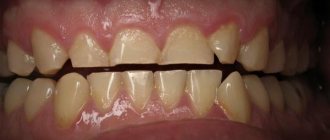
Dental practice confirms that most people's bite is not ideal. Sometimes parents pay attention to this problem from the first years of a child’s life, children of less attentive parents turn to orthodontic treatment when they reach adulthood, while many, attributing the problem solely to aesthetic imperfections, prefer to ignore it altogether.
In fact, in addition to a visual defect, an incorrect bite can cause various dental problems, and often leads to permanent injury to the tongue and the inside of the cheek. This last inconvenience is very painful, and we will talk about it in this article, looking in detail at how to protect yourself from the problem, what to do if an injury has already been received, and what kind of bite is called incorrect.
What is “bad bite”
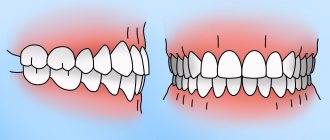
Bite (or occlusion) is the closing of the jaws at the moment of their natural compression. The standard is considered to be central occlusion, in which the number of points of contact between the teeth of the upper and lower jaws is maximum.
But all other options for interaction of the jaws when closing are malocclusions. Today it is customary to identify the main forms of malocclusion:
- open: there is no tight closure of the dentition
- cross: the antagonist teeth of the upper and lower jaws overlap each other with segments (in one area the lower ones overlap the upper ones, in the other - vice versa)
- mesial: the lower jaw protrudes forward, the upper teeth overlap the lower ones
- distal: the upper row of teeth is pushed forward, overlapping the lower one,
- deep: a type of distal bite when the upper jaw almost completely hides the lower teeth.
Contrary to the opinion of many people who believe that malocclusions are not a cause for concern, you should know: malocclusion of any form in most cases causes dental problems, and sometimes problems of a different nature.
The absence of several teeth and loose jaw closure can provoke:
- deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent headaches;
- development of facial asymmetry;
- premature appearance of facial wrinkles.
An incorrect primary bite can affect the growth of permanent teeth and lead to even greater deformation of the jaw system.
And very often, malocclusions cause permanent injury to the mucous membrane, including a strong bite of the tongue and the inner surface of the cheek. And the presence of open wounds in the oral cavity is a direct path to infection and the development of inflammation.
Don’t leave the problem unattended, contact your orthodontist on time!
Symptoms
The main signs of the disease are:
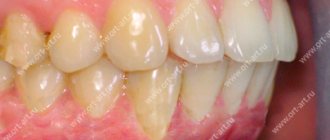
- the appearance of uneven plaque with pronounced white spots;
- ulcers form along the entire surface, gradually spreading to the rest of the oral cavity;
- tongue mobility is limited, sharp pain appears when talking or eating;
- color changes, local spots of different shades are visible;
- swelling, there are tooth marks on the side areas;
- impaired salivation;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
In some cases, the sense of taste changes or disappears, and a burning or itching sensation is felt at the slightest movement. As it progresses, body temperature rises, cervical and submandibular lymph nodes enlarge.
Why does malocclusion form?
Statistics show that 90% of people have some signs of occlusion; The root cause of anomalies is considered to be genetics. However, heredity is far from the only factor.
According to orthodontic experts, the following factors influence the formation of the dentofacial apparatus in children:
- artificial feeding: when breastfeeding a newborn, the jaw apparatus is formed more correctly, while the habit of sucking a pacifier inherent in “artificial babies” affects the process negatively;
- difficulty changing teeth: loss of baby teeth too early or, conversely, with a delay can affect the health of the jaw apparatus;
- injuries, untreated caries, inflammatory gum diseases (all this is fraught with jaw displacement).
A child’s habit of sucking their thumb in their sleep can also lead to malocclusion in the future. But for adults, the greatest danger is the loss of teeth: the absence of even one unit in the dentition can lead to a violation of the load distribution, as a result - to deformation of the occlusion (this is another argument in favor of dental implantation, and the dentition must be restored as quickly as possible - before a problem such as malocclusion appears).
