2938
The use of cobalt-chromium alloy is widely used in the practice of orthopedic dentists. The resulting metal products are reliable, durable and relatively safe for the patient’s health.
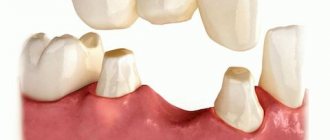
Structures made of hard alloys are used for the manufacture of both single crowns and bridges.
General overview
The alloy of cobalt and chromium has a wide range of applications. It is used for the manufacture of crowns, bridges and clasp systems. In implantology it is used in the production of abutments.
Recently, this type of alloy has been used less frequently, as the latest developments have made it possible to produce more durable materials.
Cobalt-chrome crowns are installed in the following cases:
- if there is a need to restore the crown part of a tooth with significant destruction;
- when pathological abrasion of the surface enamel occurs;
- in case of severe manifestation of fluorosis;
- if chips or cracks appear as a result of injury;
- with an abnormal tooth shape.
Prosthetics with the installation of a bridge connection (from high-alloy steel) occurs according to the following indicators:
- if partial adentia leads to the loss of several teeth standing in a row in a row;
- in case of expiration of the service life of the bridge (planned replacement);
- lack of alternative to another type of prosthetics.
Installation of orthopedic structures using cobalt and chromium is not carried out in the following situations:
- when the patient has an allergic reaction to the alloy components;
- if periodontal disease has led to the loosening of dental units that are supposed to be used as supporting ones;
- low coronal part;
- advanced forms of abnormal bite, and impaired functionality of the mandibular joint;
- dental diseases in the acute phase (gingivitis, stomatitis).
Reasons for the development of a cyst under the tooth crown and treatment of pathology in modern dentistry.
Come here to find out the purpose of tooth depulpation before prosthetics.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/kombinirovannuyu-luchshe-vyibrat.html we will consider the positive properties of a cast combined crown.
Low-melting alloys in orthopedic dentistry
Low-melting alloys (Mellota, Wood, Rose) - contain Bismuth, Tin, Lead
– their melting point is about 70 C.
They are used for dies when stamping crowns, counter dies, and making collapsible models.
Low-melting metals in dentistry
Wood's alloy.
Melting point 68 C.
Composition: Bismuth – 50%, Lead – 25%, Tin – 12.5%, Cadmium – 12.5%.
Toxic because it contains cadmium.
Mellot alloy.
Melting point 63 C
Composition: Bismuth – 50%, Lead – 20%, Tin – 30%.
Rose alloy for dentistry.
Melting point 94 C.
Composition: Bismuth – 50%, Lead and Tin 25% each.
Overview of materials
Orthopedic structures made of high-alloy steel have been used since 1933. They contain the following components:
- Cobalt. The percentage of this component ranges from 66 to 67%. Its presence provides the main mechanical properties of the product.
- Chromium. Its percentage should not be less than 30%. The presence of this component ensures the hardness and strength of the structure, and also increases the material’s resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
- Nickel. Its content in the alloy does not exceed 5%. It ensures the malleability and ductility of the material.
- Molybdenum. A small concentration (up to 5%) gives the material a fine grain structure, which makes dental products durable.
- Manganese. Simultaneously performs several tasks - improves the characteristics of the finished product and increases its strength; the quality of casting improves; The melting point decreases, which ensures comfortable production and subsequent processing.
- Carbon. An additional element that gives the alloy fluidity properties and reduces the melting point.
In addition to the above materials, nitrogen and silicon can sometimes be added to the high-alloy steel composition. In this case, the content of the first element should not exceed 0.1%, and the second 1%. Otherwise, the products will lose their plasticity and their fragility increases.
It is important to note! Abroad (USA), beryllium and gallium are added to the cobalt-chromium alloy. In Russia, such components are not used due to their toxicity and ability to accumulate in the body.
Dental stainless steel alloy - dental steel
Steel is the most common alloy in the world. Its properties are well known. And due to alloying agents, it can be given any desired properties.
Dental steel is very cheap.
Among the disadvantages: steel is heavy (density about 8 g/cm3) and chemically active. May cause allergies, galvanosis.
