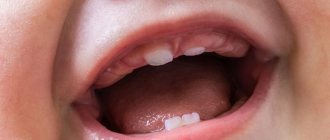
The order of eruption of baby teeth
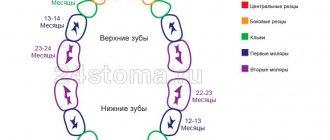
Everyone is different, but it is still important to know how most babies develop. Children's first teeth usually erupt almost simultaneously on the right and left. The sequence is as follows: first the anterior ones (incisors, canines), then the posterior ones.
It is important to understand that this pattern of teething in children is average, and in your case it may happen in a different order or at a different time. This does not necessarily indicate any violations.
Doctors have compiled an approximate, average diagram of teething in children:
Don't worry if you don't meet these standards for several months. If the parents got teeth late, most likely the children will have the same. Heredity has a very strong influence on development. The teething pattern should not become an unnecessary source of parental anxiety. This is just a guideline, like all other norms.
Both the sequence and timing of teething in children can vary greatly. Only if you are “late” by more than 6 months (for example, nothing appears until a year), it is worth discussing this with your doctor. There are genetic disorders when the rudiments of teeth do not develop at all. However, this is extremely rare. Some diseases also affect the timing of teething, but these conditions in children always manifest themselves with some more obvious symptoms.
In any case, there is no remedy that would “cut teeth” - we won’t pull them out of the jaw. We also do not regulate the cutting order. All that remains is to observe the process in children and take care of their health in general.
Why is the sequence broken?
The dentition is formed individually. This is influenced by many factors, for example, genetic predisposition. Therefore, the baby receives from the parents:
- Timing and order of birth of masticatory organs.
- Quality of enamel and strength of crowns.
If mom or dad had an incorrect pattern for the teething of units, the baby may also have them out of order. Non-standard appearance of units and discrepancies in terms are normal if:
- The baby tooth begins to emerge a month earlier or later;
- The order of appearance of the incisors is disrupted, that is, the upper one is born first, and then the lower one;
Remember that there is no method of influencing the time and speed of eruption in medicine. There are other reasons when a baby’s teeth grow out of order.
- Features of the pregnancy process, complications and illnesses of the mother: influenza, infectious diseases. Bad habits of a woman in labor have a negative impact.
- Infectious diseases that the child suffered: scarlet fever or measles.
- Lack of breastfeeding weakens the work of the newborn's facial muscles. His lower jaw does not develop enough, since sucking from a bottle is done with his lips. This provokes the initial appearance of incisors on the upper jaw.
- An ordinary pacifier if abused.
- Changes in climatic conditions.
- Parents of different nationalities.
These processes cannot be treated. It is important that all chewing organs come out so as not to miss the child’s gum inflammation. Medicine is not aware of cases where children are left without incisors and molars due to unbalanced eruption of units. They will grow up, you need to wait and take care of the little one.
What problems may arise during teething in infants?
Difficulties do not always arise. But sometimes, about 3 days before and 3 days after teething, the baby’s condition changes:
- gums swell;
- saliva flows more strongly (although a lot of it can be released without connection with teething);
- the temperature rises slightly;
- mood deteriorates (child is less active, cries more often);
- sleep becomes restless;
- stools become slightly looser and more frequent;
- your cheeks turn slightly red (no need to immediately look for allergens and change your diet).
These symptoms may not all appear, in any combination.
The difficulty is that the same symptoms, but usually stronger, can also occur in children with infections. Therefore, if your condition has changed significantly, consult your doctor.
Red flags (tell your doctor if your child has):
- temperature above 38 degrees in the absence of cold symptoms;
- a rash that is unfamiliar to you, which appeared along with a high fever;
- diarrhea, vomiting;
- lethargy;
- mouth ulcers or other sores.
- Eruption cyst (hematoma).
Assess how much the child's condition has changed. If he begins to clearly feel unwell, there is no need to attribute this to the teething of baby teeth. In this case, you need a doctor to rule out more serious problems.
When can I expect my baby's permanent teeth to appear?
When the eruption of baby teeth ends, parents feel relieved and forget that this is only the first stage of the formation of the dentition. Be prepared that after a while you will have to help your baby transfer the change of baby teeth to molars.
Thanks to a certain order of eruption of molars, children develop a correct bite. The first teeth to appear are the incisors, which occurs around 6–7 years of age. Then comes the turn of the canines and premolars. The last teeth to be replaced in children are molars. In the case of permanent teeth, the principle of paired appearance also remains. The entire dentition is replaced by adulthood, but wisdom teeth may appear much later.
