Hypersalivation in children is a process of increased salivation that occurs both at night and during the day. Babies from 3 to 6 months suffer from the pathology, and parents must be attentive and immediately identify the problem, since in children the disease is subject to adequate treatment.
If symptoms of hypersalivation occur in adults, this condition is already considered pathological. A synonym for the disease is ptyalism; its etiology may be associated not only with increased activity of the salivary glands, but also with swallowing dysfunction. For what reasons does pathology occur in children and adults, how to identify and treat it in time - will be discussed today.
Choking on saliva: What are the causes and how to prevent it
Although choking on saliva happens to everyone from time to time, repeatedly choking on saliva can indicate an underlying health problem or bad habit.
Here's what you need to know about choking on saliva, including causes and prevention. Choking on saliva can occur if the muscles involved in swallowing weaken or stop functioning properly due to other health problems. Swallowing and coughing when you have not drunk or have a symptom of choking on saliva. You may also experience the following:
Sometimes choking on saliva may not be a cause for concern. But if it happens frequently, identifying the causes may prevent future occurrences. Possible causes of choking on saliva include:
Acid reflux
Heartburn can also irritate the lining of the esophagus. This can make swallowing difficult and allow saliva to pool in the back of the mouth, causing choking.
Other symptoms of acid reflux include:
Sleep associated with abnormal swallowing
This is a condition in which saliva accumulates in the mouth during sleep and then enters the lungs, leading to aspiration and suffocation. You may wake up gasping for air and choking on your saliva.
Lesions or tumors in the throat
Benign or malignant lesions or tumors in the throat can narrow the esophagus and make it difficult to swallow saliva, causing choking.
Poorly fitting dentures
Saliva production may slow down as your body adjusts to the dentures. If not, consult a doctor. Your dentures may be too high for your mouth or may not fit properly into your bite.
Neurological disorders
Treatment depends on the neurological disorder. Your doctor may prescribe medication to reduce saliva production and teaching techniques to improve swallowing. Medicines to reduce saliva secretion include glycopyrrolate (Robinul) and scopolamine, also known as hyoscine.
alcohol abuse
Choking on saliva can also occur after using heavy alcohol. Alcohol is a sedative. Consuming too much alcohol can slow down muscle response. Being unconscious or incapacitated from drinking too much alcohol can cause saliva to pool in the back of the mouth rather than flow down the throat. Sleeping with your head elevated can improve saliva flow and prevent choking.
Talking excessively
Saliva production continues as you say. If you talk a lot and don't stop swallowing, saliva can move down your trachea into your respiratory system and cause choking. To prevent choking, speak slowly and swallow between phrases and sentences.
Allergies or breathing problems
Other symptoms of an allergy or respiratory issue include:
Hypersalivation during pregnancy
This problem may gradually improve. There is no cure, but drinking water can help flush excess saliva from the mouth.
Drug-induced drooling
Some medications may also cause increased saliva production. These include:
You may also experience drooling, difficulty swallowing, and the urge to spit.
Talk to your doctor if producing too much saliva is causing you to choke. Your doctor may switch medications, change the dosage, or prescribe medications to reduce saliva production.
Source
Can a baby choke on drool while sleeping: how to avoid the danger
Children under one year of age often experience increased activity of the salivary glands. This can be caused by various reasons: from teething to acute respiratory disease. The main thing is to correctly determine the cause of this condition. In most cases, this problem does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
Baby drooling is a common occurrence.
Causes of increased salivation at night
If a child chokes on saliva in his sleep, he should be moved from a position lying on his back to his side or stomach, then the mucus will not flow into the lungs, causing a cough. The problem is worse at night because:
This condition should not be considered a pathology; it is normal in children under one year of age.
The most common reason for the active formation of saliva is teething. Also, the volume of mucus secreted increases sharply when a child suffers from acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections. When the period of recovery begins, this condition passes. The baby begins to choke on saliva because mucus from the mouth constantly gets into the throat, and the baby does not have time to spit it out.
The most likely cause of the problem is active teething
Emergency help for choking on saliva
Parents often wonder whether a baby can choke on saliva and why this happens. This is really possible if the baby sleeps in a supine position. Also, a sleeping baby may choke when burping. To prevent this from happening, after feeding you should keep the baby in an upright position for about 15 minutes and only then put it in the crib.
