing periodontal disease is increased in smokers. Tobacco smoke negatively affects the immune system and directly affects the oral mucosa. A noticeable influence of the genetic factor, caries, and significant deposits of tartar was noted.
Disinfectant solutions
Disinfectant solutions are used in the acute stage, when the problem is accompanied by severe inflammation of the soft tissues. For the treatment of periodontal pockets the following is prescribed:
- Chlorhexidine 0.2-0.6%;
- Potassium permanganate solution – 0.02-1%;
- Dioxidin – 0.5-1%;
- Miramistin;
- Iodinol – 1%.
Solutions prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity.
One of the ways to combat periodontal disease is to rinse the mouth with Chlorhexidine.
Diagnostics
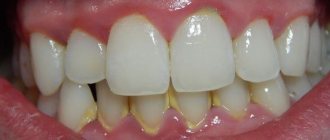
Periodontal disease is insidious, difficult to treat, and it is especially difficult to make a correct diagnosis. The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on this, but the complexity is aggravated by the fact that in the early stages it does not cause discomfort. People turn to the dentist much later, when the gums begin to bleed and become inflamed, and the teeth begin to loosen, exposing their necks. Soreness and swelling of the gums, a rotten smell immediately after brushing, and a reaction to hot, cold and sour appear.
Changing toothpaste will not give results, because it helps with prevention, not treatment, and cannot eliminate inflammation, especially since it does not exist with periodontal disease. Folk remedies in the form of decoctions, rinses and rubbing will not help here, and antibiotics are completely useless and even harmful. It is impossible to stop the destructive process by destroying the flora, and if a problem arises, you first need to consult an orthodontist.
A disease with similar symptoms is occlusal injury, and it is caused by the following reasons:
- the tooth is outside the main row;
- stands at the wrong angle;
- grew abnormally;
- the jaws have an incorrect bite.
With such characteristics, you can restore the necks and put fillings as much as you like, but the subsidence will continue, the fillings will chip, and periodontal therapy will not bring positive results. It is necessary to correct the occlusion, since the dental apparatus is destroyed by the force of chewing pressure, which causes bone tissue to decrease. Following this, the associated gum decreases and sinks along with the bone.
Expert opinion. Before treating periodontal disease, it is necessary to get rid of the disorders caused by occlusion before they develop into a more severe form, when suppuration and inflammation appear, and then several problems will have to be solved at once. Relieving inflammation with antibiotics will not eliminate the main cause, and the process will continue indefinitely.
Antibiotics for periodontal disease
Most often, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used for gum inflammation. The drugs are produced in the form of:
- tablets;
- ointments and gels;
- antiseptic solutions for local treatment of affected areas;
- rasters for injections into the gums.
The best effect is provided by drugs in tablet form, since they have an antimicrobial effect on the entire body. The results from their use are observed much faster than from other forms of medications.
Often, for gum inflammation, doctors prescribe antibiotics in tablet form.
Why do you need an orthodontic consultation?
Treatment for recession (recession of the gums exposing the roots) depends on the stage of the disease. If it has already started, and the orthodontist cannot correct the changes, an orthopedist comes to the rescue - the patient will undergo plastic surgery and prosthetics. At the initial recessive stage, the orthodontist can install orthodontic structures, braces or aligners. It is he who determines the effective technique in a specific situation: each tooth must be in an even row with the correct bite so that there is no excess load on any of them when chewing.
Only in this case does the subsidence of the gums stop, and to raise them to the previous level, the work of an implantologist and a plastic surgeon is necessary. Without preliminary therapy to straighten the dentition, plastic surgery is useless : the problem will recur as bone degeneration continues.
If you treat the consequences without eliminating the cause, the disease cannot be overcome either by plastic surgery or implantation.
Expert opinion. If the patient sees in the mirror that the gums have receded/raised and the necks are exposed, you need to go to a professional doctor who will make the correct diagnosis.
Gingivitis
This is the first and reversible stage of periodontitis. Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. This disease is very dangerous during pregnancy - due to changes in the hormonal levels of the pregnant woman, the disease progresses faster than usual, can lead not only to the loss of teeth in the pregnant woman herself, but also cause dental problems in the future in the child, and even provoke premature birth.
If you notice the following signs, then most likely these are symptoms of developing gingivitis:
- gum inflammation, bleeding,
- bright red gum color,
- pain and swelling in the gum area,
- bad breath, quickly forming plaque and stones.
Treatment
If, after consultation with an orthodontist, it turns out that there is no occlusion disorder (pathology of contact between the upper and lower jaws when they are closed), the periodontist will prescribe a treatment complex, but first he will remove tartar, old worn-out fillings, and sharpen the sharp edges of the tooth.
Professional cleaning is carried out chemically (using alkaline preparations), sonic (ultrasound or sandblasting), and mechanically. Then the doctor will treat the oral cavity with an antiseptic. Antibiotics are not used for periodontal disease unless there is an inflammatory process.