Why your tongue burns: the most common reasons
Fans of spicy food know firsthand how the tongue bakes.
As soon as spicy food touches your tongue, your taste buds instantly react to the pepper. Sometimes this condition is not associated with eating peppered foods. According to statistics, about 1% of people suffer from burning mouth syndrome. This is when the tongue and oral cavity “burn” for no apparent reason. Moreover, when carrying out diagnostic procedures, doctors often shrug their shoulders without understanding the cause of such a symptom.
The most plausible explanation for burning mouth syndrome is the theory of a pathological change in the nerve endings of the tongue. Most likely, the burning sensation on the tongue in this case is a consequence of a change in the polarization of nerve cells. For reasons that are still unclear, burning tongue and oral cavity syndrome occurs 5-7 times more often in women than in men.
In most cases, doctors are still able to determine the cause of this symptom. Let's look at the most common types of diseases and conditions that cause a burning tongue:
- Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity . The most obvious reason is dental pathologies. For example, these are gingivitis, periodontitis, advanced forms of caries and others. The causes of burning and soreness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue are inflammation, which occurs against the background of infection or a non-infectious inflammatory process.
- Action of chemical and physical agents . Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity develop when exposed to chemical or physical aggressive agents. For example, this is gastric juice in gastroesophageal disease, stomach ulcers or vomiting. In this case, the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus and oral cavity, where it has an irritating effect. Some types of treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation, also have a negative effect on the condition of the oral mucosa.
- Fungal infection of the mouth . A common reason for a burning tongue is a fungus. Typically, this is an infection with yeast-like fungi from the genus Candida. Accordingly, this disease is called candidiasis. It is popularly known as thrush. This name is due to the characteristic external manifestations, namely, a white cheesy coating on the tongue. It is noteworthy that candida are representatives of the normal human flora. A certain amount of these fungi is always found in the mucous membranes and skin. However, as soon as the immune system fails or the balance of microflora is disturbed (for example, when taking antibiotics), the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably. This is how thrush occurs. In rare cases, oral candidiasis occurs without a white coating on the tongue, but a burning sensation is present.
- Stomatitis . Often a burning sensation of the tongue is observed with aphthous stomatitis. This is a type of stomatitis in which rounded aphthae (or pockets of erosion) form on the tongue. Such formations appear not only on the surface of the tongue, but also on the cheeks, palate and other parts of the oral cavity.
- Allergic reaction . A burning sensation on the tip of the tongue or other parts of it is sometimes triggered by an allergic reaction. Typically, this is a reaction to a food allergen. In this case, you should be especially careful with some exotic fruits. Often it is overseas fruits that become a source of allergens.
- Medicines . The instructions for some medications state in black and white that a burning sensation in the mouth is possible as a side effect. This effect often occurs with blood pressure medications, antidepressants, sedatives, and some antibiotics.
- Diabetes . It is known that high blood sugar levels have a toxic effect on the body. First of all, blood vessels suffer (angiopathy develops) and nerve fibers (neuropathies develop). Diabetic neuropathy sometimes affects the nerve endings of the tongue, resulting in a burning sensation, changes in taste, tingling or numbness. Accordingly, such symptoms are also possible in some neurological pathologies, for example, multiple sclerosis and others.
- Glossitis . A common cause of burning sensation or pain in the tongue is glossitis. These are inflammations of the tongue that occur due to infectious and non-infectious causes. Often the cause of this symptom is the so-called “geographical tongue” or migratory glossitis. In this case, the tongue becomes covered with spots, and its external outline resembles a map of the world.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals . A burning sensation in the mouth is also possible due to a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, in particular B vitamins, iron or folic acid. In this case, hypovitaminosis may be caused by various diseases that prevent biologically active substances from being absorbed in the small intestine. For example, this is celiac disease, a disease in which gluten intolerance is noted.
