Absolutely every person has heard that caries needs to be treated on time. But despite the warnings of dentists, there is a large amount of information on the Internet on the complications of advanced caries - people come to the clinic when the caries has become deep or has turned into pulpitis or periodontitis.
How deep caries will be treated - we will tell you about this below and will definitely tell you in the article:
- About what deep caries is;
- Consider the symptoms of deep caries;
- Let's look at the stages of treatment for deep caries;
- We’ll tell you whether it’s painful to treat deep caries;
- We will indicate the prices for the service in Moscow
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Definition of the concept in dentistry
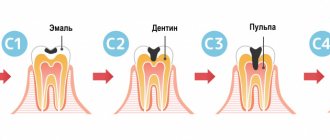
Deep caries is the last stage of the carious process occurring in the tooth, which is characterized by extensive damage not only to hard tissues, but also to the deep layers of dentin. In general, the concept of “deep caries” reflects the depth of the lesion.
Caries can be:
- primary - a consequence of untreated secondary caries;
- secondary (recurrent) - the occurrence of a carious process under a filling in a previously treated tooth.
Based on the sensation of pain and clinical examination, the disease is divided into 3 forms:
- Acute form. It is determined by the narrow entrance opening of the carious cavity and the wide base (during examination), as well as by descriptions of the patient’s sensations - reaction to food temperature and chemical irritants.
- Chronic form. It is characterized by a wide (funnel-shaped) inlet and a narrow base. The patient feels pain when the “hollow” is clogged with food and during examination with a probe by the dentist.
- Deep cervical caries. It is characterized by the development of demineralization of enamel tissue and the carious process in the cervical area of the tooth (near the gums).
According to the clinical course, caries is also divided into several forms:
- compensated,
- subcompensated,
- decompensated.
Prevention
To prevent the development of deep caries, it is recommended to observe the following preventive measures:
- careful adherence to oral hygiene;
- regular visits to the dentist for preventive examinations;
- timely treatment of diagnosed caries;
- limiting the consumption of sweet foods and drinks.
Modern technologies and materials make it possible to very effectively treat even very advanced forms of caries. If it is not possible to save a tooth with deep caries, the dentist will select the most suitable type of prosthetics for you.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, diagnostics are carried out, which include:
- external inspection using a mirror;
- instrumental examination using a probe;
- voicing symptoms (complaints) by the patient;
- thermal diagnostics (checking the reaction to cold and hot);
- electroodontic diagnostics (testing the reaction to exposure to current);
- radiography (performed if the presence of secondary deep caries is suspected or to exclude it).
If upon examination significant damage (destruction) of the tooth crown is detected, expressed by the presence of a deep carious cavity and accompanied by pain during probing, then this confirms the presence of deep caries in the patient.
In the acute form, the carious cavity is filled with light, softened dentin. In chronic deep caries, the walls and bottom of the cavity are filled with a layer of dense pigmented dentin (from brown to black). Percussion of the tooth is not accompanied by pain.
What are the differences from other forms of the disease?
Deep caries is very similar to some forms of the disease, but there are still visible and invisible differences.
Difference from pulpitis
Pulpitis is a complication of advanced caries. The forms of the disease can be distinguished from each other by their characteristic symptoms:
- Defeat. With pulpitis, the nerve is affected; with caries, the nerve remains unharmed.
- Feelings of pain. With pulpitis, pain can occur spontaneously, even without exposure to irritants on the tooth. With caries, pain disappears along with the disappearance of irritants.
- Night sleep. With pulpitis, sleep can be disturbed due to severe pain; with caries, the tooth does not hurt at night.
Difference from average caries
The similarity between the two forms of the disease is that the patient in both forms feels pain from cold, sour or sweet foods. However, with average caries they go away within 1-2 minutes, with deep caries they last longer.
Medium caries is characterized by the fact that in this form the carious lesion does not affect the tooth pulp and does not cause inflammation of the nerve, as in deep caries.
Nutrition rules
Doctors recommend limiting the consumption of sweets, replacing carbonated drinks with compote, and confectionery with dried fruits. After each meal you should rinse your mouth thoroughly.
A balanced diet must include:
- fermented milk products;
- nuts;
- fresh herbs;
- cheese;
- dietary fish varieties with low fat content;
- meat.
It is better to refrain from eating too cold or hot foods or drinks. Alternating temperatures negatively affects enamel. As a result, cracks appear, which promotes the growth of bacteria.
Stages of treatment
Treatment of deep caries is impossible without anesthesia (pain relief) and it takes place in several stages.
- Anesthesia. It is carried out using injection (infiltration or conduction) administration of an anesthetic substance.
- Drilling out a carious cavity using a drill. In this way, the specialist can reach and remove all affected areas of dentin, which is very important to prevent relapse under the filling.
- Treatment (disinfection) of the walls of the tooth and the bottom of the cavity.
- Installation of a therapeutic insulating pad and temporary or permanent filling.
- The final stage involves grinding and polishing the filling.
The following factors influence whether a filling will be installed - temporary or permanent:
- at what distance from the pulp is the carious cavity located;
- parameters of dentin, which separates the pulp from the tooth cavity;
- degree of pain.
