31.10.2019
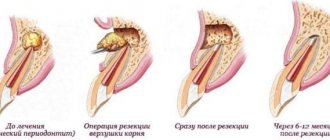
Many people are familiar with the procedure for removing the dental nerve (depulpation), which is used in case of inflammation in the pulp, acute pain and other indications. If you do not perform this manipulation, you can lose the entire tooth. But you need to understand that to save a tooth, removing the nerve alone is not enough. You need to carefully monitor your oral hygiene, prevent chips and cracks, and visit your dentist regularly. Read on for more details about the features of pulpless teeth. Let's consider how long a tooth lives without a nerve, and how to extend its “life” so that the tooth can last as long as possible without a removed nerve.
Indications for dental nerve removal
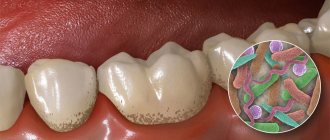
The pulp is a bundle of small vessels and nerve endings. Among patients, it is better known as the dental nerve. It is thanks to him that the tooth remains alive and is able to respond to external irritating factors.
When a nerve in a tooth becomes inflamed and cannot be treated, the doctor prescribes depulpation to preserve the organ. This procedure has the following indications:
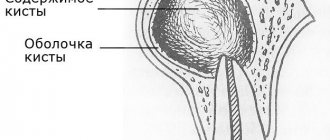
- With the development of a cyst;
- Improper treatment of pulpitis, caries and other diseases;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth, which exposed the nerve;
- Increased sensitivity that occurs after dental prosthetics. Read more information about why the tooth under the crown hurts in this material;
- Dental prosthetics for the treatment of deep caries and other pathologies;
- Damage to the pulp by potent antiseptics and toxic substances.
The first symptom of inflammation of the dental nerve is its reaction to cold and hot food.
Why is a tooth without pulp considered dead?
The main thing that changes in the condition of the tooth after depulpation is that the trophism (nutrition) of the hard tissues is lost, the tooth becomes very fragile and reacts sharply to external factors.
The absence of nerve endings affects the protective function of the tooth: in the absence of a pain reaction, a person can damage the tooth by biting something hard on it and not notice it. The pulp ceases to protect the tooth from microbes, as a result of which it becomes more susceptible to caries.
As you can see, a pulpless tooth requires additional care, as it is more vulnerable than healthy ones.
Procedure technology
The depulpation procedure can be carried out in three ways:
- vital extirpation – removal of the pulp occurs completely and is carried out under local anesthesia. The procedure involves removing the nerve in just one session, but requires careful examination;
- Devital amputation is the use of a special drug to mummify part of the nerve. It involves applying a special paste that leads to pulp necrosis. This technique is used extremely rarely, since it can cause a number of complications associated with necrotic processes in the nerves. Can only be found in low-budget dental offices;
- diathermy - necrosis of the nerve occurs by applying a current discharge, after which the dead nerve is removed. An electrode is inserted into the pulp area, passing a current through itself, which not only kills the nerve, but also cauterizes the wound.
After the depulpation procedure, you may experience pain for several days that occurs when you squeeze your jaw or eat hot or cold food (drinks). This pain does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
What is the procedure for devital tooth depulpation?
After the dentist is sure that the anesthesia has worked, the procedure itself is carried out:
- the specialist opens access to the pulp cavity using a drill;
- a special substance is placed into the cavity, which will lead to the death of the nerve;
- the cavity with the medicine is closed with a temporary filling;
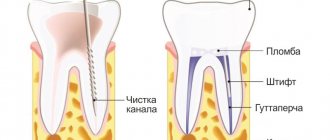
- when you return to the dentist’s office, the pulp is removed along with the neurovascular bundle, the doctor cleans the tooth cavity of dead tissue, and performs instrumental and medicinal treatment of the canals;
- after the doctor is convinced that the source of inflammation has been completely eliminated, the canals are sealed;
- The dental crown is restored using filling composite materials.
