We are publishing an article by Natalya Lvovna Mayorova, a dentist, therapist, and head of the therapeutic department of the Dentalika clinic.
Pain relievers used in modern dental practice can work wonders. After receiving an anesthetic injection, the patient does not feel any pain or even particularly unpleasant sensations. To ensure that the injection itself is painless, before the procedure the doctor “freezes” the injection site with a special preparation with a delicious smell of cherry, lemon, or apple.
Local anesthesia is the main method of pain relief used in dental practice. With local anesthesia, the patient remains fully conscious, and this allows the doctor to fully control the entire course of treatment, communicate with the patient, and monitor your reaction.
The quality of dental interventions depends on the results the doctor obtained during local anesthesia. Therefore, achieving 100% pain relief is necessary not only for the patient, but also for the doctor, in order to carry out treatment calmly, slowly, and efficiently. Hence the following requirements for local anesthetics:
- they must have a strong analgesic effect, easily penetrate into tissues and remain there for as long as possible;
- have low toxicity, causing a minimum number of both general and local complications
Based on these wishes, we chose several widely used drugs:
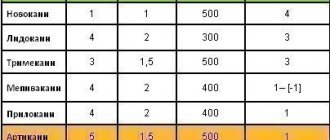
- Ultracaine DS forte (4% articaine, adrenaline 1:100,000);
- Ultracaine DS (4% articaine, adrenaline 1:200,000);
- Scandonest SVC (3% mepivacaine; without vasoconstrictors - adrenaline).
Now in more detail about their action.
Ultracain DS
The analgesic basis of the first two drugs is ARTICAINE (amide anesthetic from the thiophene series), an antispasmodic - lowers blood pressure. It is characterized by rapid action - anesthesia occurs in 0.5-3 minutes. Articaine is 2 times stronger than lidocaine and 6 times stronger than novocaine (anesthetics of previous generations), less toxic, relatively quickly eliminated from the body. Its half-life is, on average, 22 minutes, that is, all traces of the drug disintegrate in 44 minutes and are then completely eliminated from the body. Has high penetrating ability. It is distinguished by high purity of the solution. Allergic reactions to articaine are very rare - one in one hundred thousand injections ; the use of articaine, according to studies, is safe in 99.4% of cases. They also contain a vasoconstrictor (a substance that causes constriction of blood vessels and a decrease in blood flow in them) - adrenaline. The use of a vasoconstrictor continues and enhances anesthesia. The drug also contains antioxidants (sulfites) - substances that prevent the oxidation of adrenaline.
Ultracaine does NOT contain parabens (anesthetic preservatives), which significantly reduces its toxicity. In addition, parabens can cause allergic reactions.
Thus, ultracaine is:
- a strong anesthetic with moderately low toxicity, due to its components;
- the safest drug for pregnant women, because articaine does not penetrate the hematoplacental barrier - the barrier separating the blood of the fetus and the blood of the mother (Ultracaine DS).
School-age children can also use Ultracain DS. We always remember that the administration of an anesthetic solution with adrenaline is CONTRAINDICATED for children under 5 years of age, patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system, with endocrine pathologies, taking antidepressants, thyroid hormones, drugs that block beta adrenergic receptors; - an anesthetic that practically does not require postoperative pain relief;
- a drug that provides a rapid onset of anesthesia, depending on the anesthesia tactics chosen by the doctor, the effect occurs within 30 seconds to 3-5 minutes);
The duration of anesthesia is, depending on the technique chosen by the doctor, from 1.5-2 hours to 5-6 hours. The choice of different techniques (infiltration, conduction anesthesia) depends on the planned dental procedure. For example, there is a difference between the treatment of caries of one tooth and the complex removal of a wisdom tooth. - good local and general tolerability. According to studies, only 4.3% of patients experienced toxic reactions, which was caused by the presence of adrenaline and sodium disulfate in the anesthetic solution.
- For standard procedures, a small amount of anesthetic is required (0.9 ml-1.8 ml).
I would like to note that for standard dental operations it is better to use Ultracain DS (adrenaline 1:200,000). A strong anesthetic provides high-quality anesthesia even during complex, long-term interventions, and a small amount of vasoconstrictor ensures low toxicity of the anesthetic solution. And we prefer to consider Ultracaine DS forte (adrenaline 1:100,000) as a “reserve anesthetic” in more complex situations:
- anesthesia of the lower lateral teeth (molars) for their treatment and depulpation;
- pain relief for inflammatory processes in the maxillofacial area (periostitis, osteomyelitis);
- for particularly traumatic interventions;
- in patients with a low pain threshold.