Stainless steel in orthopedic dentistry - grades:
- STEEL GRADE 1 X 18 H 9T (EYA-1)
Dental alloy for crowns COMPOSITION:
1.1% carbon; 9% nickel;18% chromium; 2% manganese, 0.35% titanium, 1.0% silicon, the rest is iron.
Used for fixed prostheses: individual crowns, cast teeth, facets.
- STEEL GRADE 20Х18Н9Т
COMPOSITION: 0.20% carbon, 9% nickel, 18% chromium, 2.0% manganese, 1.0% titanium, 1.0% silicon, the rest is iron.
The following are produced from this type of steel in the factory:
- standard sleeves used for the production of stamped crowns;
- clasp blanks (for ChSPP)
- elastic metal matrices for filling, as well as separation strips
STEEL for dentistry GRADE 25Х18Н102С
COMPOSITION: 0.25% carbon, 10.0% nickel, 18.0% chromium, 2.0% manganese, 1.8% silicon, the rest is iron.
APPLICATION: manufactured in the factory:
- teeth (lateral upper and lower) for stamped-soldered bridges;
- frames for metal-plastic bridges, for cladding;
- orthodontic wire with a diameter of 0.6 to 2.0 mm (step 0.2 mm).
Silver solder PSR-37 or Cetrina solder is used as solder for non-precious alloys.
Contains silver - 37%, copper - 50%, Manganese - 8-9%, Zinc - 5-6%
Melting point – 725-810 C
The process of creating structures
The process of manufacturing crowns and bridges from cobalt-chromium compounds occurs in stages in the following sequence:
- At the first appointment with the dentist, the oral cavity is examined , after which tactics for the treatment process are developed.
The material is selected and the cost of the product is announced. If necessary, additional research methods are prescribed (an X-ray or computed tomography is performed). - During the preparatory stage, the destroyed part of the crown of the tooth is restored. For this purpose, pins or stump inlays can be used.
To prevent the development of possible complications, pulp devitalization is performed. This is due to the fact that when grinding there is a risk of burns. Removal of the nerve also occurs when the visible part of the tooth is severely destroyed. - Preparation takes place for reliable fastening of the future orthopedic structure. For this purpose, burs with a diamond attachment are used.
If the manipulation occurs on “living” teeth (when the pulp is not removed), then it involves the use of local anesthesia. The thickness of the surface to be turned does not exceed 2 mm. A minimum degree of grinding is allowed if cast products are to be installed. - Impressions are made using a special silicone mass. It is applied to a special spoon and placed in the oral cavity, repeating the shape of the jaw row.
The impression is sent to the laboratory to make a model on the basis on which the orthopedic structure (bridge or crown) will be made. - After successful fitting, the finished products are fixed in the oral cavity using a cement composition.
Metal structures can be manufactured using the following techniques:
- Casting. This technology provides the best final result, due to which the structure adheres well to the tooth surface without putting increased pressure on the gum tissue.
This minimizes the chance of pathogenic microflora penetrating under the prosthesis. In addition, the technique allows you to take into account the individual characteristics of the dentition. - Punching. It is used in rare cases, since the technique is considered outdated. Products obtained in this way do not take into account the anatomical features of the patient’s oral cavity, which is why the edges of the structure do not fit tightly to the gums.
The video shows the process of welding a denture made of cobalt chromium.
What is made from CHS
The following are made from CHS:
1. Crowns.
2.Bridges.
3. Prostheses.
4. Implants.
Let's look at each product separately.
Crowns
Crowns are cap-shaped microprostheses that completely or partially cover the coronal part of the tooth. They are used for defects that cannot be eliminated with onlays, inlays or fillings . That is, when the degree of destruction exceeds 50–80% of the crown part of the tooth.
A KHS crown can consist of one metal or be a metal frame coated with ceramics, plastic or powder coating.
Metal-ceramic crowns (KHS, bioalloy)
Metal-ceramics is one of the types of dental prosthetics that can solve many problems associated with the restoration of damaged and lost teeth. Thanks to the metal base, this type of tooth reconstruction is very durable and allows you to restore chewing function in full. The reliability of the design ensures long-term use. Ceramics, in turn, allows you to achieve a natural look and recreate the natural shape and color of the tooth. Metal ceramics are made individually and follow the contours of the dentition. The appearance of the metal-ceramic crown is maintained throughout the entire period of operation.
