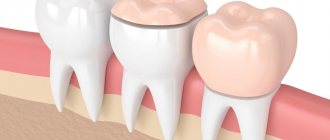
Crowns are one of the types of dentures that can be used to restore lost or severely damaged teeth. Crowns are used in classical prosthetics and are placed on implant abutments after dental implantation.
Crowns are always selected taking into account a number of factors, and the area of the tooth that needs to be restored is always taken into account. What should crowns be like for chewing teeth? Let's look at this important issue together.
What is a metal crown?
A crown is a microprosthesis that covers the entire surface or a separate part of a destroyed tooth in order to restore its anatomical integrity.
Externally, the manufactured structure resembles a cap used when the tooth structure is destroyed by more than 50%, and a conventional filling is not able to correct this situation. If the segment is completely destroyed, the prosthesis is fixed using adjacent teeth or special implants are used.
Crown installation is a restoration method in which a pre-prepared prosthesis is placed on the remaining tooth (like a cap). Today, in addition to functionality, prosthetics can also solve any aesthetic problems, because modern designs are identical in appearance to natural teeth.
Video on the topic:
Operating period
Steel bits have a long service life. The characteristics of the material allow the product to be used for about 15 years, but many patients manage to walk with the structure for 20 years or more.
Experts recommend changing them every 10 years. This is due to the fact that prolonged use leads to receding and atrophy of the gums, exposing the edge of the crown. These changes lead to disintegration of the structure and the occurrence of pain.
The length of wear depends greatly on the manufacturing method. Thus, stamped products will last a little less than cast ones due to the small thickness of their walls.
The service life is also affected by operating conditions, the professionalism of the doctor and technician who manufactured and installed the product.
Important! To increase the service life, you must adhere to the rules of wearing and care, avoid excessive chewing loads and periodically visit a doctor for a preventive examination.
Indications for installation
Prosthetics are prescribed by the attending physician in cases where:
- you need to straighten a crooked tooth or change its size/shape/shade;
- fluorosis was detected;
- the inflammatory process damaged more than half of the coronal part of the tooth, and the pulp was removed;
- there is a need to restore a damaged or lost tooth;
- Due to the incorrect location and size of the teeth, dental anomalies are observed. Contraindications include:
- advanced stages of periodontal disease;
- allergic intolerance to the material used;
- malocclusion;
- thinned tooth walls;
- low location of the coronal part of the segment.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to install a steel crown in the following cases:
- the presence of an allergy to any of the metals;
- violation of occlusion of the dentition;
- in case of severe damage to the tooth, affecting its roots;
- looseness of the unit due to an advanced form of periodontal disease;
- very thin tooth walls;
- insufficient height of the coronal part.
It is also contraindicated to place it if the patient already has structures made of other materials installed in the patient’s mouth, especially for damask steel and gold.
When in a humid environment, these metals, together with steel, create a galvanic current. The steel in this case acts as a positively charged electrode, and the other metal present acts as a negative one. This mini-system is connected by saliva, which plays the role of an electrolyte.
The first signs of such a side effect are:
- tingling in the mouth;
- metallic taste;
- burning sensation in the mouth;
- headache;
- slight numbness of the mucous membrane and tongue.
Important! This effect is dangerous for the body and always leads to its intoxication.
If there are the listed restrictions on prosthetics with steel crowns, the doctor will always offer an alternative option for replacing them.
Types of dental crowns
In orthopedic practice, well-known metal crowns are still popular. Despite the fact that a wide variety of innovative methods of prosthetics have appeared, metal structures do not lose their positions due to their affordable price and impressive service life.
Sputtered gold crowns were the very first to appear, after which durable steel prostheses began to be actively used.
Depending on the manufacturing method , metal crowns are divided into three groups:
- Stamped. Standard products that require pre-processing with a special machine to give the desired shape. Installation is possible only if at least a third of the tooth crown remains intact.
- Solid cast. Crowns that are created based on the patient’s individual impression. The precision casting method is used, as a result of which it is possible to reproduce the desired anatomical shape of the tooth.
- Combined. These can be either cast or stamped products, the surface of which is lined with plastic or porcelain.
Stamped
Solid cast
Combined
Metal crowns: pros and cons
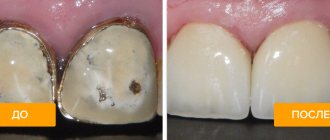
In appearance, a metal dental crown resembles a cap that is put on a damaged tooth or fixed to an implant if the first one is completely missing. The thickness of the metal crown is 0.2 – 0.3 mm. Its main advantages are the ability to withstand maximum chewing loads, affordable price and durability.