Differences between regional and infiltration anesthesia and the advantages of ultracaine
Regional methods of pain relief include spinal and epidural anesthesia, anesthesia in the area of large nerve plexuses, as well as conduction anesthesia in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. In this case, a drug depot is created in the area of passage of the conducting nerve trunk and the sensitivity of the entire zone of its innervation is blocked. The anesthetic is delivered directly to the fiber and almost immediately gains access to the nerve cell membrane, minimally interacting with tissue fluid.
Infiltration anesthesia involves injecting the drug directly into the area that needs to be numbed. By saturating the tissue, the anesthetic inactivates the smallest nerve endings, so pain is not felt. In this case, part of the anesthetic, without reaching the point of application of its action, is inactivated by tissue fluid, especially if anesthesia is carried out on inflamed tissue.
The differences in the effects of ultracaine and lidocaine are fully manifested during infiltration anesthesia, especially under conditions of inflammation. The effectiveness of conduction anesthesia differs slightly.
The advantages of ultracaine appear during infiltration anesthesia. Due to its resistance to tissue fluid, ultracaine acts better and penetrates deeper into tissues than lidocaine with a similar administration method. Less susceptible to the action of an acidic environment, ultracaine provides a satisfactory level of pain relief during infiltration of inflamed tissue.
Scandonest SVC
If the patient belongs to a risk group (with severe concomitant diseases , in particular cardiovascular pathology ), the use of an anesthetic solution with adrenaline, a vasoconstrictor, should be completely abandoned. In such cases we use Scandonest SVC . This anesthetic exhibits a vasoconstrictor effect, i.e. has vasoconstrictor properties and can therefore be used without adrenaline, which means that the drug does not contain sulfites and can also be used in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic conditions (after an allergy test). Scandonest SVC is a medium-strength anesthetic; provides anesthesia, depending on which part of the jaw the doctor disconnects from pain sensitivity, for 20 - 90 minutes, which sets it apart from the group of other non-adrenaline anesthetics.
Features of the chemical structure of ultracaine
In solution, the anesthetic interacts with water molecules and transforms into an active ionized form, shifting the acid-base balance to the alkaline side. In an acidic environment, a neutralization reaction occurs as a result of which the amide bond is destroyed and the anesthetic becomes inactive. Human tissue fluid normally has a slightly acidic environment, but in the area of inflammation the acidity increases. Therefore, inflamed tissues are less pain relieved.
In addition to the amide group, which connects the lipophilic and hydrophilic parts, the articaine molecule (the active ingredient of ultracaine) contains a more reactive ester group. In the acidic environment of tissue fluid, it undergoes hydrolysis first of all, ensuring the preservation of amide groups, therefore, in general, the effect of ultracaine in comparison with lidocaine is longer.
Allergy tests
If you have previously experienced allergic reactions to medications, you have doubts, and you do not fully know which local anesthetics are safe for you, we strongly recommend that you undergo tests for allergic reactions at an allergy center before visiting the dentist. The addresses of such centers can be obtained from the reception of the Dentalika dental clinic. The test results can be completely trusted. This recommendation especially applies to parents of children who bring their children to the dentist for the first time. Unfortunately, from year to year the number of children susceptible to allergic reactions in our city is only growing. A visit to the allergy center will completely protect your child from possible complications.
Mechanism of action of amide series local anesthetics
The spread of a pain impulse in a nerve fiber occurs due to a change in the polarity of the cell membrane. The change in potential is ensured by the work of special membrane protein complexes, sodium and potassium channels. The former are responsible for the excitation and spread of the sensitive impulse, the latter – for restoring the original balance.
The local anesthetic molecule consists of fat-soluble and water-soluble fragments, which are linked by an amide bond. The lipophilic aromatic ring allows the anesthetic to penetrate deep into the cell membrane of the nerve fiber, and the hydrophilic group acts from the inside, blocking the activity of sodium channels. Sodium transport does not occur across the cell membrane, so the pain impulse is blocked.
Children
It should be noted separately the features of local anesthesia in children. The technique of local anesthesia in children must be planned so that 100% pain relief is achieved at all stages of treatment, otherwise it will be impossible to carry out the necessary manipulations.
As mentioned above, children under 5 years of age are given an anesthetic without adrenaline (3% scandonest SVC, or septanest 4% SVC).