The symptoms of baby and permanent tooth eruption are very different. The appearance of molars is not accompanied by vomiting, sleep disturbances, loss of appetite and other signs, but a slight increase in temperature or itching of the gums is possible.
Photo of baby teeth erupting
Medicines for teething in children
When your baby is in pain, you would like to have a reliable, effective medicine that you can give and sleep peacefully. As in the case of colic, when teething, the pharmacy will offer you a variety of remedies. Pediatric experts do not advise giving any medications without a doctor's permission.
Why? Homeopathic medicines are divided into true homeopathic (containing no active substance at all, and therefore ineffective) or pseudo-homeopathic. The latter contain some amount of plant components (usually chamomile and other, more exotic plants). The first ones do not work under any conditions, including teething in children, but at least they are harmless. Homeopathic remedies for pain containing belladonna (which was not even always listed in the composition) caused many deaths and were therefore strictly prohibited in developed countries.
In our country, the Commission of the Russian Academy of Sciences recognized homeopathy as a pseudoscience, but, unfortunately, there is no strict ban on potentially dangerous drugs. Since manufacturers do not always indicate belladonna in the composition, we recommend that you generally refrain from using any homeopathic remedies for teething pain in children.
Another case is gels with a local anesthetic drug (their name ends in “-caine”: usually benzocaine or lidocaine). Medicines like these are “freezes” that are injected into the gums when treating teeth. Although these drugs are obviously effective, they have also caused many child deaths. Substances of this group affect the functioning of the heart, because the gel is quickly washed off with saliva, and the child swallows it. It is especially dangerous if the parent uses a higher dose than recommended in the instructions. This happens often because these drugs only relieve pain for a few minutes. When the baby starts crying again, the parents apply more, often exceeding the dose. Now professional communities of doctors do not recommend the use of products with local anesthetics, but this does not stop their widespread advertising.
What to do if your teeth are cutting incorrectly
First of all, don't panic. When your toddler's teeth are cut out of order, balance his diet. After 5-6 months, a child, in addition to mother's milk, should receive complementary foods. It is important to measure the time of wakefulness and sleep. It is necessary to take the baby to the pediatrician for examination in a timely manner. If he prescribes a complex of vitamins, you must take them. Self-selection of medications can harm the child’s health.
The baby should be examined by a pediatric orthodontist. If there are no developmental pathologies, there is no need to worry. An objective assessment of the condition is the main criterion of health. If units emerge out of order, doctors advise observation and not skipping preventive examinations. When a one-year-old baby’s chewing organs do not grow, this is a reason for examination. This situation indicates a disturbance in metabolic processes. Violations in the order of birth of teeth should be closely monitored and reacted only if necessary.
What to do when children are teething?
The most natural and one of the most reliable ways to reduce pain is cold. Pick up an item - a “rodent” that can be put in the refrigerator. Freezing them is not recommended because it can damage the baby's delicate gums.
Often children prefer to gnaw on their parent's finger or, unfortunately, on their mother's breast. But parents may not have enough patience for a long time, so it is better to find a suitable teether.
It should be:
- whole and durable (the child should not bite off pieces that could cause choking);
- without ropes and beads (the rope can pinch the neck or break, creating a risk of choking on a bead);
- without paint with toxic components;
- just clean (no need to disinfect it).
You can refrigerate the fruit puree or put a few wet cloth toys in the refrigerator so you can replace them.
Of course, children chew not only objects that are ideal for this. But if with a teether made of one piece of silicone or a mitten with a silicone pad the child can be left alone in the playpen for some time, then with a bunch of small objects on a string around the neck or a bracelet made of beads, the same as with some fruit or vegetable, you need to look after it.
If cooling does not help, and the stress of teething is very severe, discuss taking pain relievers and fever reducers (ibuprofen is most often used) with your pediatrician. To be on the safe side, consult your doctor, but a single dose by weight (for ibuprofen is 10 mg/kg), given once at night for 3-4 days of active teething, will not cause harm.
In what cases can a child grow a second row of baby teeth?
The rudiments of baby teeth are formed very early, even before the baby is born, so disturbances in their growth are a consequence of the lack of space in the jaw to accommodate all the teeth.
What can lead to improper formation of buds or insufficient jaw size?
- Poor nutrition of a woman during pregnancy. For the proper formation of the baby’s body, including his future teeth, it is necessary that the mother receives vitamins and minerals in the quantities that she and the child need. If there are not enough of them, then the deficiency can lead to disruption or slowdown in the growth of both the rudiments of future teeth and the jaw bone.
- Lack of calcium and fluoride as the main elements for maintaining dental health in a child’s diet. It is necessary to carefully monitor how the baby eats so that the peculiarities of food do not become a problem for him and his teeth in the future.