What to do if the baby's temperature is 38 degrees
Emergency help may be needed if:
In these cases, parents must act correctly so as not to harm the baby.
If a baby chokes
If parents see that the child is choking on saliva, they need to give the baby an upright position as soon as possible.
A baby after six months who can sit can be placed on pillows to sleep in this position; Children up to two to three months are placed on their stomach.
If the baby cannot breathe, you need to take him by the legs, turn him head down and hold him in this position until he spits out mucus or a foreign body. This must be done quickly.
What not to do
When a child is choking and cannot clear his throat, parents should not be nervous, because anxiety always interferes with the correct action. Also, you should not slap the baby sharply on the back - this can push the mucus even further into the respiratory tract.
If the baby screams loudly, you should not interfere with this - with a scream, he can get rid of the abundance of saliva on his own. If there is increased salivation, the baby cannot be limited in liquid; on the contrary, he should drink as much as possible.
Acidic drinks (for example, cranberry juice) should be avoided - they provoke excessive saliva production.
Attention! You should not give your baby bagels or dryers instead of a teether. The baby may bite off a small piece and choke. All rattles with small parts inside that the baby takes into his mouth must be securely closed.
First aid must be provided quickly and correctly
When you need a doctor's help
Cough to the point of vomiting in a child - what to do if a baby is vomiting
If a child chokes on saliva in his sleep due to a runny nose, the snot flows down his throat and interferes with sleep. In this case, you should contact your pediatrician to prescribe antiviral drugs and vasoconstrictor nasal drops. You also need medical help if:
Typically, an infant begins a period of active drooling after six months, when the first milk teeth erupt. However, in some cases this time begins much earlier - at three to four months. In this case, it is necessary to bring your baby to the doctor, since premature appearance of teeth may indicate rickets and other diseases.
When the toddler turns one year old, the activity of the baby's salivary glands gradually slows down, but periodically resumes during the appearance of new pairs of milk teeth. At this time (up to 2.5 years), you should be especially attentive to the health and well-being of the baby and make sure that he does not suffocate from increased salivation during sleep.
Possible consequences and complications
What to do if your child is constantly sick
Situations when a child chokes on saliva are most often characteristic of acute respiratory diseases and the period of teething. There are usually no complications; any baby can choke or choke slightly, it’s not scary.
However, if a child chokes on mucus from a runny nose and finds it difficult to breathe, self-medication or improper treatment can lead to bronchitis (pneumonia). In this case, treatment with antibiotics will be required. If your baby starts coughing, you need to pay attention to this.
Constant contact of saliva on the chin of a newborn can lead to skin irritation: redness, itching, and discomfort.
In this case, it is recommended to lubricate the affected area with any moisturizing baby cream containing panthenol. Also, do not rub irritated skin with a towel.
If your baby begins to drool a lot, you can only gently blot it with soft cotton pads or a microfiber cloth.
Increased activity of the salivary glands is not a disease, but a normal physiological condition
Reflux esophagitis as one of the manifestations of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is one of the causes of reflux esophagitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, which is caused by the reflux of gastric contents into it. The main signs of reflux esophagitis are heartburn, a sour taste in the mouth, pain in the sternum and upper abdomen, discomfort when eating, hiccups and belching.
Do you suffer from sleep apnea? Contact us at the Center, we will help you effectively! Sign up by phone.
The likelihood of reflux esophagitis in patients with sleep apnea is 76%, and this is due to the following mechanism. During an episode of apnea (stopping breathing during sleep), the walls of the pharynx collapse. At the same time, the person tries to breathe intensively, straining the respiratory muscles. The diaphragm is actively involved in this process, which leads to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and, as a consequence, compression of the stomach. Conditions are created for the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus.
Manifestations
Symptoms of hypersalivation in adults and children older than one year depend on the type of disease:
Dosage form
Most of the medications that a patient takes can cause moderate or severe xerostomia, a disease accompanied by dry mucous membranes. This phenomenon is observed during radiation or chemotherapy, during the treatment of cancer. Symptoms of hypersecretion of saliva occur after taking lithium and Nitrazepam. The problem can be eliminated after stopping the medication or reducing the dosage.
Psychogenic form
It occurs quite rarely in patients, and excessive salivation has no obvious cause, since there are no signs of brain damage. This form of the disease is very serious because it is difficult to diagnose, and the patient is forced to carry a container with him all the time to spit out excess fluid from the mouth.