Children over 5 years old can use an anesthetic with low concentration adrenaline (1:200,000 - Ultracaine DS). The dose of drugs is selected depending on age. Pain relief is performed in children in 3 stages:
- First, a superficial anesthetic gel is applied
- then a small dose (0.1-0.2 ml) of anesthetic is administered;
- after which, after 60-90 seconds (time sufficient for effective anesthesia of the needle path in the soft tissues), the remaining amount of the planned dose of anesthetic is administered.
We wait 5-10 minutes until complete anesthesia occurs. The child, feeling a complete absence of pain, gains confidence in the doctor and gives the opportunity to carry out the necessary intervention.
Ultracaine and lidocaine for regional anesthesia
Since regional anesthesia involves the injection of the drug directly to the nerve trunk, the ability of the anesthetic to resist destruction in an acidic environment is not so significant. The depth of anesthesia in this case does not differ much, but still ultracaine gives a longer-lasting effect, so it is widely used to disconnect peripheral nerves and nerve plexuses. Ultracaine has been proven safe and effective for epidural and spinal anesthesia, but in this case it is not considered a drug of choice.
Category Medicines/preparations, Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog
Failed anesthesia
I would also like to touch upon the topic of unsuccessful local anesthesia. Almost every dentist has encountered this in their practice. The reasons for this phenomenon can be classified into 2 groups:
- depending on the doctor (poor choice of anesthesia technique and anesthetic solution; errors in the technique);
- depending on the anatomical and psychological characteristics of the patient.
To eliminate psychological causes in patients with a labile psyche (with increased emotionality, sensitivity, excitability), premedication is used: sedatives and sedatives.
In all other cases, the doctor must approach the choice of anesthetic and local anesthesia technique with even greater responsibility and professionalism, starting from the very first minutes of communication with the patient (history collection).
You should always remember that there are NO teeth that cannot be anesthetized, it’s just sometimes more difficult to achieve this.
High-quality pain relief minimizes patient discomfort and allows dentists to perform the necessary interventions.
Natalya Lvovna Mayorova doctor - therapist - dentist October 2009
Dear Colleagues! When copying information, placing a link to the source site is mandatory.
What is the difference?
Both drugs are local anesthetics. The purpose of their use is to block the transmission of pain impulses along the nerve fiber into the central nervous system. The anesthetic is injected directly into a large collection of nerves in the area where pain relief is needed. The sensitivity of several nerve fibers is turned off, and no pain signal is sent to the central nervous system. Ultracaine and Lidocaine do their job perfectly. However, there is a difference between Lidocaine and Ultracaine, which is determined by the composition of the drugs and the characteristics of the active substances.
Ultracaine is a combination drug. It contains:
- Articaine
- has a local anesthetic effect; - Epinephrine
is added to increase the duration of anesthesia. The substance constricts blood vessels, and the anesthetic dissolves more slowly. Pain relief time lasts from 45 minutes to 2 hours.
Lidocaine is a one-component drug. Active ingredient: lidocaine hydrochloride
, both an antiarrhythmic and anesthetic agent.
Due to the presence of an additional ester group in the articaine molecule, Ultracaine has less systemic toxicity. This allows repeated injections of the drug without serious risk of causing side effects. The analgesic effect for both occurs quickly: after 1-5 minutes.
The international name of Ultracaine is Articaine. It was synthesized in 1969. Available as an injection solution in ampoules. The drug is produced by the French company Sanofi-Aventis in Germany. In the Russian Federation, “Ultracaine D-S” (contains articaine and epinephrine) and “Ultracaine D” (only articaine) are sold. The form of the drug with the letter “D” is needed when adding epinephrine to a local anesthetic is not necessary or the use of vasoconstrictors is undesirable. Pain relief occurs quickly, but the effect lasts only 20 minutes. Ultracaine D-S Forte differs from the usual one in double the amount of epinephrine - 12 mcg/1 ml, instead of 6 mcg in Ultracaine D-S.
Lidocaine was synthesized by a Swedish chemist in 1943 under the name Xylocaine. It is included in the WHO list of essential medicines as one of the most effective and safe (if the patient is not allergic) drugs for local anesthesia. In Russia it is produced by a number of pharmaceutical companies: Biosynthesis, Organika, Pharmsintez, Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, etc.
Available in the following forms:
- ampoules with injection solution 2%, alone or in combination with epinephrine;
- spray for local and external use 10% with or without an antiseptic (for example, Lidocaine-Asept with chlorhexidine);
- eye drops, used for local anesthesia in ophthalmology.
