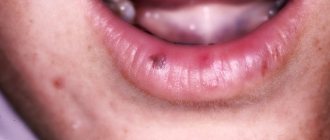
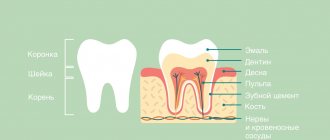
A purulent formation on the gum is popularly called gumboil. Very often it is not taken seriously, but it is not just a small swelling that will go away on its own. Flux is an ontogenic periostitis, a complex infectious disease that affects the periosteum and jaw bone. Periostitis occurs quite often, but without adequate treatment it is fraught with serious complications, including blood poisoning.
It is almost impossible to cure gumboil without the help of a dentist. The treatment program includes therapeutic, physiotherapeutic, and surgical methods.
Have you noticed purulent formations on your gums and swelling of your cheeks? Do you have acute pain in your tooth or gum? Come for a consultation with a dentist at our clinic. Timely treatment of flux allows you to get rid of the problem within about 7 days.
Why does flux form?
Dental diseases are always the precursor to gumboil. Most often lead to suppuration:
- Untreated caries. If caries is not treated, the inflammatory process begins to spread to other tissues. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Mechanical injury. Injury can lead to more than just crown destruction. Very often, an inflammatory process develops in injured tooth or gum tissues. Without treatment, purulent processes develop and gumboil forms.
- Periodontitis. In more than half of the cases, gumboil develops precisely against the background of periodontitis, as its complication. This is due to the fact that purulent processes from periodontal pockets can spread to the neck of the tooth.
- Poorly sealed canals. Before filling, the canals must be completely cleaned and the filling material must completely fill the cavity. If at least one of the conditions is violated, the infection from the canal spreads to other tissues.
Causes
Inflammatory (infectious-inflammatory) diseases of the maxillofacial area are caused by microbial microorganisms, which are usually part of the normal microflora of the oral cavity. Microbial pathogens are staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, diplococci, gram-positive and gram-negative bacilli (intestinal, protea, etc.). In addition, during flux, fungi, mycoplasmas, treponema, and protozoa from the Trichomonas family are found in foci of odontogenic infection. According to various authors who analyzed the microbial flora in foci of odontogenic infection (flux), the microflora is represented by a monoculture of staphylococcus (aurus and epidermal) or streptococcus of groups D, F and G. Associations of the above microorganisms are often identified.
The question arises of how non-pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms trigger the initiation of an infectious-inflammatory process (flux). For the occurrence of a disease, the presence of only non-pathogenic or pathogenic microorganisms is not enough. The answer to this question is given by the so-called Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon. According to the infectious-allergic theory, its essence boils down to the following: under the influence of a foreign serum protein, which has antigenic properties, antibodies are produced, which leads to sensitization of the body. Sensitization of the body is the acquisition by the body of increased sensitivity to foreign substances (proteins) - allergens. Against this background, repeated introduction of the protein into the vascular bed causes the formation of antigen + antibody complexes, which are fixed on the membranes of blood vessels and turn into target cells. Then the cell membrane is damaged, enzymes are released, mediators (from the Latin mediator - mediator) of inflammation are released. This is accompanied by activation of the third platelet factor and can cause intravascular coagulation, which leads to impaired microcirculation and necrosis (death) of tissue. This immunopathological reaction is also involved in odontogenic infection, leading to the occurrence of gumboil. The waste products of microbes participate in the role of antigen. This explains why in many patients non-pathogenic microorganisms are found at the site of inflammation.
The dynamic balance between the focus of chronic odontogenic infection and the body is ensured by the connective tissue capsule surrounding the focus. It limits the penetration of microbes into the tissues and vascular bed adjacent to the lesion, and limits the effect of immune factors on the infectious focus. The balance is also maintained by the fact that part of the waste products of microorganisms and tissue decay through the root canal of the tooth, fistula or periodontal fissure is released from the infectious focus into the oral cavity.
An imbalance can be caused by a disruption in the outflow of exudate from the lesion through the root canal due to food masses entering the carious cavity or when filling a carious cavity by a dentist. In the infectious focus, the concentration of microbes, their toxins, and waste products, which penetrate through the connective tissue capsule into the surrounding tissues, increases. Here their direct damaging effect on tissue can occur, and upon penetration into the vascular bed, the mechanism of the Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon is triggered. Clinically, this is manifested by an exacerbation of a chronic focus of odontogenic infection and the occurrence of gumboil.
Another mechanism of imbalance between the focus of chronic infection and the human body is associated with damage to the connective tissue capsule itself. This can happen when a tooth is removed, when there is increased load on the tooth while chewing hard food, etc. Damage to the capsule leads to the spread of microorganisms (their toxins, waste products) beyond the infectious focus, which in a sensitized organism leads to the occurrence of the Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon. These are the reasons and the main mechanism of exacerbation of odontogenic infection, leading to the development of gumboil.
When do you need dental help?
Flux has pronounced symptoms. The main one is the appearance of an abscess on the gum next to the diseased tooth. The abscess develops gradually. At first, the gums swell a little and a small red or whitish bump is noticeable on it. After some time, a noticeable fistulous tract forms on the lump, from which pus flows. The development of periostitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Swelling and swelling of the gums, lips, cheeks. Sometimes they can be so large that facial features are distorted.
- Severe cutting pain in the tooth area. Innervates the temporal region, orbits.
- The diseased tooth begins to become very loose, even if there was no mobility before or it was insignificant.