For purulent inflammation, lincomycin is prescribed. For periodontitis (a concomitant disease), it is appropriate to use medications in the form of a powder or gel. Microorganisms are not the cause of gum atrophy, but the affected periodontal tissues are less resistant to pathogenic bacteria, which leads to complications, and in this case the use of antibacterial agents is justified. They are prescribed by a doctor when a secondary infection occurs. The main effect of the drug is on gram-positive organisms that cause the inflammatory process.
Antibiotics kill pathogenic bacteria, relieve inflammation and reduce pain. In dentistry, antibacterial Metronidazole, Trichopolum and other drugs of similar action are also used, as well as vitamins and mineral complexes that increase immunity. The gels Cholisal, Elugel, heparin ointment, Troxevasin, and Solcoseryl paste have a good therapeutic effect. They are prescribed in a course of tablets, injections and topically, in the form of applications or polymer plates.
After brushing your teeth, the medicine is applied to the edge of the gums, followed by gentle pressing into the interdental spaces. The plates are held for about 6–10 hours, and the residue is washed off with warm water.
Important! Uncontrolled use of antibiotics can lead to bacterial resistance to them and intoxication of the body, so taking them without a doctor’s prescription is unacceptable.
However, it is incorrect to believe that antibacterial agents for periodontal disease have any effect on receding gums. They reduce the symptoms of inflammation as a manifestation of periodontitis, that is, they treat a completely different ailment that develops against the background of the main diagnosis.
Vitamins and minerals
To restore damaged tissues, the body needs a wide variety of nutrients, which are not always contained in the required quantities in the daily diet. That is why the drug treatment regimen for periodontal disease often includes taking vitamin complexes. The best effect can be achieved by taking special complexes, for example, the vitamin-mineral complex for teeth ASEPTA.
The ASEPTA complex includes a whole range of substances necessary to strengthen gums and teeth. Vitamin C strengthens the walls of capillaries and blood vessels, helping to improve blood circulation in the gums, disruption of which is one of the main causes of periodontal disease. Vitamins B3 and B6 help reduce gum sensitivity, strengthen bone tissue and promote healthy mucous membranes. Vitamin A is involved in all metabolic processes occurring inside the body and increases protection against inflammatory and infectious diseases that often accompany periodontal disease.
In addition to vitamins, the complex also contains green tea extract - a natural component that has an antimicrobial effect, eliminates unpleasant odors, and slows down the aging process of tissues. An equally important component of the complex is coenzyme Q10, a substance that is a rich source of energy for the growth and restoration of cellular structures. Taking coenzyme promotes accelerated regeneration of damaged gums.
The complex also includes substances intended to strengthen the hard parts of the tooth, which are subject to increased stress during periodontal disease - coral calcium, which is well absorbed by the body, and vitamin D3, necessary for the proper absorption of calcium and phosphorus.
Other recovery methods
The most expensive, but also the most effective surgical method is the use of special membranes that are planted under the gums to reattach bone tissue. During treatment, an alveolar process is created that secures the mobile tooth.
Stem cells, fibroblasts and growth factors - protein structures that strengthen and restore blood and lymphatic vessels - will also help restore bone.
Medicines that reduce sensitivity have proven themselves well; they also alleviate the patient’s condition and improve his quality of life.
A strict diet is aimed at treating a disease that causes a lack of blood circulation to the mucous membrane. In case of systemic atherosclerosis, food products should contain a reduced intake of carbohydrates and animal fats, with the addition of statins. For diabetes mellitus, methods are used to reduce blood sugar concentrations. The presence of systemic pathologies requires their compensation to the stage of remission.
Tablet forms
What antibiotics should I take to combat the problem? The most popular types of drugs for periodontal disease are:
Antibiotic for dental flux
- Metronidazole. Destroys protozoan microorganisms and pathogenic flora of an infectious nature. The therapeutic effect of taking the medicine is achieved due to the detrimental effect on the DNA of microbes.
- Doxycycline. Prevents the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity. Destroys gram-positive microorganisms.
- Ericicline. It is considered a broad-spectrum drug. The product contains erythromycin, chlortetracycline and oxytetracycline. Fights against gram-positive infectious pathogens that are resistant to penicillin drugs.
- Azithromycin is a semi-synthetic agent with a broad spectrum of action. Destroys extra- and intracellular pathogens of periodontal disease.
- Rondomycin is a tetracycline antibiotic. Fights against different types of gram-negative bacteria by disrupting their protein synthesis.
- Lincomycin. Fights against gram-positive and some types of gram-negative infectious pathogens.
You should know! Antibiotics are considered the main drugs in the fight against periodontal disease. Some forms of the disease cannot be eliminated without the use of antimicrobial and antifungal agents. You should not take medications without a dentist’s prescription, as they cause many adverse reactions.