When the product is administered under the skin and mucous membranes, the analgesic effect lasts about an hour. The effect of the spray occurs after 5 and lasts 10-25 minutes.
Bottle of 10% spray with lidocaine for 650 doses (Hungary)
Reviews from doctors
Grigory, 33 years old, dentist, Nizhny Novgorod: “Over several years of medical practice, I have become convinced of the effectiveness of Ultracain, if all the individual characteristics of the patient and the problem that brought him to the dental office are taken into account. There were a couple of cases with side effects, but everything ended well.”
Tatyana A., 43 years old, neurologist, Minusinsk: “I use lidocaine at the request of patients, and when I doubt the choice of remedy, although such problems are rare.”
What are the similarities and differences between these anesthetics?
Let's sum up the intermediate results. Despite the fact that lidocaine is a common anesthetic, and ultracaine is an adrenaline one, these two drugs have much in common. At least that most often both of them are used in dentistry. But for standard procedures (treatment, removal of a simple tooth) lidocaine is used. If the operation involves severe pain, or the intervention requires more time, take ultracaine.
Also, these two anesthetics have the following in common:
- excellent analgesic effect;
- scope of application (local and infiltration anesthesia);
- possibility of developing side effects.
The difference between lidocaine and ultracaine is, first of all, in composition. The presence of adrenaline in one of them makes the two drugs different in terms of effectiveness. There are also differences in the mechanism of drug distribution at the cellular level, but this concerns only cytologists. It is enough for the dentist performing anesthesia to know the principle of action of lidocaine and ultracaine. And the patient needs even less - to be sure that the anesthesia is good and that during medical procedures he will not be in pain.
Characteristics of lidocaine
This anesthetic is familiar to most patients. Perhaps novocaine is more popular than it. Lidocaine was synthesized in 1943 and became one of the few painkillers that also have an antiarrhythmic effect. That is, it is also used as a cardiac depressant. This means that the anesthetic suppresses the activity of the central nervous system (its effect is similar to that of alcohol), so in large doses it can work as a sleeping pill.
By the way! Some people feel drowsy after undergoing major dental surgery with lidocaine (for example, wisdom tooth removal). This is precisely due to the fact that for one hundred percent pain relief, the doctor plays it safe and administers a large dose of “freezing”.
What does it look like
In its natural form, lidocaine is a gray-white powder that easily dissolves in water to form a hydrochloric acid solution. It is in liquid form that it is mainly used.
There are also other dosage forms of lidocaine:
- solution for infusion (for conduction or epidural anesthesia)
- patches that are glued to damaged areas of the skin for quick local anesthesia;
- skin spray (for bruises);
- spray for mucous membranes (on open wounds, on gums, on the throat during the FGDS procedure).
How it works
When applied, it blocks the generation of impulses at the endings of sensory nerves. Due to this, a person does not feel pain at the site of application. Lidocaine quickly evaporates from the surface of the skin, so the effect is short-lived. And when administered under the skin, the drug dissolves over a long period of time, so the feeling of pain relief lasts for 70 minutes or more.
The anesthetic effect of lidocaine occurs quickly enough, but not immediately. The doctor first injects the operating area with an anesthetic, then waits 2-3 minutes, asks the patient if he feels anything, and only then begins the manipulations.
Contraindications and side effects
Lidocaine has very few of them, which allows it to be used everywhere and often. This anesthetic is not used for atrioventricular block, low blood volume (for example, after severe blood loss), or allergies. Ignoring contraindications to lidocaine or non-compliance with dosages leads to side effects:
- anaphylactic shock;
- increased excitability;
- leg paralysis;
- decreased visual and hearing acuity;
- dyspnea;
- local swelling;
- arrhythmia.
All this happens extremely rarely, because atrioventricular block is a rare pathology. And allergies to lidocaine are also not common.
Scope of application
The usual use of Ultracain is in dentistry for depulping teeth, removing them and other manipulations. The anesthetic penetrates well into bone structures and anesthetizes inflamed tissue. Due to this, Ultracain D-S is preferred when performing operations on ENT organs (removing tonsils, correcting a deviated nasal septum, etc.).
Lidocaine is used much more widely. In addition to pain relief, it is an antiarrhythmic drug that is used in cardiology. In addition, the drug is administered intravenously to relieve acute surgical and chronic pain; used in general anesthesia in combination with propofol. Lidocaine is convenient for superficial anesthesia during gastroscopy and other endoscopic examination methods. And, of course, it is still used as a local anesthetic in otolaryngology and dentistry.