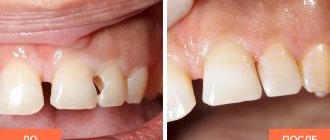
- Why a temporary filling is placed: types of material
- Why does a tooth with a temporary filling hurt: the main reasons
- Standard activities after installation of the material
- Temporary filling hurts when pressed: how to cope with the disease
Many patients complain to dentists that their tooth hurts under a temporary filling. For the first 2-3 days, a slight aching pain is considered normal and does not cause cause for concern or panic. It is associated with the active influence of drugs on the nerve endings of the molar or premolar.
If the temporary filling hurts very strongly and for a long time when pressed, it is recommended to make an appointment with a specialist earlier than the specified date. Dentists at the reliable A-Medic clinic will conduct a thorough examination and prescribe a diagnostic examination to find out what exactly is causing the pain. All people are scared that they have had a temporary filling installed and their tooth hurts, but most often there is no reason to worry.
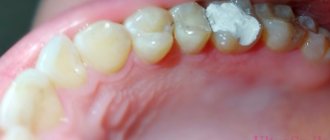
Why a temporary filling is placed: types of material
Non-permanent filling is a mandatory measure in the treatment of complicated carious lesions and root canal inflammation. It is required for medicinal treatment of an inflamed molar or premolar. It is entrusted with the protective function of the treated cavity from food ingress. Also, it prevents the medical pad from falling out.
The composition of such material differs significantly from a permanent filling. It can be made from water-insoluble or plastic components. The choice of the most suitable material directly depends on the condition of the molar or premolar and the purpose of the installation. Among the most common materials are:
- sympath. It can be of different shades - white (for filling non-pulp teeth) or light pink. The mass does not provoke irritation and other allergic reactions;
- dentin paste. It reliably protects the tooth from staining with amalgams and is characterized by water-repellent properties. The paste hardens in 100-120 minutes;
- zinc polyacrylate cement. It is characterized by good biocompatibility with tissues and high strength. The material is used for fixing prostheses (crowns) or filling (both permanent and baby teeth);
- Vinoxol. It is characterized by reliability and durability, capable of maintaining integrity for up to 4-5 months. The drug has antiseptic properties, which allows you to disinfect the tooth cavity. It hardens in 3-4 hours.
There are situations when the carious lesion did not have time to reach the nerve. In such cases, the molar or premolar is not depulped, but temporary material is installed. This is necessary for diagnosis to see whether the tooth will become sensitive or not. With the help of these measures, it is possible to completely preserve a molar or premolar (without removing the nerve) if the patient does not experience pain. If a pronounced reaction occurs (if the temporary filling hurts), the dentist will remove the nerve after placing a filling with arsenic.
Often, non-permanent filling is resorted to during prosthetics. This allows you to protect the molar or premolar from pathogenic microorganisms. The wearing period is individual and directly depends on the type of material and the reason why filling was required. It is installed by the attending dentist. On average, after 7-10, specialists replace it with a permanent filling. Sometimes, after applying a temporary filling, a tooth hurts; let’s figure out what could cause this phenomenon.
Methods used to treat pulpitis
Treatment of pulpitis most often involves a depulpation procedure, in which the doctor completely removes the dental nerve. Then the specialist must expand the root canals of the tooth with a special device and carry out antiseptic treatment with subsequent filling. This technology for the treatment of pulpitis is used in relation to adult patients: in children and adolescents, young people under 25 years of age, it is sometimes possible to treat the disease without the use of a pulp removal procedure.
Ideally, it is advisable to treat pulpitis without removing the nerve, since pulpless teeth become less durable and their enamel coating may turn gray. But in order to avoid tooth depulpation, you need to consult a dentist at the first suspicion of pulpitis, and not wait until the pain becomes unbearable and cannot be relieved with drugs from your home medicine cabinet. Next, we will consider in detail all the stages of traditional treatment of dental pulpitis.
Why does a tooth with a temporary filling hurt: the main reasons
Often, patients with a temporary filling have a toothache when pressed. In some cases, such a reaction is considered normal. The attending physician will be able to answer for sure why a tooth hurts after a temporary filling after examining the oral cavity and conducting a diagnostic examination. Let's take a closer look at the main reasons for the appearance of pronounced discomfort sensations:
- Impact of the drug. If a tooth hurts with a temporary filling and medication, then most often the source of discomfort is its effect on the tissue. You should contact a specialist if the pain is pronounced and reduces the quality of life.
