The structure of the tonsils and their number
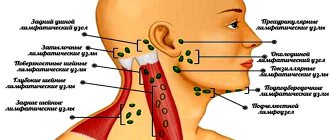
Tonsils or otherwise tonsils consist of lymphoepithelial porous tissue. They are located in the nasopharynx in a circle and are part of the Pirogov-Waldeyer (pharyngeal-lymphatic) ring.
They are divided into paired and unpaired, there are 6 of them in total. The first group includes:
- Palatal. They are located on both sides of the pharynx in a depression formed by the tongue and soft palate.
- Pipe. Located next to the auditory tube.
Unpaired formations:
- Pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal. Located on the posterior fornix of the pharynx.
- Lingual. The location is the back of the root of the tongue.
Functions of the tonsils:
- Barrier. They trap and neutralize bacteria and viruses.
- Immunogenic. B and T lymphocytes are formed in the follicles of the tonsils.
- Hematopoietic. Active during the neonatal period.
- Enzymatic. The tissues of the organs secrete some enzymes necessary for the initial stage of digestion in the oral cavity.
The tonsils are also involved in the formation of voice timbre, so their defeat leads to hoarseness.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils
Inflammation of the tonsils is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
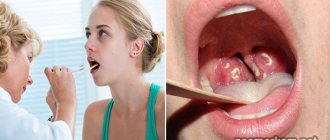
- Inflammation of the tonsils is observed on one or both sides - they become swollen and change color to dark crimson, white plaque and ulcers may appear;
- Body temperature rises. However, it is not always high and can only be observed in the evening;
- The person experiences weakness and headache, similar to the usual pain associated with colds;
- In advanced cases, a skin rash or exacerbation of other chronic diseases may appear;
- In the absence of timely treatment, inflammation of the tonsils provokes disruptions in the functioning of the heart and kidneys.
Types of pathologies
Tonsils are the first barrier that traps pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the tonsils are quite common, especially among children from 5 to 10 years old.
Angina
The term tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) refers to acute inflammation of the palatine or pharyngeal tonsils. The main signs of the disease are dry, sore and sore throat, hyperemia and enlargement of the tonsils, increased temperature, and symptoms of intoxication.
There are several forms of angina, most often diagnosed:
- Catarrhal. The symptoms are mild and, with appropriate treatment, disappear within 3-5 days.
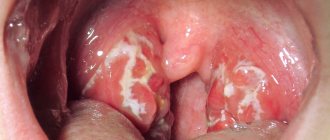
- Follicular. Follicles are affected. A characteristic symptom is pain when swallowing, radiating to the ear. The temperature can rise to 38 degrees or higher; upon examination, enlarged tonsils with whitish-yellow dots are visible.
- Lacunarnaya. The manifestations are similar to follicular, however, the symptoms of intoxication can be more pronounced. A yellowish-white coating covers most of the inflamed tonsils.
Treatment of sore throat involves the use of antibiotics, frequent gargling, and lowering the temperature if necessary. In the first days of acute inflammation, bed rest is necessary; compliance with it reduces the risk of complications.
Chronic tonsillitis
Most often it is a consequence of an untreated form of acute tonsillitis. It occurs with periods of relapses and remissions. A chronic focus of infection often becomes the cause of the development of dangerous diseases such as rheumatism, lupus erythematosus, and nephritis.
The treatment is complex. Antibiotics and drugs that enhance immunity are selected for the patient. If there is no effect from conservative therapy, partial or complete removal of the tonsils is recommended.
Hypertrophy
Tissue proliferation in most cases is characteristic of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. The disease is otherwise called adenoiditis and young children who often suffer from ARVI are susceptible to it. Primary signs are a frequently recurring runny nose, noisy breathing and snoring during sleep, a cough that gets worse at night, and mucous discharge from the nose.
Advanced forms of adenoiditis lead to chronic hypoxia, which causes lethargy and inattention. Lack of timely treatment can cause improper formation of the bones of the facial skull. Depending on the severity of hypertrophy, treatment can be medicinal or surgical.
Abscesses
They are characterized by the formation of cavities filled with pus near the tonsils. Most often, abscesses occur against the background of a sore throat. Symptoms are severe pain on the affected side, fever, high temperature, intoxication of the body. Abscesses are opened surgically.
Neoplasms
Cysts can form on the tonsils. A malignant lesion cannot be excluded, which at an early stage is manifested by tissue enlargement and periodic pain.