The disadvantage of a metal crown is its aesthetic imperfection - metal is much inferior in this sense to all other materials for making crowns. Therefore, such structures are installed mainly on the back teeth, where they are securely hidden from prying eyes.
Are metal crowns harmful?
It is fair to note that there is a possibility of galvanic reactions and allergies to metal crowns after their installation. To avoid such complications, clinics carry out thorough diagnostics, which makes it possible to identify the presence of allergies before a permanent structure is placed.
What materials are they made from?
Most people, especially older people, are accustomed to associating the word “crown” with a gold tooth, but modern medicine has advanced so much that the prosthetic products used are practically no different from real teeth.
Reference! The main difference between such designs is the material, the type of which will determine the service life and external aesthetics of the manufactured crown.
Metal
Despite the fact that metal crowns are still used, in the modern world such structures should long ago become a relic of bygone days. Even such significant advantages as high wear resistance and incredible strength do not cover their one, but impressive drawback - an extremely unaesthetic appearance.
In addition, it is quite difficult to place a metal crown on a damaged tooth segment. And finding a clinic that uses such outdated restoration methods is not so easy.
There are two main types of metal crowns:
- from alloys of precious metals : prostheses made from the most popular precious metal - gold. There are also silver structures, but in terms of their characteristics they are significantly inferior to gold prostheses, so at present they are almost never installed;
- from alloys of base metals : crowns made of titanium, which do not have a long service life, but at the same time boast an affordable price.
Gold crowns
Titanium crowns
Metal ceramics
A distinctive feature of such designs is the use of a ceramic coating, which in its appearance resembles real enamel. Metal-ceramic crowns are durable, and their cost is relatively low, so among all the proposed options, these prostheses are the most optimal in terms of price and quality ratio.
There is also a significant drawback: the lack of translucency of the coating when fixed to the front teeth reveals the artificiality of the design. After installation, a gap remains between the gum and the crown, in which the metal base of the product is visible. Because of this, an unaesthetic dark stripe is formed.
There are two varieties :
- on alloys of precious metals : made on the basis of the metal we have already discussed - gold. They differ from ordinary metal products in a more advantageous appearance, but at the same time they are just as wear-resistant and hypoallergenic;
- on alloys of non-precious metals : an alternative to expensive gold products are models made from an alloy of nickel, cobalt and chromium. This material is highly durable, however, over time, the gums under the prosthesis become very dark, and some people may even develop allergic intolerance.
Gold-based metal ceramics
Combined
Metal-plastic
A special plastic overlay is attached to the metal base of the prosthesis, which imitates the structure of tooth enamel.
Such crowns quickly lose their original appearance, change shade and do not have high strength. However, the affordable price and the possibility of rapid production make it possible to use such products as temporary prosthetics.
Metal-ceramic crowns: can they be called the best for prosthetics of chewing teeth?
In some materials on the Internet you can see that metal ceramics are advertised as the best material for crowns of chewing teeth. Is it really? Let's try to figure this issue out together, but first we will briefly tell you what metal-ceramic crowns are.
A metal-ceramic crown has a metal base, which is covered with layers of ceramic mass on top. The metal frame ensures the strength of the crown, the ceramic coating provides aesthetics, and some doctors seriously recommend them to their patients as the best option for installation on chewing teeth. In fact, this is not the case; metal-ceramic crowns cannot be called the best for restoring chewing teeth for a number of reasons.
Manufacturing of solid crowns
The latest technological developments in the field of prosthetic dentistry have allowed us to reach a higher level thanks to the development of cast metal prostheses. Unlike stamped crowns, solid-cast products fit as closely as possible to the teeth, thereby achieving the exact anatomical shape of the destroyed segment.
The production of a cast structure occurs in several stages :
- The dentist conducts a preliminary examination of the oral cavity, studies the patient’s medical record, after which preparation and further taking of all necessary impressions are performed to recreate the anatomical structure of the tooth.
- Next, based on the impressions obtained, specialists make a plaster test model of the crown and model the future product using special wax.
- At the next clinical stage, the patient’s tooth surface undergoes additional grinding. This procedure is necessary to ensure that the created prosthesis fits most tightly to the surface of the tooth. A wax-filled crown is placed on the damaged segment, after which all excess wax is removed through a pre-drilled channel. The orthopedist eliminates all inaccuracies, and the finished sample is sent back to the laboratory for further production of a solid metal structure.
Find out more about the production of solid crowns:
Stamped
Since a stamped crown is a budget type of prosthetics, and the technologies used are not highly accurate, the resulting impression will not be identical to the shape of a natural tooth.
