Gingival fibromatosis is the uncontrolled growth of fibrous tissue in the gum and periodontal area. It can be hereditary or acquired, is progressive in nature and requires surgical correction. Without treatment, tissue proliferation will inevitably lead to the development of concomitant pathologies with the formation of periodontal pockets, bone atrophy, loss of healthy teeth and impaired chewing function. Children experience impaired tooth growth and severe malocclusion.
Inflammation and hypertrophy of gingival papillae - possible causes and treatment methods
The condition of our gums directly affects the health of our teeth. Therefore, when the interdental gingival papillae become inflamed and grow, you need to sound the alarm. It is better to see a specialist as quickly as possible and begin treatment to prevent the pathological process from spreading to the deep layers of the periodontium. Otherwise, you may encounter serious complications, because the dentogingival ligamentous apparatus may also be damaged, and this is a real risk of tooth loss. Read further in the article about what can provoke inflammation and proliferation of gingival papillae and how such diseases are treated today.
Interdental papillae - structure and functions
Gingival papillae are areas of the marginal gum. They are triangular in shape and are located between the teeth. Experts in the field of periodontology include the following tasks as their main functions:
- protection of the cervical area and roots from carious processes,
- increasing the depreciation of teeth while chewing food,
- retention of teeth in sockets,
- nutrition of hard tissues.
Gingival papillae are areas of the marginal gum.
Gum tissue does not have the ability to regenerate. Therefore, if the integrity of its structure is violated, for example, as a result of too intense cleansing, this process cannot be reversed. To hide the defect, gum grafting will have to be performed.
Reasons for development
In accordance with the classification adopted in dentistry, the causes of inflammation of the gingival papillae are local and general. The first category includes:
- Chronic diseases, including diabetes, heart and gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Hormonal imbalances and weakened immune system.
- Systematic use of medications with side effects.
- Bad habits, primarily the addiction to smoking.
- Development of infectious diseases.
The second group includes:
- Growth of elements related to the permanent occlusion set.
- Burns resulting from thermal or chemical contact.
- Mechanical tissue injuries caused by excessive stress.
- Failure to comply with medical recommendations for hygienic care.
- Prosthetics using low quality materials.
What diseases lead to gum inflammation
Inflammation of the marginal gums can be caused by mechanical trauma, constant exposure to tobacco smoke, thermal or acid burns, abundant subgingival deposits and many other factors. The following describes gum diseases that occur most often and also lead to inflammation and deformation of the interdental papillae.
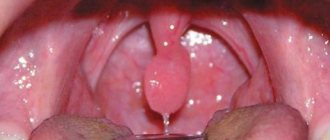
Papillitis – gingival polyp
This disease leads to inflammation of the gingival papillae located near one or several teeth. One of the common reasons for the development of this pathological process is an allergic reaction. In other cases, characteristic symptoms arise against the background of carious processes in the cervical area. According to statistics, in almost 40% of cases, the provoking factors are diseases of the cardiovascular system, as well as malfunctions of the endocrine system and gastrointestinal tract1.
The photo shows a gingival polyp
The clinical picture is as follows: the papillae noticeably turn red or acquire a bluish tint, obvious swelling occurs, and bleeding appears at the time of mechanical irritation. Patients complain of pain while brushing their teeth, eating, and even talking.
Gingivitis – inflammation of the gums
Gingivitis is a disease in which the inflammatory process spreads to the gum tissue and provokes unpleasant symptoms such as redness of the mucous membrane, swelling and bleeding. In this case, inflammation can cover only the interdental papillae, including the marginal gum or its entire surface.
This is what gingivitis looks like
“I had gingivitis just when I was pregnant. The gums were all red and inflamed. I was scared, I remember running to the doctor. There they reassured me, they said that this often happens against the background of hormonal changes, nothing to worry about. We brushed my teeth there, prescribed rinses and some kind of ointment, I don’t remember the name. A week later everything went away. So there is no need to panic ahead of time, but in no case should you delay going to the doctor.”
NikaS, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
The most common forms are hypertrophic gingivitis with the proliferation of affected tissues and the atrophic, that is, chronic stage of the disease. In the first case, hypertrophy of the mucosa can lead to overlap of the crown by almost half, as well as disruption of the dentogingival bonds. In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10), this pathological phenomenon is assigned the number K06.1.
Periodontitis – inflammation of periodontal tissues
Periodontitis is an inflammation of periodontal tissues, in an advanced stage leading to the destruction of the periodontal ligamentous apparatus, loosening and loss of teeth. Most often, this pathology develops against the background of advanced gingivitis. At the same time, the disease is considered incurable, but with a competent comprehensive approach to treatment, it is possible to achieve its stable remission and prevent disastrous consequences. The development of the disease is accompanied by redness and bleeding of the gums and painful sensations.
Symptoms may indicate the presence of periodontitis
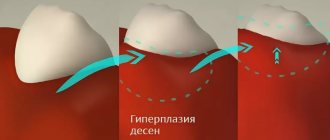
Fibromatosis and soft tissue hypertrophy
The pathology is a tumor-like lesion of the mucosa, in which hypertrophy occurs, that is, the growth of the gingival papilla, as well as the marginal and alveolar gums. With this clinical picture, the gingival tissue usually greatly increases in volume, which causes discomfort and bleeding, especially during meals. How it looks from the outside is shown in the photo below.
Fibromatosis is an overgrowth of gum tissue
It should be noted that fibromatosis is often diagnosed in children during the eruption of permanent incisors and molars, as well as in patients against the background of hormonal changes.
Why does gum fibromatosis occur?
Causes of the disease:
- genetic pathology - single gene mutations, some forms of Down syndrome;
- long-term use of certain medications - antiepileptic drugs, immunosuppressants;
- hormonal disorders – diseases of the endocrine system, long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, anabolic steroids, etc.
Surgery can also provoke tissue proliferation.
In addition, symptoms similar to fibromatosis appear in some types of chronic infectious stomatitis.
A genetically determined form of gum hypertrophy is diagnosed after dental prosthetics and can last a lifetime, requiring periodic treatment. Dosage and hormonal forms can appear regardless of the patient’s gender and age and disappear completely after the cause is eliminated: for example, discontinuation or replacement of the drug, treatment of an endocrine disease.
How to treat inflammation and hypertrophy of gingival papillae
If obvious signs of inflammation appear, you should immediately contact your dentist. The sooner you do this, the easier and faster the doctor will be able to diagnose the problem and solve it. As part of the diagnostic examination, the specialist will conduct a visual examination and will likely send you for x-rays. In some cases, a CT scan, blood and urine tests, and biochemistry may be required.
Having established the exact cause of the symptoms, the specialist will prescribe adequate treatment. Below we briefly describe the main directions of therapy that are relevant in such cases.
Coagulation - cauterization
We are talking about a modern method of surgical treatment, in which wounds and ulcers on the mucous membrane of the mouth are cauterized using an electrode with a force of 2 amperes. Under the influence of current, blood clots and wounds are clogged, which helps stop bleeding. Additionally, coagulation ensures disinfection of damaged tissues.
During coagulation, wounds are cauterized using an electrode
Medication therapy
Therapy using medications is aimed at stopping the inflammatory process and eliminating its characteristic symptoms, including reducing the sensitivity of tissues. For inflammation of the interdental papillae, the following procedures are usually prescribed:
- rinsing with antiseptic solutions such as Chlorhexidine and Miramistin,
- local applications using antibacterial and anti-inflammatory gels and ointments,
- irrigation with lidocaine spray to relieve pain,
- applications using vitamins A and E,
- rinsing with decoctions of medicinal plants, such as chamomile and oak bark.
Ointments and gels promote rapid absorption and action.
Additionally, therapy is carried out aimed at strengthening the immune system and improving metabolic processes in the body. For this, the patient is prescribed multivitamin complexes, for example, “Vitrum” or “Complevit”.
Antibiotics for purulent processes
Powerful drugs related to antibiotics are usually prescribed in cases where the inflammatory process has already led to the release of pus in the soft tissues. Such medications should never be taken without a doctor's prescription. Moreover, the treatment will be effective only if the pathogenic microorganisms are sensitive to the components of the antibacterial agent. For gum inflammation, Amoxiclav, Erythromycin, or, for example, Cephalexin may be prescribed.
For purulent processes, antibiotics are prescribed
Surgical intervention
Against the background of advanced hypertrophy of gum tissue, the level of the mucous membrane usually changes, and the interdental papillae greatly increase. Subsequently, such an aesthetic defect can be removed surgically. The doctor literally excises the excess overgrown tissue using special instruments or a laser. This operation is usually performed for hypertrophic gingivitis or fibromatosis.
If the situation is the opposite, and the inflammatory process has led to gum recession and exposure of the cervical area, soft tissue is built up by moving one’s own flap of mucous membrane to the place where it is missing, after which the doctor applies sutures. Such an operation is usually required for atrophic gingivitis, periodontitis, to eliminate the consequences of soft tissue necrosis.
The photo shows an operation to eliminate recession
What does traditional medicine offer?
As part of maintenance therapy, doctors often recommend rinses and applications using decoctions and infusions prepared from medicinal herbs. Such products are allowed to be used only after consultation with a specialist. Otherwise, self-medication can lead to worsening of the condition and dangerous complications.
Plants such as sage, oak bark, chamomile, calendula and rosemary have pronounced antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties. You can also prepare a decoction from the herbal collection. To do this, just take a teaspoon of each dried flower, pour boiling water, let it brew, strain and then use the resulting rinse at least 4 times a day.
Herbal decoctions can be used at home
Gum fibromatosis: treatment
For successful treatment of drug and hormonal forms of the disease, it is sufficient to eliminate the underlying cause (replacement of medication, elimination of hormone imbalance). The main method of treating hereditary gum hypertrophy is regular surgical treatment with a scalpel or laser. Moreover, each course of surgical intervention is carried out in stages and takes several weeks.
Sequence of surgical procedures:
- introduction of anesthesia - infiltration or conduction;
- excision of fibrous growths;
- removal of all loose teeth (if necessary);
- antiseptic treatment of the wound and application of a special membrane.
The healing process takes 1–2 weeks, after which the procedure is repeated on the other jaw. The frequency of procedures is individual and depends on the rate of progression of fibromatosis.
How to prevent inflammation of the mucous membrane after filling
There are cases when the gums become inflamed after the filling procedure. Of course, the situation is extremely unpleasant, because it would seem that the patient went to the doctor and is now waiting for relief, but in the end a new problem arises. To minimize the risk of encountering such a nuisance, it is better to spend time finding a good clinic and an experienced doctor. And experts in the field of dentistry cite the two most optimal options for preventing such complications.
Use high-quality modern materials to cover proximal cavities
When filling complex cavities, which include approximal ones, it is recommended to use modern materials: photocomposites or glass ionomer cements. Light-curing composites are rightfully considered the best choice for filling procedures. They contain an optimal ratio of large and small particles, which increases their functional characteristics after hardening. Such materials adhere firmly to dental tissues and closely correspond to them in terms of key indicators, including biocompatibility.
When treating teeth, you should choose only high-quality materials
Use restoration tabs
If the cavity is too large or complex, due to which the use of photocomposite or glass ionomer cement cannot guarantee the integrity and reliability of the filling, it is better to resort to the help of a restoration inlay. We are talking about a microprosthesis, which is created from impressions in the laboratory and is used to restore the integrity of a damaged tooth. Such inlays are usually used for various forms of carious lesions, mechanical damage to crowns, pathological abrasion, or after unsuccessful attempts at filling using the classical method.
The photo shows dental inlays
Marginal periodontitis – complex treatment
If the inflammation is caused by marginal periodontitis, the most important thing is to eliminate the causative factor as quickly as possible. This could be an incorrectly installed filling or an uncomfortable orthopedic design that creates a constant mechanical impact on the mucous membrane. Next, the patient must undergo appropriate treatment from a periodontist.
Anti-inflammatory therapy using local drugs
To treat marginal periodontitis, doctors usually prescribe a whole range of different procedures aimed at relieving inflammation and restoring affected tissues. As part of the therapy, rinses, applications, gingival dressings, injections and oxygen therapy are prescribed. Additionally, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions, ointments and gels are prescribed for self-use at home.
General drug treatment
If the gums near the tooth become inflamed, more powerful medications, such as antibiotics, may also be prescribed. Medicines of the following pharmacological groups are also usually prescribed: multivitamins, desensitizing drugs, adaptogens, and immunostimulating agents.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy is also often used to treat gums. This category of procedures includes the following methods: laser or ultraviolet treatment, microwave therapy, heat treatment using paraffin applications, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis.
Physiotherapy is also used to treat gums.
Hyaluronic acid in the treatment of diseases of the temporomandibular joints
Disruption of the temporomandibular joints can be caused by their overload due to malocclusion, increased tone of the masticatory muscles, or other reasons.
Pain when opening the mouth, clicking in the TMJ - these are common complaints with which the patient consults a doctor. How can hyaluronic acid injections help?
Hyaluronic acid is the basis of synovial fluid - the fluid that fills the joint capsule and reduces friction of the articular surfaces. Joint dysfunction is usually accompanied by a decrease in the amount of hyaluronic acid. The depreciation in the joint decreases, the articular surfaces are less lubricated, which increases friction, and, as a result, there is pain when chewing and restrictions in opening the mouth.
Injections of a drug containing hyaluronic acid temporarily restore the functions and properties of the joint fluid, which leads to the elimination of pain and increases the range of motion in the joint. Hyaluronic acid helps restore cartilage tissue and intra-articular structures, stimulates the production of hyaluronic acid in joint tissues, and improves the properties of synovial fluid.
Indications for the use of hyaluronic acid for problems with the temporomandibular joints:
- osteoarthritis of I-III degree,
- post-traumatic changes in the temporomandibular joints,
- prevention of osteoarthritis with increased tone of the masticatory muscles and overloaded joints due to malocclusion.
The dose, frequency of use and duration of the drug course are determined by the doctor only after a face-to-face consultation.
Injections of hyaluronic acid can be recommended for patients who are allergic to ibuprofen, aspirin and other drugs that are usually prescribed for joint inflammation, as well as when physical therapy is ineffective. Minor discomfort after administration of the drug and the appearance of slight swelling are completely offset by the pronounced therapeutic effect.
Home care during treatment of inflamed interdental papillae
The main condition for assisted home therapy is proper comprehensive hygiene. It is important to regularly brush your teeth twice a day with the right brush and toothpaste. After each meal, experts recommend using floss and rinsing your mouth. As an additional hygienic tool, it is worth purchasing an irrigator, which, by supplying an air-water jet under high pressure, allows you to efficiently clean even hard-to-reach places. And, of course, it is important to regularly visit the dentist’s office to undergo appropriate therapeutic and preventive procedures.
An irrigator is an additional device for maintaining oral hygiene
Inflammation in the gums spreads very quickly, so at the first suspicious symptoms you should immediately consult a doctor. It is easier to treat any mucosal disease at an early stage than to later try to cope with chronic processes and complications.
1Glebov, K.G. Difficulties in the differential diagnosis of papillostenosis and papillospasm, 2014.
Diagnosis of gum fibromatosis
The examination involves examining your mouth in the dentist's office. The mucous membranes are checked for soreness, color shade, tissue density and their level relative to the tooth crown.
Fibromatosis is classified as a tumor disease, so during the examination it is important to differentiate it from other types of neoplasms. To do this, additional diagnostics are prescribed:
- Biopsy and histological analysis of tissues make it possible to separate the disease from similar manifestations of poliomyelitis, periodontitis, and cancer.
- X-ray evaluates the condition of the alveolar processes of bone tissue and the structure of the jaws as a whole.