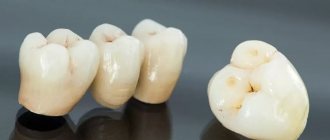
Solid crowns (KHS)
A solid crown is a metal crown that is made from a cobalt-chromium alloy using the modern solid casting method. This method assumes that the entire structure is cast simultaneously. In the case of making bridges, this completely eliminates the need to solder crowns to each other.
Bridge prostheses (BDP)
Bridges are installed when there is a defect of no more than three teeth in the chewing area or 4 in the frontal area. As a rule, the MVP frame made of cobalt-chromium alloy is made by casting. This ensures the accuracy of the design.
The advantages of such prostheses include high strength, rare cases of individual intolerance (compared, for example, with nickel-chrome frames), and cost-effectiveness.
The main disadvantage of bridges is the need to grind the teeth (reducing their service life), and overloading the supporting units, which sometimes leads to the destruction of their periodontium.
Removable clasp dentures
Cobalt-chrome is considered the best material for making the frame of arched prostheses, due to its strength, compactness, durability and cost-effectiveness. The structure is made by casting.
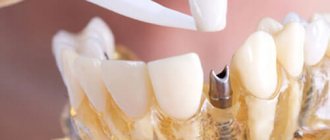
Superstructures for implants
The orthopedic part of intraosseous implants, made of cobalt-chrome and lined with ceramics, provides a clinical effect comparable to gold alloys.
Advantages and disadvantages
This type of material when used has the following advantages:
- There are no changes in its structure during the manufacturing process. Raw materials are not subject to contamination during the melting process.
- There is no loss of physico-chemical properties due to the absence of significant thermal effects. During the manufacturing process, overheating of the workpiece and tools is avoided.
- The products practically do not shrink , which eliminates the appearance of microcracks. The material is resistant to corrosion and oxidation processes.
- The alloy composition does not tarnish for a long time, and is lightweight in comparison with structures made of platinum or gold. The products are well stamped and soldered together.
- The low cost makes it possible for people with varying incomes to get prosthetics.
The disadvantages of products made of chromium and cobalt include:
- Possibility of developing galvanic syndrome. In this case, the patient has a sour taste in the mouth and discomfort when eating. These symptoms can only be eliminated by removing the prosthesis.
- Low aesthetic value. The products are not used for prosthetics of frontal incisors.
- Prolonged wear may cause a change in the color of the gingival surface (it becomes blue), which comes into contact with the installed crown or bridge.
Does the price of a metal-free crown per tooth correspond to its quality characteristics?
In this publication we will tell you which dentures for chewing teeth are the best.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/metallicheskuyu-s-napyileniem.html you will find detailed information about metal crowns with white coating.
Common parameters
Each alloy option for dental prostheses has its own composition; manufacturers often use their own developments and combinations.
The main thing is to bring the composition and characteristics of the substance to a certain standard and obtain a combination of certain qualities:
- safety. The metal must be absolutely safe, maintain its parameters and not emit harmful compounds during operation;
— corrosion resistance. Raw materials must resist corrosive processes, which eliminates oxidation and related problems throughout the entire guaranteed service life;
- strength. Components made from an alloy must withstand significant variable and static loads, such as compression, bending, and methodical movements in a certain direction;
- aesthetics. The use of parts should not come at the expense of appearance; first of all, it is necessary to recreate the appearance of natural units and obtain acceptable operational parameters;
- availability. This version of prostheses, although inferior to others in a number of aspects, surpasses them in the combination of price and quality. For example, the products are aesthetically comparable to zirconium dioxide, but the price tag is several times lower.
The alloy is non-toxic, but during service, especially if the processing features, recommended composition or care are not followed, they can release components that provoke reactions in the body. Because of this, the designs are considered more allergic and will require a comprehensive examination in the dentist's chair before choosing this type of denture.
The metal resists corrosion for a long time, but can cause another negative effect - a galvanic reaction. It can only be provoked by the presence of artificial components made of another metal, in particular stainless steel, in the oral cavity. Therefore, before carrying out operations, you need to make sure that no conflict will arise. Often in this case, existing elements are replaced with ones similar to those being installed.