Interestingly, dentists used to often immediately close a pulpless tooth with a permanent filling, that is, they performed a vital pulpotomy. Today the practice has changed. In almost all cases, a temporary filling is first installed, allowing the specialist to assess the effectiveness of treatment and the stage of healing.
After depulpation, a tooth reaction to hot food may be observed as a result of mechanical intervention. Unpleasant sensations may persist for up to two weeks. To alleviate the patient’s condition, a specialist may prescribe special medications for this period to relieve pain.
Important: if after two weeks the painful symptoms have not disappeared, a repeat x-ray is taken, since prolonged symptoms may be an indicator of a relapse.
Possible complications
Complications can arise for several reasons: low qualifications of the dentist, his careless attitude to work, inattention, outdated equipment and much more.
Complications after depulpation occur if:
- the filling material has protruded beyond the upper part of the root;
- the filling came out;
- there was bleeding in the dental canal;
- the nerve is not completely removed;
- poor-quality filling with the formation of voids;
- a piece of instrument or other foreign object is stuck in the canal.
Some time after filling, the tooth may change color. If endomethasone was used in its treatment, the crown will begin to acquire a yellowish tint, and if resocin-formalin is used, it will turn light pink. The latter version of the filling material is used extremely rarely and the reason for this is its toxicity.
If complications still arise after removing the nerve, it is better to contact a more experienced specialist.
Problems arising after depulpation
The first problem that patients encounter after removing the nerve from the problematic element is blackening of the enamel, which is a serious aesthetic defect. The reasons for crown darkening include the following factors:
- improperly performed dental work;
- insufficient intake of microelements;
- the use of dental instruments containing silver or resorcinol - formaldehyde during the intervention;
- damage to the blood vessels of the element and further disruption of blood supply.
A tooth that has turned black after depulpation.
Another problem after the intervention, which is often noted by patients in dental clinics, is pain in a tooth without a nerve. Discomfort may occur when pressing on the unit, tapping on it, or biting into food. The opinion that a “dead” tooth cannot hurt is considered erroneous. The cause of discomfort may be previous illiterate treatment, inflammation of periodontal tissue, etc. In such cases, the patient should immediately consult a doctor in order to identify the cause of the problem.
In a normal state, the “dead” element continues for another 7–10 days after depulpation. Sometimes the cause of discomfort is not the unit that has lost its nerve endings, but the healthy neighboring one. It will seem to a person that the cause of the problem is a previously treated tooth, since toothache is sometimes vague and difficult to determine its exact location. Sometimes pain is associated with damage to the gums during depulpation of elements that react to cold or hot food.
Pain immediately after dental procedures is normal. The main thing is that the intensity of the discomfort gradually decreases. Discomfort disappears, as a rule, 3 weeks after removal of the nerve endings from the tooth. An increase in pain symptoms is a sure sign of the development of infectious complications. In this case, the patient should contact a highly qualified dentist as soon as possible.
Why was the nerve removed, but the tooth hurts when pressed?
Why else can a filled tooth hurt? Some reasons for the problem include:
- Incomplete removal of nerve endings, and, as a result, preservation of their sensitivity;
- Poor quality canal filling. If the filling material is not placed tightly, pores remain in the tooth canals, in which pathogenic flora multiply over time. Bacteria destroy the tooth and the soft tissue located next to it. Which leads to pain.
- Doctor damage to the root. As a result of the error, inflammation often develops in the tissues located next to the element.
- Poor quality treatment of the tooth and its canals with antiseptic agents.
- Allergic reaction to components of composite materials.
- A cheap composite that will deteriorate over time.
- Foreign body in the tooth cavity. As a result of dental procedures, fragments or microscopic parts of instruments may remain in the dental tissues. Over time, this leads to severe pain in the jaw and the development of serious complications.
And also the “dead” unit is characterized by increased fragility. Cracks invisible to the naked eye may form on its surface. Because of them, a person feels discomfort while chewing food.
