1. Lipomas
Formations on the genitals come in several varieties. The reasons, patterns, mechanisms of their occurrence in some cases are known and understandable, in others they remain not entirely clear. Different types of formations affect specific tissues. The following types of formations on the external genitalia are divided: lipoma, atheroma, bartholinitis, papilloma.
Lipomas
most often form in the subcutaneous fat layer. It is impossible to clearly identify the reasons for their occurrence, but a certain statistical connection with hereditary predisposition has been established. Moreover, the growth of lipomas has nothing to do with fat consumption or a tendency to develop subcutaneous fat deposits. The incidence of lipomas in thin and overweight people is the same. Lipomas can range in size from 1 to 15 cm and are usually not painful or itchy, presenting only a cosmetic problem. Cases of malignant degeneration of lipomas are very rare; More often, mechanical damage carries the threat of suppuration and infection. Lipomas up to 3 cm are treated non-surgically - by injecting them with a drug, the action of which leads to the resorption of the formation. Large lipomas are removed surgically: with laser, electrocoagulation or radioknife.
As a rule, a new lipoma does not appear at the site of a well-performed operation. However, it is not uncommon for new lipomas to form in nearby tissues.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Swelling of the labia.
In women, swelling is often combined with itching and burning, discomfort, redness of the mucous membranes, the appearance of erosions, pathological watery discharge mixed with pus or blood, and inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes. Pain may occur when walking, playing sports, or having sexual intercourse.
Swelling often occurs as a result of abrasions or wearing synthetic underwear, due to insufficient hygiene, allergies and sexual intercourse. But there are also more serious problems.
Why do the labia swell? Causes of swelling of the genital organs.
Various factors can cause swelling of the labia:
Candidiasis (thrush).
A characteristic symptom of the disease is white curd-like discharge, a sour smell, possible itching and burning, swelling, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. Yeast infections most often occur when the immune system is weakened and during pregnancy.
Bacterial vaginosis.
The result of an imbalance in the vagina. Green or gray discharge often appears, a fishy odor is felt, and swelling is possible. But asymptomatic progression of the disease also occurs.
Genital infections. Quite often, the labia become swollen due to irritation from pathological vaginal discharge caused by sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea). Other signs may appear: itching, irritation, unpleasant odor, painful urination.
Vulvodynia.
Accompanied by pain of varying intensity in the vulva area. It occurs suddenly, worries for a long time and often goes away just as abruptly. May sometimes cause swelling.
Vulvitis.
The main symptoms are swelling of the genitals, redness of the skin and burning. Inflammation of the vulva can occur due to poor hygiene and frequent changes of sexual partners, as a result of allergies, long-term use of medications and certain diseases.
Vulvovaginitis.
The main symptoms are skin flushing, abnormal discharge, pain when urinating, severe itching, causing the desire to scratch, which can lead to swelling. Often, inflammation of the labia develops due to poor hygiene and active masturbation, as a result of allergies or infections.
Bartholinitis.
Bartholin's glands are located in the vestibule of the vagina. When infected, they become inflamed, which is accompanied by redness and swelling of the genitals. If the gland duct is blocked, pus accumulates inside, which contributes to the formation of a cyst. In this case, discomfort and pain occur, which intensifies with movement.
Allergic reactions.
An allergy to fragrances contained in soap or intimate hygiene gel, components of washing powder, spermicides, latex condoms, tampons, low-quality pads, linen fabric, certain foods or medications can cause irritation. In addition to swelling, rashes are often found.
Contact and atopic dermatitis.
It develops with hypothermia, severe depilation of the bikini area, wearing tight synthetic underwear, and exposure to allergens. In the acute form, edema appears unexpectedly and grows rapidly, while in the chronic form it can periodically disappear and then reappear.
Sexual contact.
As a result of rough friction during sexual intercourse due to lack of lubrication (natural or artificial), damage to the labia and vagina is possible, which is accompanied by discomfort and swelling. In some cases, wounds and hematomas may form.
Stressful state.
Sometimes severe stress can cause itching of varying intensity and swelling in the genital area, which makes a woman distracted from the problems that have arisen.
Phthiriasis. (Pubic lice, lice)
You can become infected with lice not only through sexual intercourse, but also through everyday contact. The problem can be diagnosed quite easily by identifying bite marks or parasites. Lice cause severe itching, causing scratching, which causes swelling of the labia and pubis.
In addition to lice, swelling can be caused by mosquito bites, wasps, and bed bugs. In this case, bite marks are clearly visible, and the skin color may be red or bluish.
Hormonal disorders.
During the premenopausal period, the synthesis of estrogen decreases, which is why the woman feels dryness and burning, and possibly swelling of the genitals.
During pregnancy and the premenstrual period, blood flow to the tissues increases, which can lead to increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane. As a result, even the usual gel causes itching, burning and swelling.
Genital herpes.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way until favorable conditions arise (hypothermia, colds, vitamin deficiency, weakened immunity). The main signs are watery blisters, erosions, itching, swelling, twitching.
Tumor.