- Unfinished therapy. Often, after the pain has subsided, a person decides to stop therapy and does not come to an appointment to replace it with a permanent material. Temporary material is not intended to be worn for several years, so sooner or later it will fall out. It is recommended to replace at the appointed time.
- Allergic reaction to cementitious agent. If a tooth with a temporary filling aches and hurts a lot, the reason may lie in an allergic reaction. In such a situation, it would be more advisable to replace it with another cementing agent (depending on the period of wear).
- Lack of material. There is a high probability that it fell out while drinking or eating food, so external factors (irritants) come into direct contact with the soft tissues. An infection could have entered the tooth cavity, causing an inflammatory reaction.
- Prolonged wearing of the cementing agent (longer than the prescribed period). The material is quite fragile; when worn for a long time, it begins to lose its tightness, allowing pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria) to enter the cavity of the molar or premolar.
The biggest cause for concern is discomfort after installation of permanent material. This is an alarming signal that may indicate incorrect installation, untreated pathology, or emerging complications. In this situation, you need to make an appointment with a specialist to determine the main source of pain.
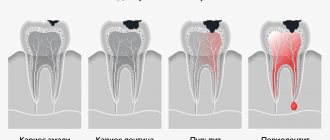
Acute pulpitis
This phase of the development of the disease will be characterized by sharp and unbearable pain, which manifests itself in attacks. Most often, pain in acute pulpitis bothers patients at night, starting with minor pain and gradually turning into painful sensations. If treatment for pulpitis is not started, attacks will gradually become more frequent, and the pain will become more severe.
In acute pulpitis, pain in the tooth usually manifests itself without exposure to external irritants, but sometimes painful manifestations can occur after eating something cold or hot.
Pain provoked by an external irritant may subside after it is eliminated, but it will take a long time to subside for about 20-30 minutes. This characteristic feature makes it possible to distinguish tooth pulpitis from other dental diseases. In case of carious lesions of tooth tissue, pain symptoms disappear immediately after the external factor that provoked discomfort in the area of the diseased unit is eliminated.
Sometimes, with acute pulpitis, even the patient himself cannot accurately determine which specific dental unit is hurting, since painful manifestations from the pulp can be transmitted along the nervous tissue to healthy “neighbors”. At the slightest suspicion of acute pulpitis, treatment should begin in the dentist’s office, since the process can become purulent.
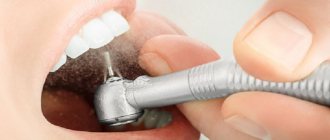
Standard activities after installation of the material
Do not drink or eat until the material has completely hardened, as it may crack or fall out completely. Also, food can get into the cavity of a molar or premolar. After a non-permanent filling, it is not recommended to eat soft food for the first 2-3 hours, and hard food for 10-12 hours. This will avoid a number of negative consequences. When chewing solid food in the future, you should use less of the side on which the filling was performed.
While wearing the material, hygiene rules must not be neglected. You should brush your teeth twice a day, and after eating, rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions and floss. If the temporary material is installed for several months, it is recommended to use a brush with softer bristles during this period. To avoid possible complications, the material is removed on a strictly designated day.
Stages of treatment of pulpitis of a multi-rooted tooth
Treatment of pulpitis begins with an initial visit to the dentist, during which the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient and makes a diagnosis (most often after an x-ray). Further therapy for pulp inflammation is divided into the following main stages:
Temporary filling hurts when pressed: how to cope with the disease?
People often ask the question: “if you have a temporary filling installed and your tooth hurts, what should you do?” When a tooth hurts under a temporary filling, this is a normal condition, do not panic. If the dentist said that there is no cause for concern, you should be patient and wait out the unpleasant symptom. When a temporary filling causes severe pain in a tooth, and you run out of strength to endure the pain, you can use the following recommendations:
- rinse your mouth with antiseptic and soothing solutions. You can prepare them yourself at home from natural ingredients. For example, chamomile and sage are poured with boiling water and the resulting product is used to rinse the mouth;
- do not allow food and drinks (mainly hot or cold) to come into contact with the treated tooth;
- take a painkiller (analgesic). “Nise” and “Ketorol” give good results;
- make lotions with valerian tincture. A moistened cotton swab of valerian is applied to the painful area, the gum near the tooth. This will temporarily relieve the irritation.