If there is a high probability of inflammation developing in the pulp area, the dentist will place a temporary filling. And only if there are no complaints of pain and discomfort for several days, the patient will have the temporary filling replaced with a permanent one.
Possible complications
Possible complications of deep caries are:
- inflammation and necrosis of the pulp;
- periodontitis;
- secondary caries;
- change in the color of the tooth crown.
The most likely complications of deep caries are pulpitis and periodontitis. Pulpitis is an inflammation that affects the nerve, and periodontitis is a disease that causes suppuration. Such complications may lead to the need to remove the tooth.
After treatment of deep caries, mild, short-term pain may be observed in the treated tooth for several days. If the pain does not stop over time and increases, then you should contact your dentist again, as this means that one of the complications has developed. The development of complications after treatment of deep caries may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature and swelling of the gums.
Pulpitis can be acute or chronic. In acute pulpitis, the patient complains of aching pain in the tooth that occurs in the evening and at night. When exposed to hot and cold irritants, pain in the case of pulpitis does not go away immediately after the effect of the irritant is over, but only after 5-10 minutes. Chronic pulpitis can be asymptomatic and can only be detected using x-ray diagnostics. In order to save a tooth in the event of pulpitis development, it is necessary to carry out depulpation, for which the coronal pulp is removed, the root canals are expanded, they are treated mechanically and medicinally, and then filled. After this, the pulpless tooth loses its shine, its color gradually changes, and the risk of cracks and chips increases.
If the inflammatory process extends beyond the tooth, periodontitis develops. When treating this disease, the root canals must be cleaned of pathogenic tissue and treated with antibacterial agents. Anti-inflammatory and painkillers are also used. If the signs of inflammation disappear as a result of treatment, the doctor removes the temporary filling, fills the root canals and restores the tooth crown. In some cases, a dental microscope is used to better fill canals and treat inflammation at the root apex. Treatment of periodontitis may take several weeks. It is not always successful and may result in the need to remove the tooth. Some parents believe that it makes no sense to treat caries on children's baby teeth, since they will soon fall out. This is fundamentally wrong, because caries progresses faster in baby teeth than in permanent teeth. With deep caries, it can penetrate the gums and affect the permanent tooth even before it grows.
Deep caries of the front teeth. What are the differences in treatment?
Deep caries of the front teeth should be treated as carefully as possible so as not to burn the pulp. The main difficulty in treatment is:
- minimum thickness of all tooth tissues;
- inconvenient location of the cavity, if we are talking about caries located in the interdental space.
When infection penetrates into the pulp, pulpitis develops rapidly. A few hours is enough. The disease is accompanied by increasing pain. It needs to be treated immediately.
Oral hygiene
Individual hygiene procedures are exogenous methods of prevention. It is imperative to monitor the quality and condition of the brushes, follow the correct cleaning technique and do it regularly. It is advisable to use rinses, irrigators and dental floss as additional care methods.
Pastes for caries prevention
At home, you can use compounds that have therapeutic and preventive effects. When used daily, they compact the enamel, remove soft plaque and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
Fluorinated
Such pastes contain active amino fluoride. The action of this component is based on the natural mechanisms of fluoride, which is independently integrated into the enamel layer and prevents the leaching of calcium. Using these cleansers twice a day reduces the likelihood of developing the disease by 50%.
Without its content
Drinking water contains a certain amount of fluoride. If the indicators are within normal limits, then the enamel is independently saturated with this mineral. To maintain health, 1.2 mg/l is enough. In such situations, fluoride-free toothpastes are used to prevent dental caries in adults. They contain large amounts of calcium and also have an antibacterial effect. Used for everyday hygiene 2 times a day.
Dental floss
Unlike other products, it is able to remove food debris in the interdental spaces. These areas are inaccessible to brushes, so this is where problems most often arise. Fibers of synthetic or natural origin are used for manufacturing. To achieve maximum effect, the thread is impregnated with special solutions containing fluorides or antimicrobial components. It is advisable to use it after every snack or at least in the evening before brushing your teeth.
Mouth rinses
To further strengthen the protection, fluoride-based solutions are used at home, which have an anti-caries effect. They neutralize the aggressive effects of acid, which destroys enamel, and also prevent the proliferation of pathogens. Experts recommend rinsing your mouth with these products after each meal, as well as before bed.
Toothpicks
These devices are not an effective measure. They are used as an alternative when you don't have a brush or floss to hand to get rid of food stuck between your teeth. Doctors recommend giving preference to plastic or wooden products. Toothpicks must have a smooth surface without chips or cracks. Make sure that the end is slightly rounded, otherwise you may damage your gums.
Is it possible to treat deep caries of a wisdom tooth?
The patient can make the decision to remove a wisdom tooth if pain occurs on his own. But only a highly qualified dentist can make a verdict on its treatment.
Treatment of a carious "eight" is considered rational if it has a partial covering in the form of a hood of gum, as well as an antagonist - the third molar located on the opposite side.
Removal shown:
- with a horizontal tooth position;
- presence or absence of 1st and 2nd molars;
- impossibility of treatment due to incomplete opening of the mouth;
- displacement of teeth in a row due to wisdom teeth.