Quite often, in the initial stages, malignant neoplasms do not cause any symptoms. Occasionally, mild itching and slight swelling may occur, to which women do not attach much importance.
Additional factors.
With dermatological diseases, various parts of the body itch. The genitals are no exception. The woman begins to itch, causing swelling.
Diabetes mellitus causes increased dryness of the labia, which causes cracks and swelling. The wounds are irritated by urine, increasing the itching.
In rare cases, edema can occur due to diseases of the internal organs (heart, kidneys, liver, intestinal dysbiosis).
Treatment methods.
If swelling does not decrease within 24 hours and other symptoms become noticeable, you should visit a gynecologist. He will conduct a diagnosis, determine the cause of the pathology and select an effective treatment method. If necessary, he can refer you for consultation to other specialists (endocrinologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, nephrologist, allergist, venereologist).
Most often, local antiseptic treatment is carried out, and antibacterial or antifungal medications are prescribed. For candidiasis, suppositories containing antifungal substances, immunostimulating drugs, and a special diet are used.
For allergies, antihistamines will be helpful. For vulvitis, analgesics are used, and sometimes antihistamines and antidepressants may be needed. Herpes is treated with antiherpetic and immunomodulatory medications.
Timely consultation with a doctor helps to quickly get rid of problems. Self-medication can aggravate the situation, leading to the development of serious diseases and infertility.
2.Atheromas
Atheroma
is a cyst filled with a yellowish fluid formed by fat cells, epidermis and sebum. Since all this in the cyst is in a state of stagnation, when opened, the substance that is usually removed has an unpleasant odor. Causes of atheroma: increased oily skin, acne, poor cleanliness, hormonal changes, heredity. Atheromas form where there are many sebaceous and sweat glands. When they grow to a size of 5 cm, tension occurs on the surface of the skin and even internal inflammation is possible. It is always recommended to remove atheromas without waiting for complications, although they also degenerate extremely rarely.
The atheroma is completely removed by isolating it from the tissue. At the same time, they try not to disrupt its integrity and make sure that no particles of the cyst shell remain, otherwise this may cause a relapse in the same place.
Visit our Gynecology page
Disease prognosis
Varicose veins of the uterus and perineum are not a life-threatening disease. But it is important to note that the quality of life of patients is significantly reduced. In addition to aesthetic discomfort, large perineal phleboectasis can cause painful symptoms during menstruation and complicate sexual life. Sometimes varicose veins become inflamed, causing a lot of physical suffering to patients. You should not count on the therapeutic effect of ointments and tablets - such therapy is not effective, but only eliminating the causes of varicose veins and the venous nodes themselves using sclerotherapy or miniphlebectomy allows one to achieve excellent therapeutic and aesthetic results in all patients. At the Innovative Vascular Center, complete treatment of this disease is possible. We successfully perform endovascular correction of deep vein pathology, eliminate varicose veins of the small pelvis and venous vessels on the genitals.
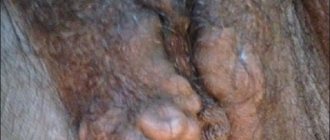
3.Bartholinitis
Bartholinitis
- This is a consequence of blockage of the Bartholin gland. It is located at the entrance to the vagina and is involved in lubrication (moistening) of the external genitalia. During moments of sexual arousal, this process is especially intense. When a blockage of the gland duct occurs, a cyst is formed in which the produced secretion accumulates. If therapeutic measures are not taken, infection and cyst rupture often occur. This gives relief because the cavity is freed from accumulated secretory masses. However, the consequences of such spontaneous opening against the background of an abscess can be very dangerous. You should definitely consult a doctor at the first sign of a lump at the entrance to the vagina. If treatment is not carried out or the cyst does not open spontaneously, general malaise begins: the temperature rises, pain is felt when walking, and signs of acute infection appear. In the most difficult cases, the abscess can spread to the internal genital organs: the uterus, appendages.
Treatment of bartholinitis in uncomplicated cases by opening the cyst is not difficult. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. In more severe cases or when a postoperative relapse is established, a decision is made on bartholinectomy (complete removal of the Bartholin gland). This is a rather complicated operation, but in some cases it cannot be avoided.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Catheter placement – Word
This is a modern method of surgical treatment for Bartholin’s gland cyst, especially in case of its recurrence.