The strength of the alloy is maintained only under strict compliance with the processing conditions, composition and recommended parameters of the implanted elements. You can get a low-quality product due to the negligence of the technician or the company producing the blanks. In the second situation, problems most often arise when purchasing blanks from untested and little-known companies. You can navigate by price; high-quality ones cannot be too cheap, but there is no point in purchasing prohibitively expensive ones.
Metal ceramics are one of the examples of the best products in terms of compliance with natural units. Components (crowns) are obtained by layer-by-layer application of a ceramic composition to the alloy surface. Due to the possibility of color adjustment, it is possible to bring products into full compliance with natural teeth, either preserved ones, or to fulfill non-standard wishes of the client.
Material forms
- Ingots weighing 7-10 g. Produced by casting in an atmosphere. Disadvantages include casting defects due to the increased gas content.
- Rods. The molten metal is sucked into metal or quartz tubes, acquiring their shape as they solidify. Subsequently it is cut into cylindrical blanks. This is the most common manufacturing method
- Discs of various diameters and thicknesses. Manufactured in induction vacuum installations. Used for the manufacture of prosthetic structures using CAD/CAM technology.
- Granules. It is obtained by pouring the alloy into a liquid.
Physical and chemical properties
The set of alloy parameters completely depends on the constituent elements.
In the case of dental cobalt chromium, these are the following components:
- base in the form of cobalt. The element must be at least 66-67 percent; it is responsible for the increased mechanical properties of the resulting metal;
- chromium is in second place, it should be at least 26-30 percent. The component is responsible for increased hardness and improved resistance to oxidative processes and corrosion;
- Nickel is the third most important, it is responsible for increasing technological parameters. At a percentage within 3-5 percent, the material becomes more malleable, ductile and viscous. Aspects make it possible to obtain a simpler substance in terms of release;
— molybdenum gives the structure a fine grain, which has a positive effect on the strength characteristics. The element can be added no more than 4-5.5 percent;
— manganese serves to solve a whole range of problems. Firstly, it increases the strength parameters of finished products. Secondly, the quality of casting increases due to the modernization of the alloy structure. Thirdly, the melting point of the substance drops noticeably, which is beneficial under production conditions and subsequent processing. Fourth, sulfur compounds, which are considered toxic to humans, are removed.
Two more components that can be found in blanks are beryllium and gallium. The problem is that the components are toxic and during operation can release a large amount of harmful substances, some of which can be accumulated by the body. The production of such products is carried out only by the USA, adding within 2% to the composition for the purpose of alloying it. You won't find such products in Europe.
These first three elements are the main ones, thanks to them the alloy matrix is formed, therefore cobalt-chromium-nickel should be at least 85%. The data is fixed by an international standard, therefore, when purchasing a workpiece of any brand, you can expect consistently high quality and similar characteristics. If components break during molding, the chromium content threshold of 30 percent is most likely exceeded, which causes the alloy to become brittle and the mechanical and casting parameters to drop.
This is interesting: Dental implants: types, cost, pros and cons, which dental implants are better?
Another important element is carbon, however, it is not found in all products. Its positive quality is an increase in fluidity in the molten state and a decrease in the melting point.
Nitrogen and silicon have a similar effect, but they need to be added in a very small percentage:
- no more than 0.1 percent for the first;
- up to 1% for the second.
If this threshold is exceeded, plasticity will suffer.
The downside of carbon is that it can damage the ceramic layer during the release process of the prosthesis. During high-temperature firing, it can be released in the form of gas, entering the lining. Because of this, bubbles appear at the junction of metal and ceramics and the connection between the components weakens, reducing the service life and reliability of the finished oral element.
Due to these weaknesses, a number of companies, including many domestic ones, are engaged in the production of carbon-free billets.
If the composition is observed, the finished material has a mechanical viscosity twice that of gold. Metal melts at more than 1450 degrees.
Lifetime
Crowns and bridges made from an alloy of cobalt and chromium have high strength, which is why products of this class can last from 15 to 20 years.
