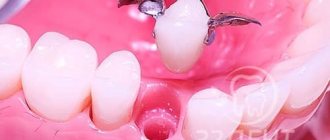
From this article you will learn:
- what are gum diseases,
- how do they differ from each other,
- treatment and symptoms of gum disease in adults.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Gum disease is a whole group of diseases, among which the most common are “gingivitis” and “periodontitis”, and much less frequently are diseases such as periodontal disease. The latter term is known to everyone, but in most cases patients use it incorrectly, using it to refer to inflammation of the gums. Although real “periodontal disease” occurs without inflammation at all and is only a degenerative gum disease.
In professional language, gum disease is usually called “periodontal disease,” and dentists who specialize in the treatment of this pathology are proudly called periodontists. Therefore, if you have one of the gum diseases, we recommend that you contact periodontists for advice and treatment, and not regular dental therapists. The same applies to regular removal of dental plaque.
What is periodontium (periodontal disease) –
This is a complex of tissues surrounding the tooth, which includes - 1) the gums around the tooth, which is part of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, 2) periodontium - the ligamentous apparatus due to which the tooth is attached to the bone, 3) the bone tissue around the tooth. In accordance with the fact that various gum diseases are accompanied by inflammation and/or destruction of the constituent parts of the periodontium, these diseases are called the specific term “periodontal diseases”.
In addition to gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease, periodontal diseases include 2 more groups of diseases. Firstly, quite rare “idiopathic periodontal diseases” (these include desmontosis, histocytosis-X and Papillon-Lefevre syndrome). Secondly, these are benign tumor-like formations, called “periodontomas”. These include, for example, diseases such as gingival fibromatosis, epulis and periodontal cysts.
Why is the tooth root exposed?
The reasons for the development of gum recession can be different, and in some cases there is a combination of several factors at the same time.
- aggressive brushing with a toothbrush - there is such a thing as brush gum recession. They occur when there is excessive pressure on the toothbrush when brushing, or when using a brush of unsuitable stiffness (hard). If you have increased tooth sensitivity when brushing, if your toothbrush becomes deformed over time (the villi move in different directions), you should consult a dentist about proper self-hygiene.
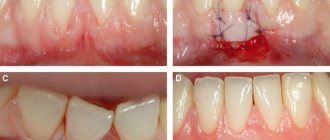
An example of brush gum recession on the upper jaw.
- incorrect position of the tooth in the dentition. Sometimes even a small bite problem can lead to gum pathology. This occurs because the tooth bears excess load when chewing or when teeth are closed, which over time leads to atrophy of the tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, including the gums. In addition, excessive protrusion of the tooth root from the dentition also leads to gum atrophy.
Multiple gum recessions caused by malocclusion.
- caries - in cases of gingival caries, gum loss often occurs due to the presence of an infectious focus in the immediate vicinity of the gingival margin.
Gum recession caused by tooth decay in the immediate vicinity of the gum margin.
- Tartar can also cause root exposure.
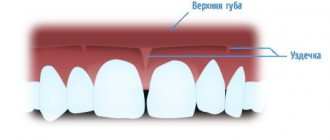
- anatomical features - for example, a thin biotype of gingival tissue in combination with other factors can lead to recession. Shallow vestibule of the oral cavity (in which the muscles of the lips attach very close to the gingival margin and gradually “pull back” it, exposing the roots of the teeth). In addition, improper attachment of the lip and tongue frenulum can contribute to gum recession.
The frenulum of the lower lip, a thin tissue biotype, caused the exposure of the lower incisor root
- bad or professional habits - for example, chewing a pen/pencil, biting threads (for a seamstress), pinching metal objects with teeth, etc.
- lip or tongue piercing - constantly touching the gums and regularly injuring it, metal jewelry can lead to exposure of the roots of the teeth.
- periodontitis - with inflammatory diseases of the gums, the roots are often exposed due to the resorption of the tissues surrounding the tooth, including gum tissue. Unlike “normal” gum recession, periodontitis is treated differently and the prognosis for such recessions is somewhat worse (as a rule, it is impossible to restore the volume of lost gum by completely covering the exposed root).
Gum disease: symptoms and treatment
Gum diseases in adults and children occur in the same way. Below we will analyze each disease - with a description of its characteristic symptoms and photographs of the patients’ teeth and gums. The information will allow you to easily distinguish one disease from another, and understand how much professional treatment you will need in different situations.
The author of the article has more than 10 years of experience as a periodontist, and therefore our recommendations really work (state-issued documents on advanced training in the Periodontology program can be viewed in the editorial section).
How to treat gum recession?