A stamped prosthesis is created as follows :
- To make a model, as in the production of a cast prosthesis, at the initial stage the tooth surface is prepared to give it the desired shape.
- Then impressions are made of two jaws: the one where the crown will be installed, and the opposite one with antagonist teeth. Based on two casts, a plaster model is made, which is later installed in a special occluder.
- At the next stage, wax modeling of the crown is performed, after which they begin to make a plaster stamp. Based on the created plaster model, the subsequent creation of a metal stamp will be carried out.
- At the end of the process, a suitable blank sleeve is selected and the final stamping of the product is done.
How stamped crowns are made:
Stamped crowns. Manufacturing principles
The production of stamped crowns has been used for more than a hundred years; many dentists consider this process a relic of the past, but, nevertheless, it is still used because it is very cheap. Cylindrical blanks of different diameters are made from stainless steel, from which metal crowns are stamped on special machines. Such a product must have certain qualities for proper installation and comfortable wearing.
The stamped crown must fit exactly the size of the tooth, cover it tightly, without gaps or voids. Otherwise, it will provoke inflammation of the gums, which can lead to atrophy. For a tighter fit of the crown to the tooth and its fixation, special dental cement is used. The crown should not go deep into the gums, as this can cause gum disease, such as periodontitis. In addition, it must match the shape of a healthy tooth so as not to violate the integrity of the row, and be of an appropriate size to avoid injury. The product is designed to restore tooth function.
Preparing a tooth for a crown
The successful outcome of a dentist’s work largely depends on preliminary preparation for prosthetics.
If necessary, depulpation is carried out and the root canals are filled. If the carious process has led to further tissue destruction, a mandatory stage of prosthetics is performed - preparation. To do this, hard layers of dental tissue are removed and the segment is ground to the desired shape. Preparation is performed using several methods:
- Ultrasonic turning. The doctor uses special ultrasonic tips with replaceable attachments. This method perfectly levels the tooth surface without leaving any cracks or chips.
- Laser preparation. This type of turning is based on the use of an erbium crystal, which processes tissue using laser irradiation.
- Tunnel grinding method. It is based on the use of turbine units, which, in turn, contributes to excessive heating of tooth enamel. A fairly radical method of treatment, in which it is difficult to avoid painful damage to the gums.
- Air abrasive method. Grinding of the tooth surface occurs due to the impact of an air flow mixed with special powders.
- Chemical preparation. A swab soaked in lactic acid is applied to the desired segment, after which the treated tissue is easily ground down using dental instruments.
Taking an impression to make a crown:
Indications and contraindications for the use of stamped crowns
Stamped metal crowns are used:
- In case of incomplete tooth decay. In this case, the tooth is ground to the required size, all its defects and carious lesions are eliminated to prevent further destruction.
- If removable dentures, for example, clasp or bridges, will be installed. Crowns are installed to protect supporting teeth.
- To restore a damaged baby tooth
There are some contraindications to their use:
- Bruxism (teeth grinding, which destroys enamel).
- Complete tooth destruction, in which there is nothing left to save.
- Infectious diseases of the oral cavity.
Fitting and installation
Installation of a denture occurs in three stages :
- Fitting. Before final fixation, the doctor must try on the manufactured product. In order for the frame of the metal structure to fit tightly to the stump, any flaws and inaccuracies must be excluded. If mistakes are made and the shape is incorrectly made, the prosthesis is sent for additional processing.
- Installation on temporary cement. If the model is made correctly, the specialist proceeds with the subsequent fixation of the crown. First, temporary cement is used to assess the state of the bite and the reaction of the teeth. If any defects are found, the product can be easily removed without any harm to the tooth.
- Installation on permanent cement. If the patient does not experience any discomfort while wearing a crown with temporary cement, the product is removed and fixed with permanent cement.
Installation
It is impossible to restore a tooth with a crown in one visit to a specialist. To do this, a person will have to come to see him several times.
The installation procedure proceeds in the following sequence:
- Visual examination of the oral cavity . When diseases of the teeth and gum tissue are detected, therapeutic measures are taken to eliminate them, and professional dental cleaning is also required.
- Grinding. The restored unit is prepared to the required dimensions, i.e., up to 0.5 mm of tissue is removed from it (which is significantly less than when installing analogue structures made of other materials).
If crowns are intended to be placed on mammary units, then their lingual and buccal surfaces are not ground down. - Making impressions . An impression is taken of the prepared tooth, and then a temporary prosthesis is put on it to protect it from accidental injury and external irritants.