Bulbar and pseudobulbar form
The amount of saliva secreted here depends on the severity of the pathology and on its type - it is a vascular disease, poliomyelitis, degenerative changes, syringobulbia or another problem. In some cases, the amount of saliva secreted per day exceeds 1 liter, which is why the patient is forced to keep a handkerchief, towel or container ready at all times to collect excess liquid.
Hypersalivation in cerebral disorders
With cerebral palsy, incoordination of the oral muscles occurs, which makes it impossible to fully swallow saliva. In this case, the glands function quite normally, and there is no excess of the amount of fluid secreted.
Somatic form
Here, the culprits of excessive salivation are somatic diseases, helminthic infestations, toxicosis in pregnant women, ulcerative stomatitis, gingivitis, diabetes mellitus and other pathologies. A doctor must determine the cause of somatic hypersalivation, while the symptoms of the conditions are also different and can manifest themselves during the day, at night or constantly.
To identify the root cause of the development of the pathology, the patient is referred to a therapist, and this doctor, if necessary, will send the patient for a consultation with a gastroenterologist, neurologist, dentist or endocrinologist. In the case of helminthic infestation, intervention by an infectious disease specialist will be necessary.
The disease must be treated immediately after detection to eliminate consequences
Salivation
Salivation
(sialorrhea, hypersalivation) is normally observed in infants, pregnant women, and also with mechanical irritation of oral receptors. Common etiological factors are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, teeth, ENT organs, damage to the central and peripheral nervous system. To diagnose the causes of drooling, saliva is examined, blood and urine tests are performed, and instrumental visualization of the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system is performed. To relieve symptoms, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease. To reduce salivation, anticholinergics and botulinum toxin preparations are prescribed.
Causes of drooling
Physiological factors
The symptom is observed in most women in the first trimester of pregnancy. The appearance of drooling is associated with reflex irritation of the nerve centers that control the production of saliva. The intensity of the manifestations varies: from single nighttime episodes of sialorrhea to constant and uncontrolled flow of saliva, when a woman loses up to 3-5 liters of fluid per day. Drooling is normal in infants and children during the eruption of primary and permanent teeth.
Mechanical irritation of the oral cavity
Hypersalivation, with saliva flowing from the corners of the mouth, is a common problem for people who start wearing removable dentures. Over the course of several months, adaptation to the foreign body occurs, and the amount of saliva released gradually decreases. Short-term sialorrhea is observed during dental procedures, the use of chewing gum or sucking candy. Drooling occurs in many smokers.
Dental diseases
Sialorrhea often develops with stomatitis, gingivitis, and dental caries. The symptom is associated with irritation of M-cholinergic receptors in the mucosa. Drooling is moderate and appears more often at night. During the day, there may be a slight leakage of saliva, which accumulates in the corners of the mouth. In addition to increased salivation, patients complain of soreness and burning in the mouth, pain when chewing and swallowing, and bad breath.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Sialorrhea is possible when the stomach and initial parts of the intestines are affected. Its most typical appearance is in chronic pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and peptic ulcer. The symptom occurs at any time of the day and is often accompanied by heartburn and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. A combination of drooling with abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and stool disorders is typical.
ENT diseases
The flow of saliva is typical for people who have difficulty breathing through their nose and sleep with their mouth open. It occurs in patients with sinusitis, chronic rhinitis, and in children with adenoids. Drooling develops primarily during sleep. Due to the constant drying of the mucous membrane, a small amount of viscous saliva is released, accumulating on the skin of the perioral zone or leaving marks on the bed linen.
Worm infestations
The reproduction of helminths in the gastrointestinal tract causes irritation of peripheral receptors, reflexively activating the secretion of saliva. A specific sign of helminthiasis is salivation, which is disturbing at night. A person will know that there is a problem by wet spots on the pillowcase and pajamas. Dried crusts of saliva are visible in the corners of the mouth after waking up. Symptoms are supplemented by abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders, and itching in the anal area.
The dangers of increased salivation during sleep
Hypersalivation is a phenomenon of increased salivation. And if this is a typical picture for young children, then in adults it can be a symptom of a serious disease.
Normally, much less saliva should be produced during sleep than during the day. Excessive salivation during sleep is a dangerous phenomenon: not only is it aesthetically unattractive, but there is also a danger of choking on saliva during sleep.
Sleeping on wet sheets is usually not fun either.
Why do you drool in your sleep?