Features of a tooth without a nerve: how long will it last with strengthening from the dentist
With the removal of the nerve, the supply of blood to the tooth stops, and with it the necessary minerals. As a result, the enamel becomes thinner and further destroyed. To prevent this process after the extraction procedure, tooth restoration is required. A qualified doctor can extend his life to ten years. But even if you use the highest quality materials, the enamel will lose its strength and may eventually chip or crack.
If the chip is deep and has affected the root, the chewing element can be restored by installing a crown or modern implantation. The most widely used crown is metal-ceramic. It is tightly installed on the root of the tooth, which prevents the entry of air, food and pathogens.
Restoration using a ceramic inlay is advisable if at least 30% of the tooth is present. Its service life exceeds a standard filling, which extends the life of the chewing element.
A competent approach to treating a tooth from which the nerve has been removed allows you to preserve its integrity for a sufficiently long time, so it is better to entrust this work to an experienced dentist. If a tooth without a nerve reacts to hot food, then this is a sign of poor-quality therapy.
Tooth restoration is also possible using a reflective filling, which can extend its service life up to 10 years. This period is largely influenced by the quality of the sealed canals. Mistakes made at this stage can lead to the development of flux, cysts, fistulas and other pathologies.
If a chewing element without a nerve begins to develop complications due to improper filling of the canals, then such a tooth must be removed. That is why any dental procedures, and especially pulp removal and canal filling, must be trusted only to high-quality specialists. You may be wondering how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction.
To prevent complications and destruction of a pulpless tooth, thorough cleaning is required at least twice a day, as well as regular visits to the dental clinic.
Pulp - structure, functions, features
The pulp is also called the dental nerve. This is a soft connective tissue that contains a collection of nerve fibers, lymphatic and blood vessels. It is located in the tooth cavity (pulp chamber of the crown part of the tooth and in the root canals). Along the edge of the pulp there are cells, the processes of which are immersed in the dentin of the tooth. Thus, the pulp is closely connected with the hard tissues of the tooth. Through these connections, the trophic function is carried out; the pulp “nourishes” the walls of the tooth. Pain and mechanical sensitivity are also provided by the processes of pulp cells.
The blood supply to each tooth is provided by the common arteries and veins of the maxillofacial area. Small capillaries extend from them and enter the pulp, feeding the tooth. This structure protects the tooth from inflammation, proliferation of pathogens and other pathological processes.
The rich blood supply to the tooth also causes pain during inflammation. When the pulp becomes infected, a massive rush of blood occurs to its capillaries to provide a protective reaction, and swelling occurs inside the tooth. Enlarged vessels and soft tissues compress the nerve endings of the pulp, causing pain.
How long can a tooth with a removed nerve “last”?
The service life of a pulpless tooth is influenced by a number of factors:
- Conditions of care provided to the oral cavity and teeth;
- Quality of nutrition and degree of hardness of products;
- Efficiency of treatment and tooth restoration;
- Regular visits to the dental clinic.
- High-quality prevention of dental caries.
You can extend the service life of a chewing element without a nerve using comprehensive measures:
- minimize drinks that have a high acid content (citrus juices, carbonated drinks, etc.);
- do not eat too hard foods that can cause tooth fracture;
- include in your daily diet foods rich in iron, phosphorus, calcium and other microelements necessary for dental health;
- take vitamin-mineral complexes in autumn and spring;
- Avoid using toothpastes with a whitening effect. It is recommended to replace them with pastes for sensitive teeth.
The comprehensive application of the recommendations will extend the life of a tooth from which the nerve has been removed. Otherwise, its destruction will begin after 1-2 years and procedures for its treatment and restoration will be powerless. As a rule, such chewing elements must be removed.
What is vital depulpation?