- Avoiding solid foods in the infant's diet. Gnawing on harder foods is a necessary action that helps to properly position the erupting baby teeth in the jaw. If the baby receives only soft or liquid food, then he does not have the opportunity to correctly identify the places for all the baby teeth.
- Genetic predisposition to problematic growth of baby teeth. Unfortunately, genetics also influences crooked teeth. But don’t worry, because modern pediatric dentistry offers many ways to correct a child’s bite without much worry for both him and his parents.
Teeth are growing incorrectly - can this be corrected?
Of course, there are ways to correct disturbances in the growth of both primary and permanent teeth, including the growth of their second row in a child - it is difficult; a dental plate most likely will not help. You can often hear a myth that the incorrect growth of temporary teeth does not need to be corrected, because with age they are still replaced by permanent ones. This is a fundamentally wrong approach. In addition to the child developing complexes and frequent pain from malocclusion, curvature of baby teeth can lead to growth disturbances in permanent teeth, which is much more difficult to correct.
However, if permanent teeth require correction, then this is also not a reason to be too upset: orthodontists can recommend a lot of ways to correct abnormal growth of permanent teeth (aligners, trainers, braces).
Braces are placed at older ages - teenagers or adults. Since at this time the roots of permanent teeth are already formed, correction takes much longer than if it began in childhood. Often, wearing braces lasts for a year and a half, and sometimes for longer.
Whereas a doctor may prescribe a mouthguard or trainer for a child. In general, when correcting a bite, the rule is true: the sooner the better, which should always be kept in mind when detecting any problems with the arrangement of teeth in the jaw.
Of course, during the correction it is also necessary to maintain careful oral hygiene. Correction systems in the mouth can trap pieces of food, which subsequently become a good environment for microorganisms. This can lead to problems with the enamel, and in the longer term, even to caries and tooth decay.
Therefore, Asepta recommends using products to ensure oral hygiene. We have developed toothpastes specifically for children - they carefully clean, protect enamel from caries, and saturate it with minerals. Pastes also help get rid of food debris and prevent the proliferation of microorganisms on the teeth while wearing correction systems, and the antiseptic component in their composition helps disinfect the oral cavity.
What to do if a child’s tooth grows in the second row?
Sometimes such teeth sit so tightly in the gums that only their surgical removal can solve the problem. If precious time was missed, during which it was possible to easily return the permanent teeth to their place or allow them to erupt correctly, then retention may occur. Retention is the incomplete eruption of a tooth, in which it remains a small part inside the gum or, conversely, is almost completely hidden in it. It is much more difficult to correct than correcting abnormally growing permanent teeth. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to problems with a child’s bite as early as possible, even before his temporary teeth begin to change to permanent ones.
Only a dentist can make any decision regarding an impacted tooth and only after a complete examination of the small patient’s jaw. To do this, a complete photograph of the jaw is taken, which clearly shows the location of the tooth and possible paths of development of events. Next, the doctor may resort to either making an incision in the gum, followed by installing a brace system on the teeth, or removing the tooth, if nothing can be done to help. The latter, however, rarely happens. More often than not, doctors try to find a way out of any situation, and braces systems currently make it possible to solve almost any problem with an impacted tooth.
Therefore, if you notice that your child is growing second row of milk or permanent teeth, you should not panic, but you should not lose sight of the situation either. Make an appointment with a doctor and get examined. The dentist will assess the situation and offer the best approach to solving the problem. Early contact with a doctor is the key to quick treatment.
Take care of the health of your loved ones with Asepta!
Should I brush my newly erupted teeth?
Dentists strongly recommend starting to take care of oral hygiene from infancy. For newly emerging teeth, they offer special silicone brushes or wipes. A simpler option is a finger wrapped in gauze. You can simply moisten it with water or use toothpastes for children under 3 years of age (they are marked 0+ and can always be swallowed). The main thing when brushing your teeth is no violence! A little more cleanliness isn't worth the stress.
| Author Fedor Katasonov | Scientific editor Maria Gantman |
Ribbed teeth
Why do ribbed or “wavy” teeth grow? This is the norm. The front surface of the teeth should be even and smooth. But the cutting edge of permanent teeth is ribbed when they erupt. This is especially noticeable on the incisors.
Wavy edges of newly erupted teeth
On the cutting edge of the teeth, the thickness of the enamel is greater than on the front or side surfaces. It is quite enough for the teeth to wear down a little naturally during chewing. Therefore, soon the lower edges of the teeth will become smooth.
But this will only work if the teeth are closed correctly, that is, there is adequate load on the cutting edges. If the teeth are crowded or tilted to the sides, the lower (ribbed) part will not grind down and the visual defect will remain. At least until the bite is corrected.