- Fitting. At this stage, the tightness of the product to the tooth surface and the height, as well as the stability of the bite, are checked. If inaccuracies are detected, the crown can be trimmed and adjusted to the required parameters.
- Fixation. The finished structure is secured with dental glass ionomer cement. Its excess is removed with a scaler or probe, and floss is used to clean the proximal surfaces.
Once the process is complete, the entire system is checked for correct occlusion. The primary (temporary) dentition is characterized by a unique ability to adapt to an overbite of up to 0.1 cm without developing such effects.
Advantages and disadvantages of various types of prosthetics
| Product type | Advantages | Flaws |
| Metal ceramics | Affordable price. Not a bad look. Long service life. | Requires significant grinding of the tooth surface. Undesirable placement on the front teeth due to the presence of a translucent metal base. |
| Metal-plastic | Low price. Fast production. | Outdated manufacturing method. Service life is no more than two years. Under the influence of wine and coffee, the material changes its color. |
| Metal | High wear resistance and durability. The optimum ratio of price and quality. | Due to their unaesthetic appearance, they are not suitable for fixation on the front teeth. Can cause an allergic reaction. |
Watch a video about choosing the type of dental crowns:
Manufacturing methods
When a patient decides to get steel crowns, he is offered a choice of two options, depending on the manufacturing technology:
- Stamped.
- Cast.
Production by stamping
They are industrially manufactured structures based on standard sleeves. To give the required shape and parameters, they are molded and polished using special equipment.
Installation is justified if the crown part is preserved by at least a third, and the root system does not have any defects. Indications for placing stamped products are the following conditions:
- prosthetics of mammary units until they are replaced by permanent ones;
- maintaining healthy chewing elements;
- as a basis for placing bridge systems;
- a severe degree of destruction of the crown, the shape of which cannot be restored with a filling.
Outwardly, it looks like caps. Having very thin walls, the procedure for installing dentures does not involve strong grinding of dental tissues, which, on the one hand, is considered their significant advantage.
On the other hand, the thinness of the walls reduced the service life. The ease and speed of production is reflected in the cost - it is significantly lower than that of cast products.
The production and subsequent installation technology consists of the following stages:
- Tooth preparation (grinding) – no more than 0.3 mm is ground off, but the diameters of the crown and neck must have the same dimensions.
- A cast of the jaw is made.
- Modeling of a future prosthesis using plaster.
- Making a metal stamp using it.
- Driving the stamp into a pre-prepared sleeve.
- Stamping using a press.
- Alignment of the edges of the finished prosthesis.
The finished cap is placed on the prepared coronal part and is first temporarily fixed to the composite. This is necessary so that the specialist can observe the body’s reaction to the presence of a foreign object in the mouth.
The video shows the stages of making stamped crowns.
If the patient does not complain about discomfort and pain, then during the next visit the crown is removed, cleaned of the composite and placed a second time, but with zinc phosphate or glass ionomer cement.
The main disadvantage of stamped structures is their short service life . This is explained by the following circumstances:
- Loose fit to a person’s own tooth , resulting in small gaps between them. After some time, the crown will have to be removed due to caries that has developed underneath it, caused by bacteria that have easily penetrated into the cracks.
- The thinness of the walls leads to rapid abrasion of the material.
It is impossible to fully restore chewing function using this method.
Cast crowns
In the manufacture of solid steel prostheses, high-precision monolithic casting technology is used using special casting equipment.
Based on a cast of the reconstructed unit made by the dentist, a dismountable model of it is made from plaster in the laboratory. Next, the technician uses the wax to form a crown, which will then be replaced with metal, and process it in accordance with dental requirements.
It is recommended to install cast products on molars, since their thick walls can withstand full chewing load.
The advantages of solid dentures are the following characteristics:
- full compliance with the anatomical features and shape of the restored unit;
- do not require adjustment, since they are more accurate in manufacturing;
- good marginal fit, which eliminates the possibility of food and microorganisms getting under the prosthesis;
- there is no traumatic effect on the gums;
- the amount of plaque accumulation on the surface is minimal due to its smoothness;
- wear-resistant;
- service life exceeds the service life of stamped products.
But, at the same time, dentists note one significant drawback of the method - before installing the device, it is necessary to grind the abutment tooth. The grinding amount is 0.3-0.5 mm.
Also, solid cast structures have good thermal conductivity. If it is installed on a non-pulpless unit, then unpleasant sensations associated with eating hot food and drinks develop.
Important! If there is a need to restore several teeth at once, experts advise considering this budget option: install metal-ceramic crowns on the frontal teeth, and solid steel crowns on the chewing ones.