In most diseases, increased salivation continues throughout the day, saliva is released both before sleep and during sleep, and saliva is observed abundantly after sleep.
In addition, a person experiences excessive salivation during sleep:
The causes of nocturnal hypersalivation may lie in the predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) during sleep, which innervates the salivary glands. Under its influence, excessively liquid saliva is released.
However, there is also purely nocturnal drooling, which does not appear during the day. The most common causes of nighttime drooling are:
In some cases, a one-time night profuse salivation appears if a person is simply very tired, fell asleep soundly, completely relaxed, his mouth opened in his sleep and a little saliva flowed out.
It happens that due to strong muscle relaxation, saliva flows onto the pillow of a drunk person. You don't have to be an alcoholic to do this - it can happen to anyone.
Saliva is produced abundantly even after smoking - so if you smoke before bed and then quickly and very soundly fall asleep, it is quite possible that you will not be able to resist and saliva will spill onto the pillow.
Complications
Excessive drooling from the mouth affects the skin; a person sleeps for some time with his cheek on a wet pillow, so one of the unpleasant consequences may be a violation of the integrity of the facial skin or the appearance of an infectious pustular rash.
Normally, the body secretes one and a half to two liters of saliva per day. With severe drooling, a person can lose up to 10-12 liters of salivary fluid, which can lead to dehydration that is dangerous for the body. And, of course, there is incomparable psychological discomfort, stress and sleep disturbances.
Treatment
Treatment of increased salivation at night involves, first of all, diagnosing the causes that caused its occurrence and treating the underlying disease.
For diagnosis, you should contact a specialist: gastroenterologist, dentist, endocrinologist, neurologist, therapist. You need to undergo clinical tests and be checked for worms.
The specialist prescribes the necessary studies. Therapeutic treatment is selected by the doctor.
In some cases, medications with an anticholinergic effect (riabal, platifilin, scopolamine) are prescribed, which reduces the amount of saliva produced. However, you should not prescribe these drugs yourself, because side effects may occur.
In addition, drug therapy is usually short-term. And, of course, it is necessary to completely cure all diseases of the oral cavity.
Cryotherapy, a method that allows one to reflexively increase the frequency of swallowing saliva, and homeopathic treatment have proven to be quite effective methods.
In the most difficult cases, with excessive salivation, surgery is performed to remove large salivary glands.
However, this is a very complex operation that can cause a number of other problems: for example, if the facial nerves are damaged, the symmetry of the face is disrupted.
Injecting botulinum toxin into the parotid glands stops saliva production for up to 8 months.
List of used literature:
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Moderate drooling does not pose a threat to health and does not require emergency treatment. With nocturnal sialorrhea, patients are advised to sleep on their side so that saliva does not enter the respiratory tract. To prevent maceration of the skin around the mouth, you need to maintain hygiene and use nourishing and moisturizing creams. Since there is a risk of dehydration with excessive drooling, you should increase the amount of fluid you drink per day.
To reduce saliva production, doctors advise avoiding sweets, carbonated drinks and foods rich in extractive substances. Hygienic oral care is best done with slightly foaming toothpastes. For swallowing disorders and perioral muscle dysfunction, motor exercises are prescribed to help control drooling. Special massage and physiotherapy are used less frequently.
Conservative therapy
In most situations, drooling can be completely eliminated after treatment of the underlying pathology. The therapeutic regimen is selected by a doctor of the appropriate profile: gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist. If drooling is caused by acute poisoning, an intensive detoxification program is carried out in a hospital setting. With massive sialorrhea, pathogenetic therapy is required, which includes:
Surgery
Surgery is recommended for severe neurological causes of drooling if other methods are ineffective. Surgeons use several types of operations: redirection of the excretory ducts to the back of the mouth, ligation of the ducts, partial removal of the salivary glands. The methods demonstrate good results, but can provoke complications - facial asymmetry, chewing and swallowing disorders.
Source
Why is there a lot of saliva in my mouth?
Let's consider the possible causes of increased salivation
Oral diseases. These include: stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis, etc. Bacteria provoke irritation of the salivary glands, hence the excessive secretion of fluid. If these diseases are not treated, inflammation of the salivary gland may occur.
Having dentures or braces. The structures cause irritation of the mucous membrane, which provokes excessive secretion of fluid. This problem is especially noticeable in the first two weeks after installation of the structure, when adaptation occurs.
Gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, pancreatitis, stomach ulcers, etc.). The problem most often occurs against the background of increased stomach acidity. Other reasons that doctors highlight: liver dysfunction, worms, stress on the pancreas.
Diseases of the central nervous system (cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease, irritation of the trigeminal nerve, migraine). A similar condition occurs when the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted and blood pressure increases.
ENT diseases, ARVI, inflammation of the adenoids. The person begins to breathe predominantly through the mouth, as nasal breathing is difficult. The mucous membrane dries out, causing the glands to begin to work actively.
Changes in hormonal levels - problems with the thyroid gland, diabetes, menopause, etc.
Smoking. Tobacco smoke irritates the salivary glands. They begin to produce a lot of fluid. This is why smokers have the habit of spitting.
I choke on saliva in my sleep
What causes salivation during sleep and what can you do about it? This is worth paying attention to!
Very often, the cause of increased salivation can be illness. This is how our body gives signals that something is going wrong. It would seem like a small thing, but it’s not entirely true.
Runny nose
Let's start with the simple and obvious. Very often drooling is due to a runny nose. At night, the nose gets stuffy, breathing becomes difficult and the person opens his mouth. This is where increased salivation begins. This problem will resolve itself when the runny nose goes away.
Infections in the mouth
Drooling occurs due to diseases of the oral cavity: inflammation of the mucous membrane, gums, caries or periodontal disease. Reproducing bacteria provoke the production, and therefore the release, of an increased amount of saliva. Always remember to take good care of your dental health.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Inflammation, increased acidity, flatulence - all this leads to excessive salivation at night. In such diseases, salivation works as a protective measure: saliva dilutes gastric juice and reduces acidity. These symptoms should not be ignored so as not to lead to cholecystitis or pancreatitis.
Helminthiasis
Yes, that’s right, it’s not a myth at all. Of course, drooling while you sleep is not a 100% guarantee of the presence of worms, but they may well be there. Worms cause a change in acidity, which, as we have already said, leads to excessive salivation. There is a reason to get checked, get tested or carry out preventive measures.
Nervous system diseases
The symptom may occur during cerebrovascular accident, during Parkinson's disease or with trigeminal neuralgia. The same phenomenon is typical for syringobulbia, polio, vascular pathologies and even oncology.
Endocrine system diseases
Excessive salivation may be a peculiar reaction of the neuroendocrine system to some irritant. It can occur as a result of stress or endocrine diseases (thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus). Sometimes observed in diabetes mellitus.
Very often, nighttime drooling occurs due to bad habits. People who use drugs or smokers very often suffer from this unpleasant symptom. There is only one recipe - it's time to give up bad habits.
ADVICE
So what can you do to get rid of nighttime drooling? To begin with, we recommend understanding the reason for its occurrence. If there are no visible reasons, then this is a serious reason to go to the doctor.
To prevent nighttime drooling, you can try changing your sleeping position. If you fall asleep on your side, try to retrain yourself and start falling asleep on your back. If this does not help, you can try placing the pillow higher. Then the head will rise and the mouth will not open.
Excessive salivation during pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the female body. The main reasons why an expectant mother’s salivation increases.
A large amount of saliva does not threaten the fetus, however, if this is a consequence of any disease, then the pregnant woman should monitor her condition.
What complications are possible?
Reasons for development
The nature of ptyalism may be true or false. True hypersalivation is distinguished by the fact that during the day a person secretes several times more saliva than should be secreted normally. The false form is characterized by a violation of the swallowing function, while the patient feels that a copious amount of saliva has accumulated in his mouth.
Doctors believe that the causes of hypersalivation in an adult may be the following:
- stomatitis - the flow of saliva is provoked by irritation of the oral mucosa, when it is painful for a person to swallow and simply touch the affected surface;
- Parkinson's disease;
- poor blood supply to the brain, vascular pathologies, malignant neoplasms;
- stomach ulcer;
- helminthic infestations;
- the period of gestation in women, especially if pregnancy occurs against the background of severe toxicosis;
- stroke;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals - mercury, lead, iodine;
- epidemic encephalitis.