If a tooth hurts after installing a temporary filling and swelling or redness of the soft tissue appears, this may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process or the appearance of pus. In such a situation, you should re-make an appointment with a dentist-therapist. The A-Medic clinic employs qualified specialists with extensive experience. To make an appointment, just fill out the standard form on the official website of the clinic (indicating your full name and contact number). Prices are affordable, and consultation with a dentist is completely free.
Introduction of an anesthetic drug
It is impossible to do without anesthesia when treating pulpitis. When the pulp is damaged, the nervous tissue becomes inflamed and therefore any therapeutic manipulations will be unbearably painful for the patient. Therefore, before starting treatment of pulpitis, the doctor will administer an anesthetic, the action of which will remove the pain for the time necessary for carrying out therapeutic actions.
Sometimes, even after the administration of pain medication, the patient may feel pain. This suggests that either the amount of the drug was calculated incorrectly, or that the doctor made a mistake when giving the injection. Do you want to cure pulpitis painlessly and efficiently? Contact the specialists of the Vanstom dental clinic in Moscow! Our dentistry works for you at the address: Moscow, Baumanskaya metro station, st. Bakuninskaya, 17/28.
Elimination of tissue damaged by caries
Most often, tooth pulpitis is a consequence of advanced deep caries, and therefore, when treating inflammation in the pulp, a mandatory procedure is the elimination of the enamel layer and dentin with carious lesions. Damaged tissue is removed with a special tool using a drill.
However, when treating pulpitis, intact tissue will be partially removed; this is necessary to gain access to the pulp chamber and canal stomata that need to be treated.
The final stage of pulpitis treatment
The final stage of pulpitis treatment is the installation of a permanent photopolymer filling. This procedure is painless and takes a short time, but it can only be performed after the composites placed in the dental canals have dried and completely hardened. For this reason, installation of a permanent filling and filling of canals for pulpitis are never carried out in one visit to the doctor.
Having completed the installation of a permanent filling, the specialist explains in detail to the patient what oral care should be like after treatment of pulpitis, and also gives advice on the possible consequences. After depulpation, teeth become more fragile, and the shade of the enamel may also change. Such changes are explained by the fact that not only the pulp is removed from the tooth, but also the blood vessels; in fact, the tooth becomes “dead”. Its tissues do not receive nutrients and moisture and therefore the enamel coating becomes dull and loses its natural shine. However, it should not turn blue. A bluish tint to the enamel is a sign of poor-quality treatment of pulpitis, in which the canals were filled with blood residues inside.
Pulp extraction
Before removing pulp from the coronal area of the tooth, as well as from the dental canals, the manipulation area must be carefully isolated from moisture. This is done so that pathogenic microflora does not enter the canals along with saliva. For high-quality tooth isolation, a specialized latex rubber dam is used.
The process of pulp extraction itself is carried out with a special tool, on which the pulp is wound and then pulled out. Next, the doctor proceeds to a particularly important point in the treatment of pulpitis - measuring the length of the tooth canals. Measurements must be carried out with maximum accuracy, since errors in them are fraught with the following negative consequences:
• The canals will be unfilled, which can provoke various complications after treatment of pulpitis; • The canals will be refilled and excess material in them will cause pain and can even lead to trauma to the nervous tissue of the lower jaw.
To obtain accurate data on the length of the root canals, the patient is prescribed an X-ray examination, and the specialist also uses a special type of device, an apex locator. This device is equipped with K-files that are inserted into the canal stoma, and the specialist will advance them in depth until the apex locator monitor receives an alert that the instrument has reached the top of the tooth root.
An apex locator measures the length of each root, since they are unique both in this indicator and in structure. The data obtained during the measurements are recorded, but the procedure does not end there: at the next stage, the doctor enters K-files into all canals at once and takes a control image necessary to obtain the most accurate picture of the depth of the roots.