There are many reasons for the development of tonsil diseases. The main ones are infection with staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli. Inflammation can be caused by hypothermia, mechanical injury, or chemical burn. The likelihood of pathologies increases with hypovitaminosis and low immunity. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the tissues of the lymphatic ring not only directly, but also through the blood during chronic and acute diseases of other organs.
Tonsillotomy as a method of treating hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
Far from being the rarest diagnosis in children is hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils. Enlarged tonsils cause one or more problems at once:
- difficulty breathing through the nose
- sleep apnea
- snore
- shortness of breath, shallow breathing
- a sore throat
- speech disorders
- headache
- disturbances in concentration, work ability
Causes of enlarged tonsils
Doctors believe that the sharp growth of cells in the tissues that make up the tonsils is associated with the body's immune response. At an early age, a person is more susceptible to infectious diseases than as an adult. Tonsils, as one of the barriers to infection in the body, are under attack from diseases that can provoke hyperplasia - unusually rapid growth of cells in tissues without signs of inflammation.
How to determine that a child has enlarged tonsils?
Firstly, you need to visit an ENT doctor at least once a year. Upon examination, he will be able to clearly establish the pathology.
Secondly, if a child breathes predominantly through the mouth, this is an alarming symptom; nasal breathing may already be impaired.
Third, pay attention to your child's sleep. Snoring or sudden stops in breathing (apnea) are also evidence of enlarged tonsils.
How to treat hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils?
Often patients do not want to take action if tonsil enlargement does not interfere and does not affect the quality of life. However, it is necessary to treat problems in the throat - there are other organs located near the palatines to which hyperplasia can spread. Often the process involves the pharyngeal tonsils.
There are three types of treatment methods for tonsil hypertrophy: physiotherapy of the throat, surgery and the use of medications.
Physiotherapy of the throat and its organs:
- UHF;
- ozone therapy;
- mud therapy;
- ultrasonic massage.
Drug treatment for enlarged tonsils consists of a combination or isolated use of immunostimulating drugs, corticosteroids, and antibiotics. A solution of silver nitrate is also often prescribed. The drug treatment strategy is determined only by the doctor; you cannot use the drugs yourself.
Operation tonsillotomy
While monitoring the development of tonsil hypertrophy, the doctor may suggest their removal - tonsillotomy. This is a fairly common procedure and the risk of undergoing it is minimal, especially considering the possible consequences of refusing treatment.
With tonsillotomy (as opposed to tonsillectomy), the tonsil is not completely removed, but only the affected part is affected. At the same time, in the future, the tonsils will recover and will be able to continue to perform their function.
This operation is not one of the most complex, but it is performed only by the operating ENT doctor. In Voronezh you can apply for this. Our operation is performed using laser surgery. Laser tonsillotomy does not require general anesthesia; local anesthesia is used.
This operation belongs to the so-called “one-day operations” - after the procedure, the patient does not remain in the hospital, but can safely spend the night at home. The ENT doctor operating on the patient schedules a follow-up appointment in a week to ensure proper regeneration of the mucous membrane.
Contraindications to tonsillotomy surgery
The operation is not performed if:
- The child was diagnosed with diphtheria bacilli
- An infectious disease occurs in an acute form
- History of blood disease
Do I need to remove my tonsils completely?
It is possible, but not recommended unless absolutely necessary. The tonsils still act as a kind of barrier to infections that seek to penetrate the lungs, bronchi or trachea. After partial removal, the organ is regenerated and its functions are restored. Tonsillectomy does not leave the body the opportunity to restore the tonsils - complete and final removal occurs.
You can make an appointment with an ENT doctor by phone +7 or through an online appointment on the website
Disease Prevention
Strengthening the immune system prevents inflammatory processes from developing. In order to prevent the development of diseases, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle: avoid bad habits, eat right, and monitor the general condition of the body. To maintain normal tonsils, it is enough:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Avoid cold drinks.
- Eliminate all possible sources of infection: sinusitis, caries, sinusitis.
- At the first signs of infection, contact a medical facility.
First aid
It is difficult to swallow, the temperature has risen, when examining the throat, redness or pustular rashes are found - call a doctor. Before a specialist arrives, patients should not take fever-reducing pills, but only if it does not exceed 39 °C. High temperature will help the body cope with infection and destroy harmful microorganisms.
Scheme for relieving the patient’s condition:
- Drink plenty of warm drinks.
- Gargling with salt water, decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula).
- Rinse with Furacilin, Miramistin, Dioxidin and other products recommended by your doctor diluted with water.
- Dissolving lozenges with a calming and analgesic effect.
- Bed rest.
You should take antibiotics, and preferably all other drugs, only as prescribed by your doctor.