Unlike an adult disease, a child drools from the mouth more often for physiological reasons, for example, during the eruption of baby teeth - between the ages of 4 and 12 months. At an
older age, if a child drools, this symptom cannot be ignored, it may indicate the following diseases:
Symptoms of inflammation of the salivary glands
- cerebral palsy;
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system - salivation during sleep is observed, for example, with the disease PPCNS (perinatal damage to the central nervous system) or PEP (perinatal encephalopathy);
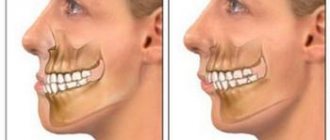
- malocclusion;
- pathologies of the nasopharynx and ears - sinusitis, sinusitis, proliferation of adenoids, acute tonsillitis;
- ulcerative stomatitis - when painful ulcers form, the baby finds it difficult to swallow saliva, at night it flows down the cheek, while the baby refuses to eat and sleeps poorly (irritated mucous membrane causes severe discomfort);
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums. Why do you drool while you sleep? This is the body’s protective reaction to an acute process; during sleep, the mucous membrane tries to recover on its own and wash out the infectious agent from the oral cavity;
- intoxication of the body.
In any case, if an adult or child suffers from increased salivation, it is necessary to consult a doctor; treatment of hypersalivation depends on the underlying cause. Most often, when the underlying problem is eliminated, for example, after treating stomach problems or helminthic infestations, the disease goes away on its own.
Causes of nocturnal hypersalivation
The secretion of saliva in a dream can be a separate symptom of the disease, while during the day a person does not experience increased work of the glands, and he himself only guesses about the problem from a wet pillow or his relatives tell him about it. Most often, such problems arise due to the predominance of the parasympathetic part of the central nervous system, since it is responsible for the functioning of the salivary glands.
Under its influence, saliva becomes too liquid, and a person does not have time to swallow it in a dream.
The most common reasons why a sleeping person has saliva flowing from his mouth:
- difficulty breathing through the nose - problems can arise from ENT diseases (runny nose, sinusitis, sinusitis), allergic reactions, curvature of the bony nasal septum;
- abnormal structure of the jaws - an incorrect bite does not allow the bones to fully close, as a result, saliva flows directly onto the pillow during sleep (this phenomenon is often observed in older people, they suffer from dysfunction of the jaw joint and relaxation of the lower jaw);
- sleep disorders.
The amount of saliva produced may increase even once; this situation is not considered pathological. For example, if a person is too tired or has experienced emotional shock. At the same time, he fell fast asleep, his body was completely relaxed, his mouth opened and a small amount of saliva flowed out.
The same problem is observed in people under the influence of alcohol or after heavy consumption of nicotine - if you drink and smoke before going to bed, it is quite possible that a one-time problem with increased salivation will arise
If there is increased salivation at night in an adult, diabetes mellitus, disease of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or hypothalamus can be suspected. In this case, the neuroendocrine system reacts violently to any stimulus during the day, and at night responds with increased production of saliva.
Treatment of hypersalivation
There is no single treatment method for all cases. However, you can use methods to reduce the activity of the salivary glands - sometimes they are recommended by doctors as an addition to complex therapy.
In rare exceptions, the salivary glands are partially removed, but the downside is that there is a risk of damaging the facial nerve.
Which doctors will help you cope with this disease? Dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.
Source
The exact cause of Guillain-Barré syndrome is unknown, but very often the appearance of this syndrome is preceded by infectious diseases, such as respiratory infections or infections of the gastrointestinal tract. Fortunately, Guillain-Barré syndrome is quite rare, occurring in 1-2 people per 100,000. Unfortunately, treatment for this syndrome is only symptomatic, but treatment can reduce symptoms and speed up recovery. Most patients recover completely from this syndrome, but a certain percentage of patients may experience symptoms such as weakness, numbness or fatigue for a long time.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome may include:
Most patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome begin to experience severe weakness within four weeks of the onset of symptoms. In some cases, symptoms can progress very quickly, causing complete paralysis of the legs, arms and breathing muscles within a few hours. Therefore, taking into account the possible rapid progression of the disease, it is imperative to consult a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
Guillain-Barré syndrome is a serious condition that requires immediate hospitalization due to its rapid progression. The earlier appropriate treatment is started, the higher the chances of a good result.
Complications
Guillain-Barré syndrome affects the nerves and can cause a domino effect on other systems in the body, such as breathing and cardiovascular function. Complications of Guillain-Barre Syndrome include:
Severe, early symptoms in Guillain-Barré syndrome significantly increase the risk of serious long-term complications. In rare cases, death may occur from complications such as respiratory distress syndrome and acute cardiovascular failure.