Under local anesthesia, the cystic area is opened with a small incision of about 5 mm, the contents are removed and sent for bacteriological examination, the cyst cavity is washed and a Word catheter is installed in it (this is a silicone tube 55 mm long, 5 mm in diameter with a channel inside, blindly ending, with thinner walls at the end, due to which the tip can inflate into a ball, which has no analogues), inflating its rubber tip to 3 ml with a physiological solution of 0.9% sodium chloride, thereby fixing it in the cavity of the cyst. For better fixation and prevention of loss during the woman’s movements, it is recommended to apply 2-3 absorbable interrupted sutures along the contour of the catheter emerging from the cavity of the cyst. The second end of the catheter is inserted into the vagina. The catheter remains in the cyst cavity for 6 weeks. This is aimed at forming a channel for the passage of secretions, the walls of which do not grow together. The study shows that the Word catheter is an easy-to-use, low-cost outpatient procedure with acceptable short-term recurrences. Treatment costs are seven times lower than with marsupialization [7]. While the catheter is in the cyst cavity, the patient is advised to have sexual rest to avoid its loss. In a number of countries there is no such restriction, since studies have shown that the pain symptom caused by both the cyst itself and the procedure performed with the catheter in the cavity completely disappears over time (by day 6) [8]
As an alternative, a Voroda or a Jacobi ring (the catheter does not have a channel, it is harder, shaped like a ring) which is installed through 2 punctures in the mucous membrane and capsule of the cyst and the 2 ends are fastened to each other.
4. Papillomas
Papillomas
external genitalia - this is the growth of the epidermis of the labia. By their appearance, papillomas are easily differentiated from other formations. They are usually located on a stalk, resembling the shape of a mushroom. Unlike other uncomplicated formations, papillomas may itch or hurt; They are often injured. The reason for their appearance is HPV, the human papillomavirus, which is activated under favorable conditions (decreased immunity, stress, hormonal changes). HPV infection occurs through sexual contact or from the mother at birth. The latent period of this virus (without any formations on the skin) can last indefinitely. The actual growth of the epidermis on the genitals can be provoked by a number of factors, mainly associated with a decrease or depletion of the body's protective resources.
Papillomas are always treated comprehensively: formations on the skin are surgically removed, and the human papillomavirus itself is subjected to systemic therapy aimed at increasing immunity, restoring hormonal balance and balanced metabolism.
It is necessary to treat papillomas. Not only can they grow to large sizes, but they also carry the risk of infecting a sexual partner.
Pathogenesis
The resulting inflammation of surrounding tissues occurs in 3 stages:
Stage 1 - Alteration the release of fluid during Stage 2 - Exudation and blood cells from the vessels into the tissue, edema occurs.
Stage 3 - Proliferation (or productive stage) does not occur, since damaging factors continue to operate and therefore the resulting swelling, thickening of the walls, narrowing of the lumen of the canal, thickening of the secretion, resulting in blockage of the duct), the secretion of the Bartholin gland being produced, accumulating, thickening, leads to the formation of a cystic cavity formation, gradually increasing in size. Local defenses fail due to concomitant diseases, decreased general immunity and the aggressiveness of the flora that causes inflammation. Reaching a size of 4 or more centimeters, squeezing the surrounding tissues, causes pain in a woman and can, turning into an inflammatory process, cause an abscess of the Bartholin gland [2] [3] [4]
The causes and mechanism of development of Bartholin’s gland abscess are described below in the “Complication” section.
Stages
There are four stages of lip cancer.
- The size of the neoplasm is small and does not exceed 2 centimeters; the malignant tissue is concentrated within the lip. Lymph nodes are not affected, there are no metastases.
- The pathological tissue increases in size up to 4 centimeters, but the lymph nodes are not affected and there are no metastases.
- The tumor exceeds 4 centimeters in diameter and affects one or two regional lymph nodes.
- Malignant tissue spreads to the jaw bones, tongue, maxillary sinus, or penetrates the masticatory muscles and pterygoid process, reaches the carotid artery and grows into the base of the skull.
Kinds
According to localization they distinguish:
- cancer of the lower lip, accounting for about 95-98% of all cases;
- Cancer of the upper lip, which occurs in no more than 2-5% of patients, but has a more aggressive and rapid course, affects mainly women.
According to histological classification, lip cancer is a squamous cell tumor, represented by two types:
- keratinizing – the most common, accounting for up to 95% of cases, which is characterized by a slow course with moderate germination into other tissues and slight metastasis;
- non-keratinizing - rarer and significantly more malignant, quickly growing into nearby tissues (usually into the anatomical structures of the jaw), forming ulcers and metastasizing relatively early through the lymph and blood flow. Metastases usually affect the lymph nodes under the jaw, in the chin and jugular vein, as well as lung tissue.
In addition, there are four clinical forms of the tumor: ulcerative, ulcerative-infiltrative, papillary and warty. The first two have a more malignant course.
Diagnostics
You can determine why a lump appears on your lip using diagnostic procedures:
- Inspection and palpation of the growth on the lip, detailed questioning of the patient, study of the anamnesis.
- Taking general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
- Hardware studies: ultrasound, x-ray, probing of gland ducts, sialography.
Instrumental diagnostics are used for neoplasms on the lip: cysts, tumors.
Which doctor should I contact?
Depending on the cause of the pathology, consultation with the following specialists may be required:
- Dentist: bite pathology, trauma after examination.
- Orthodontist: incorrectly selected and installed braces, dentures.
- Allergist: severe allergic reactions.
- Oncologist: malignant neoplasms on the lip.
- Oral and maxillofacial surgeon: the need to remove a cyst or tumor.
If the lump comes out due to fungal, bacterial or viral infections, treatment will be carried out by a general practitioner, pediatrician or family doctor.