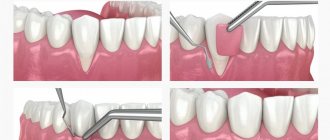
To cover the exposed root, a small operation is performed in the gum area.
There are many methods of gum plastic surgery, but they are fundamentally divided into 2 types:
- gum plastic surgery with local tissues (when the existing gum is “stretched” or moved to the root in a certain way so that the exposed area is closed, and fixed with small sutures, which are removed after healing).
- gum plastic surgery using a “patch” (the patch can be a special collagen-based material or the patient’s own tissue from the hard palate or the area of the far upper tooth - gum transplantation).
The choice of method is at the discretion of the doctor, according to each specific situation.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis in its final form is a serious infection that damages soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports the teeth. Periodontitis can not only lead to tooth loss, but worse, it can cause an increased risk of heart attack or stroke and other serious health problems.
Periodontitis is a common disease, but largely preventable. Periodontitis is usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, daily, and regular dental checkups can significantly reduce the chance of developing periodontitis.
Symptoms
You may find that you have gingivitis:
- Swelling of the gums (edema)
- Bright red or purple gum color
- Gums sensitive to touch
- Gum that “pulls away” from your teeth, making your teeth appear longer than usual
- Pus from under the gums
- Bad breath
- Bad taste in mouth
- Movable teeth
There are different types i.e. severity of periodontitis. Periodontitis is characterized by a chronic course, with exacerbations occurring.
When to see a dentist
Healthy gums are firm and pale pink in color. If your gums are puffy, dusky red and bleed easily, or show other signs or symptoms of periodontal disease, see your dentist as soon as possible. The sooner you seek medical help, the better your chances of reversing the damage from periodontal disease, potentially preventing other serious health problems.
Causes
Periodontitis is thought to begin with plaque, a sticky film made primarily of bacteria. Plaque forms on teeth when sugar starches in foods interact with bacteria that are normally found in the mouth. Brushing and flossing remove plaque. But plaque re-forms quickly, usually within 24 hours.
Constant inflammation eventually leads to pockets between the gums and teeth that become filled with plaque, tartar, and bacteria. Over time, these pockets become deeper and bacteria accumulate, moving under the gum tissue. This deep inflammation is the cause of bone resorption. If too much bone is destroyed, you may lose one or more teeth.
What can cause periodontitis?
Factors that may increase the risk of developing periodontitis include:
- Gingivitis
- Heredity
- Insufficient oral hygiene
- Tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Elderly age
- Decreased immunity, such as leukemia, HIV/AIDS or chemotherapy
- Poor nutrition
- Some medications
- Alcohol or drug abuse
Complications
Some complications associated with gum disease include:
- Complete loss of teeth
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Problems with pregnancy, low birth weight
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Breathing problems
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Asthma
Some research suggests that the bacteria responsible for periodontitis can enter the bloodstream through the gum tissue, affecting your lungs, heart, and other parts of your body. For example, bacteria can travel in the arteries to the heart and cause inflammation of the heart muscle, which contributes to heart attacks.
Is gum grafting painful?
No . Operations to eliminate gum recession are performed under local anesthesia; the surgical intervention is 100% painless. In the postoperative period, especially with gum plastic surgery using local tissues, patients often do not experience pain at all. If pain occurs, it is usually only on the day of surgery, a couple of hours after the intervention, when the effect of the local anesthetic wears off. During this period, the pain is perfectly eliminated with painkillers prescribed by the doctor. During the entire rehabilitation period, on average, 1-2 painkiller tablets are required.
In cases of gum plastic surgery using a “patch,” unpleasant sensations may be added due to the presence of a donor zone, which, according to patients, resembles the feeling “as if you grabbed hot tea,” but this does not always occur. The presence/absence of pain is determined by the area from which the “patch” is taken. If anatomical conditions allow, doctors can remove the graft from the donor area absolutely painlessly.
Gum diseases: causes
Factors that increase the risk of developing gingivitis:
- Insufficient oral hygiene.
- Hormonal changes in the body. They create a favorable environment for the formation of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. That is why teenagers and pregnant women most often suffer from gingivitis.
- Damage from impacts, burns, incorrectly installed fillings and dentures.
Periodontitis occurs if gingivitis is not properly treated in time. The inflammatory process, under the destructive influence of pathogenic bacteria, spreads to other areas of the periodontium.
Periodontal disease develops due to poor blood supply to the gums and poor nutrition. The most common causes of periodontal disease:
- gastrointestinal diseases,
- diabetes,
- heart and vascular diseases,
- taking anticonvulsants and other medications that reduce salivation.
The problem may also be hereditary.
What are the features and complications after gum recession surgery?