Most experts recommend replacing the structure after 10 years. This is due to the fact that during prolonged wear, atrophic changes occur in the gum, causing it to sag, exposing the edges of the crown. This contributes to the leaching of cement and the occurrence of pain.
The following factors may affect the service life:
- private inflammatory processes of the gums and root canals reduce the life of the crown or bridge;
- if the stamping technique was used in the manufacture of the product, then such a structure is subject to rapid wear due to the small thickness of its walls;
- eating solid foods causes deformation or breakage of the structure;
- Failure to comply with hygienic care is accompanied by the penetration of bacterial pathogens under the prosthesis, which causes its premature removal.
Rules of care
After installing crowns or bridges made of high-alloy steel, daily care is carried out as for natural teeth (twice a day). The situation is different if an alloy of cobalt and chromium was used as a frame for plastic or ceramic products.
In this case, the following rules and recommendations must be observed:
- Oral care with a toothbrush and hygienic paste should be carried out twice a day. After each meal (if this is not possible), you need to use elixirs or antiseptic rinses.
- To prevent discoloration of the crown part of the tooth, you should limit your consumption of foods with coloring properties (beets, sauces, tomatoes).
- Completely exclude rough foods (nuts, crackers) from the diet.
- Visit the dentist's office once every six months for a preventive examination. If necessary, undergo a professional cleaning procedure.
Important! During the period of cleansing the oral cavity, special attention should be paid to the place where the structure comes into contact with the gums. The accumulation of food debris leads to the development of bacterial microflora, which causes inflammatory processes.
Auxiliary alloys used in orthopedic dentistry
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Aluminum bronze (aluminum instead of tin) is used in dentistry. It is used to make ligatures for splinting jaw fractures.
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc; pins for collapsible models are made from it.
Magnalium is an alloy of aluminum and magnesium; aircraft parts are made from it (the alloy is very light and durable). In dentistry, articulators and some cuvettes are made from it.
Amalgams are an alloy of metal and mercury. Used for filling.
The topic is too broad; amalgam in dentistry will be discussed in a separate article.
Price
Despite the fact that the alloy of cobalt and chromium has practically ceased to be used in prosthetics of frontal incisors, it is often used as a base when making prostheses made of plastic or ceramics. In this case, aesthetics in the smile area are not lost, and the products become publicly available due to their low cost.
Products made from cobalt-chromium alloy have a low cost. Pricing is influenced by the status of the clinic, the region of Russia and the qualifications of the specialist.
Products using casting technology will cost from 4,000 to 4,500 rubles. Accordingly, a bridge of 3 units can be installed for 12,000 rubles.
Stamped designs have a starting price of 1000 rubles. At the same time, the final cost may be slightly higher due to the need for procedures to prepare for prosthetics.
Price issue
The cost of prosthetics using cobalt-chrome depends on the complexity of the prosthesis (number of teeth to be replaced), manufacturing technology (casting or milling using CAD/CAM technology), and lining material (ceramics, plastic, composite, spraying).
For example, installing a metal-ceramic crown with a cast frame made of cobalt-chromium alloy will cost from 6-7 thousand rubles. and more. Crowns milled using CAD/CAM technology are more expensive than cast ones.
The cost of a ceramic-lined cast bridge can be roughly calculated by multiplying the above amount by the number of crowns in the prosthesis.
The cost of removable dentures is calculated using approximately the same methodology. Clasp structures are more expensive than plate ones.
Reviews, opinions, comments
Most dental practitioners note that products made from high-alloy steel are gradually losing their relevance.
This is due to the use of higher quality materials, which make orthopedic structures not only durable, but also provide a high degree of aesthetic value.
You can share your opinions in the “Comments” section of this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags dentures fixed dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Basics of bite registration using Occlufast impression material
Next article
Aquasplint is an innovative method of treating and diagnosing TMJ abnormalities
Dental metal alloys classification
According to their intended purpose, metal alloys in orthopedic dentistry are divided into:
- A. Structural – dentures are made from them.
- B. Alloys for filling – amalgams.
- B. Alloys for the manufacture of dental instruments.
- G. Auxiliary. Metals used for other purposes (For example, low-melting metals for stamping or solders).
According to the chemical composition, alloys used in dentistry are:
- Precious metal alloys
- Base metal alloys