Since flux is caused by infection, it is characterized by symptoms that appear during any infectious process. The patient feels unwell, his temperature rises, his head hurts, and weakness appears. Lymph nodes on the head and neck become enlarged.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. The more advanced the case, the higher the risk of complications. This disease is often accompanied by other pathological processes. For example, a cyst may form in tissues affected by infection.
Alcohol after tooth extraction
Drinking alcohol-containing drinks after tooth extraction is strictly prohibited. A strict ban on alcohol in any quantity is valid for at least 3 days after surgery. If antibacterial therapy was prescribed, then for the entire period of treatment and healing. There are very important reasons for such a strict measure:
- alcohol first constricts and then dilates blood vessels, which leads to a surge in pressure and bleeding;
- strong drinks catastrophically reduce the body’s immune defense, which is very necessary to prevent complications after surgery;
- alcohol relaxes and relieves pain, so a person may not notice postoperative problems and trigger pathology;
- any medications (analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antihistamines), often prescribed after tooth extraction, are not compatible with alcohol.
The ban applies to all alcoholic drinks - vodka, beer, wine, champagne, cider. Vodka can immediately cause severe bleeding, and in combination with a pharmaceutical drug - anaphylactic shock. Beer contains yeast, which gets into the wound hole and ferments, causing inflammation. Wine greatly reduces the body's defenses against external influences, which leads to wound infection and prolonged healing. Champagne and cider, among other things, are saturated with oxygen, the bubbles of which loosen injured tissue. Any other alcohol acts similarly and certainly does not contribute to recovery.
It is important to understand that even a small amount of alcohol can cause an unexpected reaction and serious complications after tooth extraction. Therefore, you should not take risks, but rather take care of yourself.
Flux treatment methods
Treatment should be started as early as possible. If an abscess on the gum opens spontaneously, there is a risk of infection entering the bloodstream. With such an infection, blood poisoning develops, and such a complication can lead to serious consequences, including the death of the patient.
Flux treatment is always complex. The treatment program depends on the degree of tooth decay and the spread of infection.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Why is flux dangerous and how to recognize its complications?
For many, visiting the dentist turns out to be torture. Some people, even with the most severe pain, do not dare to go to specialists. This is how deep inflammatory processes develop. A frequent manifestation of long-term inflammation is flux - periostitis. There are patients who believe that it can be successfully treated independently using traditional medicine, without even knowing how dangerous flux is. To assess the degree of danger of the disease, we will consider in more detail the clinical manifestations and complications of flux.
Opening an abscess on the gum
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
Preventive actions
To reduce the likelihood of periostitis, you need to take care of your teeth and visit the dentist at least once a year. You can't start caries. As soon as a dark spot appears on the surface of the dental crown, it needs to be treated.
After eating, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with warm water. To make hygiene as high as possible, it makes sense to use not only a brush and toothpaste, but also dental floss and irrigators. It is very important to remove tartar every year at the dentist's office.
An important place in the issue of prevention is given to diet. You should eat as much fresh fruits, vegetables, and plant foods as possible. They require more thorough chewing and thus have a positive effect on the ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth. They also provide natural cleansing of crowns from soft plaque.
If you have any questions about how to remove flux, please contact the doctors at the Line of Smile dental clinic for help. We specialize in the treatment of this disease and know how to quickly rid our patients of it.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
What is allowed to drink
The drinking regime after tooth extraction should also be gentle. The reasons for this are similar to dietary restrictions. The liquid washes out the hole, making room for bacteria and inflammation, and also brings additional pain while drinking. But water is very important for recuperation, so within a couple of hours after leaving the dentist you can take a few sips of cool water.
In the first days after surgery, you are allowed to drink warm (not hot!) tea, coffee, non-sour compote, juice, and plain water. It is recommended to abstain from carbonated drinks and concentrated juices and fruit drinks for several days. You need to drink in small sips directly from the glass. Some do this through a straw to prevent fluid from getting into the wound. But this is wrong, because during retraction, additional jaw movements are made, which can open the wound and cause pain.
You should also not rinse your mouth while drinking, especially on the first day after tooth extraction. This can be done with special herbal antiseptic solutions, carefully and carefully. But recommendations regarding rinsing should be given by a doctor; in some cases they are strictly contraindicated.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
Seeing a doctor as soon as possible is the key to saving your tooth.
Naturally, experts under no circumstances recommend treating flux at home. Delay is dangerous for the tooth, in the periosteum of which an inflammatory process has developed. The longer you wait, the more likely it is that the tooth will have to be removed later.
You should definitely contact your dentist
However, many people ignore the warnings of experts. Some people are in no hurry to go to the clinic because they hope to get rid of the disease themselves. A business trip or vacation prevents someone from promptly seeking professional help. In these cases, doctors urge you to pay attention to a number of very important points, knowing about which you will not make things worse for yourself.
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
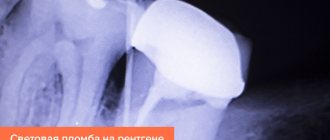
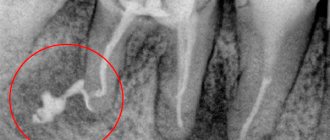
Diagnostics
To diagnose flux, methods such as questioning, examination, and additional research methods are used: radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, blood test data, culture of exudate, etc. An experienced maxillofacial surgeon who treats patients with flux, can, based on the patient’s complaints and examination, carry out an accurate topical diagnosis of the disease (localization of pus) and select the optimal surgical approach to ensure sanitation of the purulent focus and adequate drainage.