With a mild course of the rehabilitation period, patients do not note any peculiarities . But sometimes it is possible:
- the appearance of white plaque on the gums (this is normal, one of the healing options after gum surgery).
- swelling of the soft tissues of the face (from minor swelling to significant) depending on the extent of the surgical intervention (number of teeth involved), the size of the recession, the method of its closure, anatomical features and the patient’s body.
- hematomas on the facial skin (rarely encountered with gum surgery).
- increase in body temperature.
- pain (relieved by painkillers).
Gum diseases: prevention
Prevention of gum pathology consists of following simple rules:
- Correct and regular brushing of teeth.
- Balanced diet.
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Use of dental gels and rinses.
It is also necessary to visit the dentist regularly to diagnose diseases at an early stage. Unfortunately, restoration of destroyed tissue is impossible, so it is important to prevent the deterioration of oral health.
What are the recommendations and restrictions after gum recession surgery?
- Do not disturb the wound surface (with tongue, food, foreign objects, etc.) this is the main condition for good healing.
- Do not bite (food eaten should be soft or finely chopped).
- Do not brush your teeth in the surgical area with a toothbrush (hygiene in this area should be maintained only as permitted by the attending physician).
- Do not eat or drink hot foods.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Follow the recommendations of your doctor and take prescribed medications.
How to prevent gum inflammation?
WHO recommendations propose a program for the prevention of gum inflammation, where special attention is paid to health education on oral hygiene, explanation of the importance of proper brushing of teeth, a nutritious diet and its structure, risk factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the periodontium, periodic examination of the oral cavity by a doctor and a healthy lifestyle .
To remove plaque, you need to visit a dentist every six months for professional teeth cleaning. You also need to thoroughly brush your teeth twice a day (after breakfast and before bed), and thoroughly clean the crowns of your teeth and the interdental spaces. Toothpastes are of great help in oral care.
To prevent gum inflammation, you should choose toothpastes with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and plaque-removing effects. Preference should be given to those that contain substances that dissolve microbial plaque and prevent its further formation, for example enzymes. Additional assistance in the prevention of gum inflammation is provided by the use of rinses that neutralize microorganisms in hard-to-reach places in the oral cavity.
Currently, various rinses represent a promising link in the complex treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa and periodontal disease. The use of prophylactic rinses with combined herbal preparations has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Human acquaintance with the medicinal properties of plants dates back to ancient times, and in modern medicine medicinal plants not only have not lost their position, but are increasingly preferred today in the prevention and treatment of various diseases. Therefore, the medicinal plants used in the manufacture of professional mouth rinses are low-toxic and can be used for a long time without side effects.
What happens if gum recession is not treated?
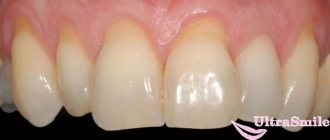
- root caries (the root, unlike the crown of the tooth, is not covered with enamel - a dense “pearl” shell, and therefore is more vulnerable). Normally, the root is covered by the gum and is not exposed to the aggressive environment of the oral cavity (acids, humidity, microorganisms, enzymes). With gum recession, the exposed root is susceptible to destruction.
- abrasion of root tissues (again, due to the lack of enamel, tooth root tissues are not resistant to abrasion).
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
- the transition of a recession to a class that is not subject to complete closure.
- more plaque (the surface of the root is rougher than the surface of the tooth crown, which means that plaque is retained more when the roots are exposed).
Large gum recession, caries of the exposed tooth root, an abundance of soft plaque on the root surface.
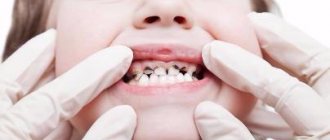
Gum diseases in adults
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane is localized around the diseased tooth; the pathological process can be acute or chronic.
Types of Gingivitis:
- catarrhal,
- atrophic,
- hypertrophic,
- ulcerative-necrotic.
If you start treatment on time, you can defeat the disease very quickly and without consequences in the form of tooth loss. If the situation is neglected, the disease can develop into a more dangerous form - periodontitis.
Periodontitis: what is it?
Periodontitis is a gum disease that destroys the supporting structure of the affected tooth, as well as the ligament between the bone and the root of the tooth. As a result of the inflammatory process, the gum partially peels off from the tooth, forming a gum pocket in which food debris accumulates, which is a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms. It is not possible to remove these accumulations with a toothbrush.
Without proper treatment, bleeding and swelling of the gums quickly develops, and pus can form in periodontal pockets. Teeth become loose and eventually fall out. The acute phase is characterized by general malaise, weakness and severe pain in the affected area.