How to treat inflamed tonsils?
The presence of a simple sore throat is not an indication for tonsil removal! There are many treatment methods that avoid invasive intervention:
- Antibiotics. It would not be amiss to remind you that the course of antibiotics must be taken completely in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations, without skipping a single dose of medication and without abandoning treatment at any stage.
- Washing with various agents with an antibacterial effect. You may even be prescribed a simple solution of chlorhexidine, which will definitely not cause harm, but may well be a good medicine.
- Application of special solutions. This could be Lugol's solution or propolis - the doctor prescribes one or the other based on your individual characteristics.
- Physiotherapy. Ultrasound, magnets, electrophoresis - all this can be a completely sufficient method of treatment without any surgery.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, strengthening the immune system and avoiding hypothermia, although not a treatment method, is an excellent method of preventive intervention in the development of severe pathologies.
You can also read our article on the treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
Removal of tonsils: pros and cons
The debate about the need to remove or preserve tonsils has been going on for a long time and with varying success. Those who advocate that nature does not deal with the structure of unnecessary organs give the following arguments about the benefits of the tonsils:
- Producing a huge amount of immunoglobulins, the tonsils of a healthy person contribute to the proper development and protection of the body from viral infections.
- The porous surface of the tonsils serves as a barrier to pathogenic microorganisms seeking to enter the throat and the internal environment of the body. Once in the center of the immune cells, the harmful bacteria die.
Proponents of surgery believe that even normal tonsils can eventually cause major health problems:
- During some diseases, for example, chronic tonsillitis or acute tonsillitis, disruptions and irreversible changes occur in the proper functioning of the lymphatic formations. The tonsils are constantly inflamed, do not allow you to breathe freely, and harmful bacteria are not eliminated.
- Frequent purulent sore throats can cause a throat abscess, a general infection of the body.
- Constantly enlarged tonsils lead to hearing impairment or deterioration of respiratory functions.
Most doctors agree with the removal of the tonsils in the most severe cases: when the body is unable to respond to medication treatment.
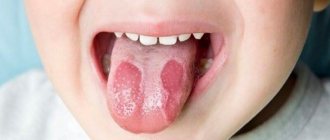
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils in children
The growth of the palatine tonsils most often occurs in childhood - during the period of active tissue construction and adaptation of the body to its environment. As the body ages, the tonsils gradually decrease in size.
There are cases when the tonsils are enlarged from birth. But most often, their intensive growth serves as a response to increased inflammation of both the tonsils themselves (called tonsillitis or tonsillitis) and neighboring organs. Inflammation develops when:
- frequent infectious diseases;
- allergies;
- irritation of the mucous membrane by chemical or thermal factors.
The tonsils are located on the sides of the pharynx. If they increase slightly, the child does not experience any discomfort (hypertrophy of the tonsils and their inflammation are not the same thing) and does not need treatment. Moreover, with the onset of puberty, their reverse development begins. If they reach a large size and block the lumen of the pharynx, then characteristic signs appear:
- difficulty breathing (especially with a combined enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsil - adenoids);
- violation of diction;
- problems swallowing food;
- night cough;
- the child may snore and wake up frequently, and a chronically sleep-deprived baby will behave restlessly during the day.
What healthy tonsils look like and where they are located
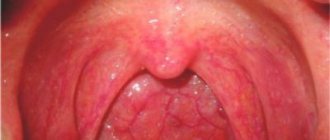
The tonsils of a healthy person are of average size; they usually do not extend beyond the arches of the pharynx. But exceptions are possible - in some people large tonsils occur due to anatomical features, not disease .
Photo: this is what healthy tonsils (tonsils) look like
The naturally uneven surface structure of the tonsils should not be pronounced and lumpy. Healthy tonsils are indicated by their color; usually it is uniform, pinkish in color, without red furrows or inclusions.
The back wall of the oral cavity, palate, and uvula with healthy tonsils are evenly colored and have no signs of inflammation. The pharyngeal mucosa should be free of swelling and have a pronounced pattern of blood vessels. There should be no purulent deposits or unhealthy plaque on the surface of the tonsils themselves.
Causes of enlarged tonsils
Tonsils enlarge if the body is infected with strepto-staphylococci or viral infections. This happens as a result:
- The transition from normal inflammation to chronic inflammation.
- Decreased immunity during hypothermia, a stressful situation or due to other reasons.
- Irritation or poisoning from chemicals, allergens, unusually spicy foods.
You can compare what normal and inflamed tonsils (tonsils) in the throat look like in the photo: