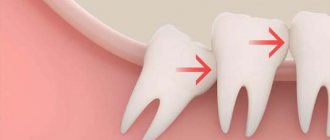
Impacted is a tooth that has not erupted and is located in the bone tissue, covered by the gum. Dystopic teeth are those that have an abnormal position - that is, they are shifted towards the cheek or tongue, rotated around their axis or tilted to the side. At the same time, some teeth can be either impacted or dystopic - that is, they are located in the bone, while being turned to the side relative to the correct vertical position. This mainly concerns “wisdom teeth” or molar eights, which are located at the very end of the dentition.
Why do wisdom teeth grow incorrectly?
Wisdom teeth, or the outermost teeth in a row, usually appear between the ages of 18 and 25. And they grow, as a rule, with serious disturbances. Only the lucky ones can boast of straight and evenly grown “eights”. Frequent problems of wisdom teeth are retention and dystopia, in most cases even both ailments at once.
The abnormal growth of wisdom teeth is explained by the fact that, firstly, they grow in adulthood, when the bone tissue is fully formed, it is very dense and hard - naturally, it is incredibly difficult to “break through” it. Secondly, modern man does not need eighth teeth - our ancestors used them to chew raw meat. Wisdom teeth don’t even have guides—baby teeth—so they have to make their own way through hard bone.
In most cases, wisdom teeth must be removed, especially if they do not appear above the gum and interfere with neighboring teeth (press on the roots of their neighbors on the side). It is also very important to check the condition of impacted wisdom teeth if you experience discomfort when opening and closing your jaw, pain in the ear, or an increase in body temperature.
Removal of impacted and dystopic tooth
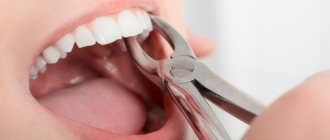
An impacted wisdom tooth can be in a straight or rotated position (dystopia) - in this case it will put pressure on the roots of its neighbor. To avoid complications, such ungrown teeth must be removed. How is the operation performed? In several stages:
- mandatory administration of anesthesia: tooth extraction is a painful operation that requires serious tissue anesthesia,
- the gum is cut - access is created to the impacted tooth,
- a hole is created in the bone using a bur,
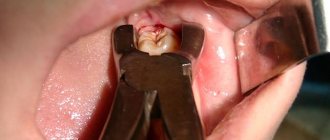
- tooth extraction: the tooth is removed immediately using forceps, or is first divided into parts using a bur and then removed from the bone tissue,
- the bone is restored: in some cases, the cavity vacated by the tooth is filled with artificial bone material, or with the patient’s own blood plasma - this measure is necessary so that empty space does not form in the bone, which can be occupied by neighboring teeth. If they begin to shift, then the entire dentition will gradually “creep” - gaps will appear between the teeth. In order to understand whether the hole will need to be filled with any material, you need to consult a doctor,
- the gum is sutured: after all manipulations are completed, the gum is returned to its place, sutures are placed on top.
The operation to remove an impacted / dystopic tooth lasts about 30 minutes to an hour. This is a fairly ordinary operation, which, when performed professionally, will not lead to any complications. In some cases, if there are a lot of uneven roots, it may take longer. The doctor can determine the approximate time of the operation based on the results of examining the image.
Complications after wisdom teeth removal
Unerupted teeth are sometimes located quite deep in the bone, so extracting them can be quite a difficult procedure and can lead to certain complications. For example, a nerve injury in the lower jaw, resulting in numbness of the lips, tongue and part of the cheek (goes away on its own after a few weeks or months), rupture of the nasal sinus (a runny nose or sinusitis forms). With complex removal of wisdom teeth, there is a high probability of fracture of the jaw, adjacent teeth or dentures. In order to avoid such complications, it is best to have wisdom teeth removed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon who has extensive practical experience in this field.
Care after wisdom teeth removal
After removal of impacted wisdom teeth, minor pain, bleeding from the wound, and rarely, suture separation may occur. Tissue swelling and pain when chewing food and opening the jaw are also observed. If the pain does not go away within 2-3 days (at this time it is necessary to take painkillers - these can be Ketarol, Ketanov, Nise, etc., depending on the prescription after the operation), you must consult a doctor. In general, rehabilitation takes from 1 to 5 days. After a few days, you must visit a doctor for a follow-up examination of the results of treatment and removal of stitches.
Concept of retention
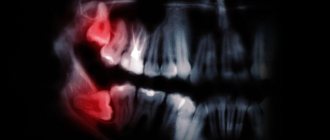
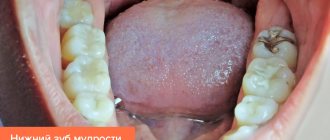
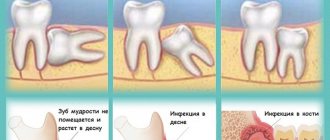
An impacted tooth is an element of the dentition that, for various reasons, could not come out of the bone tissue (complete retention) or was partially immersed in the jaw bone, and partially remained in the mucous layer of the gums (partial retention). The deeper the impacted figure eight is immersed in the bone tissue, the greater the severity of retention.
With each generation, the appearance of impacted wisdom teeth is becoming more common. Dentists believe that given the current trend, in a few generations this picture will become the norm.
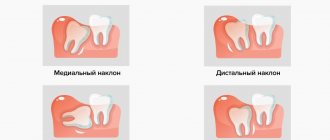
Impacted eights can have different positions and orientations:
- medial – tilted forward;
- distal – lean back;
- horizontal – horizontal in relation to the rest of the dentition;
- reverse - turned upside down.
Causes
Experts note that the number of teeth a person has is decreasing. Even now, it sometimes happens that the rudiments of eights are absent in the alveolar process, but so far such a picture is rare. Impacted teeth in most cases are unable to erupt due to lack of space in the jaw. This is due to the fact that the nature of human nutrition has changed greatly over the last century: the diet contains little solid food, which is necessary to initiate the dental apparatus to active growth. Soft food is effectively chewed by the molars, and the eights have practically lost their function.
Due to small loads on the jaw, it does not grow as large as in people living a few centuries ago. The start of eruption of eights is observed at 17-23 years of age, but by this time the growth of the jaw bones is already completely completed. In the best case, the tooth remains in the bone with an upward orientation, but in difficult cases it continues to grow in a horizontal plane, so its apex can rest against the roots of the sevens. This abnormal position is called dystopia; it is often combined with retention.
In addition to lack of space, the following reasons can lead to retention:
- hereditary factor;
- early loss of primary premolars and molars;
- vitamin deficiency at the time of formation of tooth germs (age 4-5 years);
- superset;
- rickets or mineral metabolism disorder;
- some infectious diseases.
Pathogenesis
The child’s dental system is formed and develops taking into account adequate nutrition, the health of the mother, and the course of pregnancy. If teeth are missing at the required time, doctors make a diagnosis of “retention.”
Teeth may be delayed in erupting and there are two types:
- all the teeth came out on time, but the incisors do not erupt;
- teeth erupt very slowly, with large gaps created between the teeth and pairing is disrupted.
It is impossible not to pay attention to such a process as teething and their delay. If baby teeth do not appear on time, this negatively affects permanent teeth and their formation.
Overkill or normal
Most people have wisdom teeth, one on each side of the upper and lower jaw. However, in some cases there may be not four, but eight or even up to twelve. This is not considered a developmental anomaly, since our ancestors had such a set, but now it is gradually being reduced. It is also impossible to consider a set of 38 or 48 teeth as the norm, since with modern anthropometric standards such a superset always causes problems, displacing the entire dentition and leading to obvious malocclusion. The sooner the “nines” and “tens” are removed, the fewer problems will have to be solved later, so doctors recommend removing them immediately after detection.
Symptoms
At the initial stages, impacted elements do not cause any symptoms, so their presence may come as a surprise to a person.
The symptoms that patients experience when cutting through figure eights are:
- discomfort in the oral cavity;
- swelling of the gums in the area of retention;
- slight increase in body temperature.
When using painkillers or medications that relieve symptoms, the sensations go away, but after a while they resume again.
Experts' opinion
The active components of the complex help reduce bleeding and inflammation in the oral cavity.
- A unique complex of vitamins, microelements and plant extracts, specially selected to maintain the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
- Coral calcium and coenzyme Q10 in the composition strengthen gums and tooth enamel.
- Vitamins support general immunity.
At the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, it was proven that the joint use of Asepta dental line products makes it possible to achieve a complex effect. Taking into account the active components that make up these Asepta products, their clinical properties and the effect they have on the soft tissues of periodontium, they can be used both as independent agents in the initial stages of diseases, and in combination with medications for severe forms of chronic periodontal diseases.
Considering the therapeutic and prophylactic properties of the Asepta line products, they are used for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa, such as catarrhal stomatitis, glossitis and cheilitis.
Sources:
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of mild and moderate severity using Asepta antibacterial agents (S.I. Gazhva, A.I. Voronina) S.I. Gazhva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department A.I. Voronina, aspirant, dentist, Department of Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy"
- Evaluation of the clinical effectiveness of a combined drug of local etiotropic action in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (E.L. Kalichkina, E.A. Tyo, Z.Z. Abubakarova)
Is it necessary to delete
There is a point of view that figure eights should definitely be removed, especially if they are impacted. In fact, dentists believe that if retention does not manifest itself and does not cause problems with the dentition, removal will be a premature measure.
Indications for removal are:
- pain syndrome;
- incorrect position relative to the dental arch;
- the inability to properly clean the eights due to their location;
- caries on figure eight;
- the presence of a fistula, flux, cyst or abscess;
- pressure on the nerve, leading to numbness of the face;
- inflammation of soft tissues in the adjacent area;
- osteomyelitis or the risk of its development;
- impossibility of orthodontic treatment.
Even if the eight does not cause the above symptoms, but there is a carious lesion on the adjacent seven, the retention is removed so that the doctor has the opportunity to carry out high-quality sanitation.
When a purulent inflammation is detected in a patient, the operation is performed on an emergency basis, since there is a high probability of infection.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications to removal:
- hypertensive crisis;
- diseases of the nervous system in the acute phase;
- relapse of cardiovascular diseases;
- the presence of viral or infectious pathologies;
- blood clotting disorder;
- having an abortion within the last two weeks.
They are very careful when removing retention in pregnant women. They allow the operation to be performed during the second and early third trimester.
Diagnostics
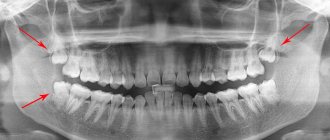
If characteristic symptoms are detected, the doctor may refer the patient for examination. Detailed diagnostics is important in order to determine the location of all structural elements of the figure eight. This is necessary to understand whether the removal of a wisdom tooth is justified and how to carry it out correctly. To study all the nuances, an x-ray is prescribed. The image will help identify dystopia or such a rare feature as penetration of roots into the maxillary sinus.
Left – X-ray, right – orthopantomogram
The final decision on removal is made by the dentist and orthodontist, who are able to assess all the risks and consequences of retention in a particular case.
What to do with a problem tooth
The difficulty and danger of removing a dystopic, impacted tooth lies in the fact that it is located inside the gum. Such formation is dangerous for the patient because the tooth may be subject to destruction that will be impossible to cope with.
But despite the complexity of the procedure, it is completely safe and painless for the patient. Modern dentistry is able to provide reliable anesthesia and quick results through the use of professional equipment.
Treatment
The operation to remove an impacted figure eight is not the easiest, so it must be performed by an experienced specialist. Injectable drugs that have a strong effect are used for pain relief. This is necessary to reduce sensitivity in soft and bone tissues. Typically, the needling is carried out on both the buccal and palatal sides.
Patients with mental disorders or very nervous people can be put under general anesthesia. In this case, an anesthesiologist must be present during the operation, and it is carried out in an inpatient department. Sometimes I use an intermediate option - sedation, which allows the patient to remain conscious, but not perceive what is happening.
The operation is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Introducing anesthetic drugs and waiting for them to take effect.
- Dissection of mucous tissue to access the jaw bone.
- Drilling a perforation into the bone using a dental drill.
- Loosening and extraction of wisdom teeth. If it is large, then crushing or sawing into pieces may be necessary, and then gradual removal.
- Removing bone fragments from the formed hole.
- Treating the wound with a disinfectant solution.
- Putting medicine in the hole.
- Stitching the wound.
Sutures are not always required. If the hole is shallow, the doctor can leave it open to heal on its own. When applying sutures, absorbable threads are usually used. If ordinary surgical threads were used, then after 7-14 days the sutures are removed.
According to statistics, removing lower impacted wisdom teeth is more difficult. This is due to the fact that they sit deeper in the bone, and the alveolar process itself is thicker, stronger and larger from below.
How is an impacted tooth removed?
Removing an impacted tooth is a complex surgical procedure that can only be successfully performed by an experienced dental surgeon. Removing impacted dystopic wisdom teeth is considered especially difficult due to its incorrect position. On average, the procedure itself takes about half an hour, but in particularly difficult situations, tooth extraction can last more than two hours. In addition, it is believed that removing an impacted wisdom tooth in the lower jaw is more difficult than removing an impacted wisdom tooth in the upper jaw. This is explained by the fact that the bone tissue in the lower jaw is denser, so the tooth can be extracted more easily. However, the upper impacted wisdom tooth is removed using the same technology, so there are no big differences here.
Stages of removing an impacted tooth:
- Consultation, diagnostic procedures. Sanitation of the oral cavity. Often, several days before the procedure, sedatives and vitamins are prescribed.
- Anesthesia (general anesthesia, sedation, local anesthesia - depending on the complexity of the case and the wishes of the patient).
- An incision is made and the gum is pulled back to access the bone tissue. Can be performed using a scalpel or laser. The second method is more modern and less invasive, but the cost of the procedure increases significantly.
- Preparation of bone tissue using a special bur to access an impacted tooth.
- Extracting the tooth using special forceps (elevators) or sawing it into several parts and removing each piece separately. The second method is considered more predictable and safe.
- Plastic surgery of soft or hard tissues, suturing (if necessary), treating the area with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions.
Recovery
Blood may ooze from the hole throughout the day. Facial swelling and pain are considered normal. To get rid of them, you can take painkillers for several days. An increase in body temperature is also normal.
To prevent possible complications, it is very important to follow the rules of the rehabilitation period after surgery:
- if a gauze swab is placed in the hole, it is not removed for half an hour;
- do not drink or eat anything for three hours;
- apply cool compresses for several days to eliminate swelling;
- do not eat cold or hot foods;
- do not rinse your mouth;
- do not chew food with the injured side of the jaw;
- Avoid overheating and physical exertion.
During this period, hygienic brushing of teeth can be difficult; it is better to leave neighboring sevens uncleaned than to damage the wound with bristles. Sometimes antibiotic therapy is necessary during the rehabilitation period. The type of antibiotic and duration of use is determined by the doctor.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid serious complications in the postoperative period, the patient must follow certain rules. Dentists at the Optimal Choice clinics give the following recommendations:
- Eating is allowed no earlier than three hours after tooth extraction surgery. In addition, while the wound is healing, you should avoid eating solid food.
- Drinking and eating cold, hot, and drinking alcoholic beverages is prohibited.
- During the first 24 hours you should not smoke.
- You are required to give up physical activity for several days. The same applies to excessive facial expressions and loud laughter. This must be done so that the stitches do not come apart and the healing of the wound does not slow down.
- Hot water procedures, including showers and baths, are prohibited. Of course, you cannot visit a sauna or bathhouse after surgery. Hot compresses to the cheek are also prohibited unless you want to harm yourself.
- Five minutes of cold compresses or ice applied to the cheek on the side where the removal was performed will help cope with swelling and pain.
- To brush your teeth, you should choose a toothbrush with soft bristles.
- Do not actively rinse your mouth. If it is necessary to treat the oral cavity, you should give preference to baths: take a medicinal solution into your mouth, hold it there calmly for several minutes and spit it out without effort. For this you can use a solution of chlorhexidine or furatsilin or infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs. Oak bark promotes healing very well.
- If your doctor has prescribed you to take any medications, you must take them according to the written regimen.
Compliance with these recommendations will reduce the risk of complications to a minimum.
Complications
If the operation is performed by a competent surgeon, complications are rare. Among the most dangerous are the following:
- perforation of the maxillary sinus;
- paresthesia due to damage to the facial nerve;
- prolonged alveolar bleeding;
- infection in the wound.
Most of them are accompanied by high fever and severe pain or discomfort. If you suspect the development of a complication, you should contact the surgeon who performed the operation as soon as possible.
Refusal of treatment
Some patients wonder whether it is possible to leave an impacted wisdom tooth without removal, although the doctor recommends getting rid of it. This often happens when there is no pain, and a person cannot adequately assess the problems that refusal to treat retention promises.
Among the complications are:
- caries damage;
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease;
- deformation and crowding of the dentition.
More serious consequences are inflammation and swelling of the ear lymph nodes, damage to the auditory nerve, the development of purulent inflammation, suppression of the function of the immune system and sepsis.
Prices for wisdom teeth removal at Implantmaster
Tooth extraction is simple:
- X-ray images
- Anesthesia
- Removal of a tooth
- Applying and removing sutures
- Postoperative examinations
Price : from 3,000 ₽ to 7,800 ₽
Tooth extraction is complicated
| from 10,000 to 20,00 ₽ |
The price of a technically complex atraumatic removal of one wisdom tooth in Moscow dentistry reaches up to 20 thousand rubles. and higher. The cost of the procedure itself may be added to the price of artificial bone used during bone grafting to minimize the risk of thinning of the jaw bone in the segment after removal.
Many doctors simply apply suture material to the wound, lowering the cost of the extraction procedure to 10 thousand rubles.