Vital pulpotomy is the amputation of an inflamed nerve under the influence of anesthetic substances. Treatment is carried out in one visit to the dentist. It consists of the following stages:
- anesthesia;
- removal of tooth enamel and dentin with a drill;
- antiseptic treatment of the mouth;
- removal of tissue (fibrous substance, neurovascular bundle) from the pulp cavity and canals;
- filling channels with a composite composition;
- closing the tooth cavity with restoration materials.
Subtleties of “dental life”
Most people visit the dental office only when absolutely necessary. But experts constantly remind that preventive examinations should be carried out twice a year. After the procedure associated with tooth depulpation, you need to visit the dentist at least once every six months. This way you can promptly identify any deviations, prevent the destructive process and save the tooth. You should also follow the instructions of your specialized doctor.
Basic Rules:
- exclusion from the diet of drinks with high acid levels;
- eating crushed, soft food;
- compliance with temperature conditions;
- proper oral hygiene.
A drink with a high concentration of acid will have a destructive effect on the mortified tooth. Even natural freshly squeezed juices can destroy tooth enamel. Since the supply of nutrients and minerals is not replenished, tooth tissue will decay much faster. And in some cases, it is no longer possible to restore such a tooth by filling or building up the walls. We have to resort to more radical methods of dentition restoration.
As for food, all solid foods should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to chop nuts and other delicacies. This way you can minimize pressure on the tooth and avoid mechanical damage. It is not recommended to drink too hot drinks or eat, on the contrary, chilled products. The temperature should be moderate. Avoid temperature changes.
Particular attention should be paid to oral hygiene. First of all, you will have to change your toothbrush. A brush with soft bristles or medium-hard bristles is ideal. Toothpaste should be enriched with fluoride. But you will have to abandon the whitening components.
Our diet plays an important role in dental health. A lack of calcium, fluoride, and vitamin D leads to a violation of the integrity of the teeth and their destruction from the inside. If such components are supplied in insufficient quantities with food, you can additionally take various multivitamin and mineral complexes.
Is removal inevitable?
Many of us think that we can restore a damaged tooth ad infinitum. But there are times when a dead tooth still has to be removed. There must be absolute indications for this. Since it is no longer possible to install a crown, all that remains is to do the implantation procedure.
Indications:
- destruction of most of the tooth;
- bleeding and violation of the integrity of the gums;
- tooth decay inside, deep in the socket;
- mobility of the dental crown.
Only after collecting a medical history and a complete examination can the dentist decide to remove the tooth. If there is a chance of saving it, the doctor will do just that. Unfortunately, like hair and nails, our teeth do not grow back. In order not to resort to radical methods of treating dental pathologies, it is necessary to carefully monitor the oral cavity and periodically visit the dentist.
An alternative restoration method is the use of ceramic inlays.
Inlays are most often made of ceramic. When no more than 70% of the tissue in a tooth is destroyed, an inlay is an excellent method of restoration, which can also serve for many, many years. In the example below, we see that the teeth on the left were restored with light-rejecting fillings, and the teeth on the right were restored with inlays. This photo was taken three years after restoration. The inlays were made by the chief physician of the Family Dental Clinic, S.V. Tsukor. The fillings were not made in our center.
You can see that the fillings have areas of darkening, peeling and other defects, but they retain their functionality and do not fall out. The tabs on the right are in perfect condition even after years of use.
Delete or restore?
In many cases, the decision to try to save or remove a problematic tooth is made by the patient himself. The desire of people to preserve a tooth at any cost is understandable and resonates with dentists, armed with the most modern and advanced methods of tooth preservation. However, some patients easily part with dental problems, explaining this action by lack of time for dental treatment or high prices for proper restorative dental treatment. I would like to remind such patients that if one tooth is removed and an implant is not installed in its place, this means inevitably provoking a gradual change in the entire dental system. Having saved money and time on the treatment of one tooth, you will have to face the need for implantation or prosthetics in the future, which require even greater costs. Family dentistry on Paveletskaya offers the patient to make the right choice, wanting to fight as hard as possible to preserve your teeth and at the same time having everything necessary for the successful restoration of problem teeth.