Periodontal disease: photo
Periodontal disease, like periodontitis, affects the supporting part of the tooth, but inflammation does not occur. There is a disruption in the blood supply to soft tissues, their dystrophy develops, the necks of the teeth are exposed, and the gums are slowly destroyed. Periodontal disease does not remain local - over time it affects both jaws, so it is very difficult to fight this disease. For periodontal disease, physiotherapy, local treatment and splinting of loose teeth are effective.
Preventive measures
To keep your gums healthy, you need to follow the following rules:
- brush your teeth regularly and do it correctly;
- eat a balanced diet;
- promptly treat existing malocclusions;
- undergo preventive examinations at the dentist annually;
- Do professional dental hygiene once a year.
It is also important to quit smoking. Tobacco smoke constricts blood vessels, causing poor blood supply to the gums.
Treatment
Gum disease should be treated under the supervision of a dentist. Good results can be achieved using techniques such as:
- professional hygiene;
- physical therapy;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- curettage;
- surgery.
Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Oral hygiene
This procedure is many times more effective than regular home teeth cleaning. Using an ultrasonic scaler, the dentist removes soft and hard deposits. As a result, the enamel becomes perfectly clean, the gums become healthier, and begin to fit more tightly to the teeth.
This treatment is sufficient if the disease has just begun to develop. Ideally, you need to undergo hygienic cleaning every year. Then the risk of periodontitis will be several times lower.
Physiotherapy
Indicated for chronic gum disease. It is not used for acute pathologies. It can act as a primary or additional method of therapy for periodontal disease. The most popular physical therapy options:
Electrophoresis. Special medicinal compounds are injected into periodontal tissue using direct current. The technique allows you to deliver important components directly to the changed areas of the oral cavity, due to which the therapeutic effect is noted after the first session. Electrophoresis perfectly fights advanced periodontitis. With its help you can remove swelling, inflammation, itching, and significantly reduce bleeding.- Massage. It can be done with your fingers or using a special vacuum apparatus. The effect on tissue increases blood supply, disperses lymph, and normalizes metabolism. With one massage it is impossible to stop all the symptoms of periodontitis and periodontal disease, but it is possible to alleviate the course of the disease.
- Vacuum treatment. Provides for the use of special alluvial installations. They artificially tear the surface capillaries, resulting in small hematomas. During the resorption of the latter, local immunity increases. The newly formed blood vessels are denser and more elastic than their predecessors. As a result, local blood flow is normalized, the atrophy process becomes barely pronounced or disappears completely.
- Darsonval. Indicated in the presence of periodontal cavities filled with purulent contents. They are treated with weak high-frequency currents, which reduces sensitivity and improves local blood supply.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Typically, patients take anti-inflammatory drugs in parallel with physiotherapy after professional hygiene. This treatment is complex and therefore turns out to be the most effective.
Medicines can be applied to the inflamed area in the form of gels, ointments, solutions, or taken orally. It is important not to use them without a doctor's prescription.
Curettage
The need for it arises if periodontal pockets are visualized. If their depth is up to 5 mm, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia. In this case, no incision is made. If the disease is severely advanced, dissection of the inflamed gum is performed to gain access to the altered root and thoroughly clean it of hard deposits.
With the help of curettage, you can significantly reduce large periodontal gaps and completely get rid of small ones. Subsequently, to maintain a satisfactory condition of the gums, it is enough for the patient to remove the stone once or twice a year with an ultrasonic scaler or laser.
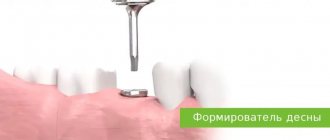
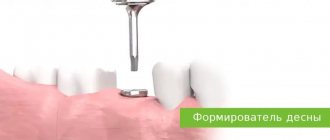
Surgery
It is used only if all the methods described above are ineffective. Then the patient is given a referral to a maxillofacial surgeon so that he can decide how to treat the disease further.
In advanced cases, surgery may be required to replace the affected areas with an artificial implant. A special membrane can also be installed between the jaw bone and gums, which accelerates regeneration and promotes natural bone growth. Flap operations are often used in surgical practice. They resemble curettage, but involve deeper penetration.
It is important to understand that surgical treatment is a last resort. It is used only if inflammation develops rapidly and cannot be stopped or at least slowed down.
How diseases manifest themselves
Usually the situation worsens gradually. First, a person notices that the gums turn red and swell from time to time. It bleeds when brushing your teeth. A little later they join:
- halitosis;
- pain when chewing solid food;
- frequent bleeding;
- exposure of necks;
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- loosening of teeth.
In advanced cases, the patient develops general weakness and body temperature rises.
It also happens that the disease occurs without obvious symptoms. From time to time the patient feels that his gums are itching. Then he notices that the gum line has noticeably dropped.