- Other diseases . Soreness and burning in the oral cavity is also possible with some other diseases - autoimmune disorders, scarlet fever, tumors and other pathologies.
Geographic language
First aid
If the tongue or the inside of the cheek is bitten, two problems arise at once:
1. Stop bleeding
solution: rinse your mouth with cold water, if possible, apply ice (cooling helps to constrict blood vessels)
If you cannot stop the bleeding on your own, you must immediately consult a doctor!
2. Pain relief
solution: cold also relieves pain, but if the pain is severe, treat the area with a special “freezing” spray or take a painkiller tablet
Associated symptoms
This symptom manifests itself in different ways. The tip of the tongue often burns, but sometimes the entire tongue or just the base burns. Often, with a burning sensation in the mouth, other accompanying symptoms are also noted. These include sore throat, dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, the appearance of white spots on the tongue, and others. The patient may also experience tingling, tingling, or rawness in the mouth. The nature of pain can be acute or chronic. If a symptom bothers you irregularly, then it is important to understand under what circumstances it develops. For example, if your tongue begins to burn whenever you eat pineapples, mangoes or other allergenic foods, then the cause is most likely food.
How to speed up wound healing
All wounds heal sooner or later - this is understandable, but the duration of healing largely depends on your actions. How to behave so that the injured mucous membrane heals as quickly as possible and without consequences? Some valuable tips for this case:
- pay increased attention to oral hygiene - this will help avoid infection of an open wound (regular brushing of teeth, careful removal of food debris and bacterial plaque);
- observe the temperature regime, avoid excessively hot or chilled foods for a while: cold is good only as an emergency measure, but subsequently it slows down the healing process; hot food and drinks both irritate and injure damaged tissues;
- use external antiseptics (sprays, ointments, lozenges): the pharmacist at the pharmacy will help you with the choice, ideally you should consult a doctor;
- rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs: the best for these purposes are chamomile and St. John's wort;
- increase the proportion of foods with vitamins B and C in your diet, which promote wound healing; To heal scratches on the mucous membrane, use ascorbic acid.
Use the advice of traditional medicine with caution: rinsing with medicinal decoctions is not so harmless, you can resort to their help only with the permission of a doctor!
Types and reasons
Depending on the nature and prevalence of changes, the following main types of glossitis are distinguished:
- Catarrhal, accompanied by swelling, redness, and the appearance of a superficial white coating. causes: candidiasis, burns or injuries of the tongue, bacterial or viral infections. It can also develop against the background of hypovitaminosis, gastrointestinal diseases, anemia, and metabolic disorders.
- Ulcerative, characterized by the development of aphthae, that is, multiple or single ulcers. They may be accompanied by severe swelling, bleeding, and sharp, severe pain.
- Purulent-phlegmon glossitis affects deep tissues, affecting the oral cavity and lymph nodes. The Patient's condition is serious, signs of general intoxication appear.
- The desquamative form is characterized by a variegated surface of the tongue. In this case, the spots quickly change location, which gave rise to the name “wandering glossitis.” Treatment is standard, the causes are gastrointestinal diseases, diathesis, helminthic infestation.
Radical solution to the problem
If cheek and tongue biting occurs regularly, the only way to get rid of the problem once and for all is to see a dentist. The specialist will examine the cause of the problem and, based on reality, will suggest:
- restoration of damaged teeth, removal of hopelessly damaged teeth, restoration of the correct distribution of chewing load through prosthetics or implantation;
- grinding of sharp edges of teeth that injure the mucous membrane;
- removal of wisdom teeth (if the dentition is displaced due to them);
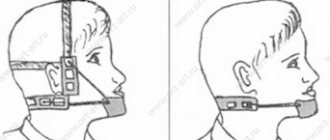
- orthodontic treatment (plates, trainers, aligners, braces, etc.)