Symptom of "coma in the throat"
Murzaeva Irina Yurievna
Endocrinologist, Preventive Medicine Doctor
December 15, 2016
This is one of the most common complaints with which a person comes to an endocrinologist.
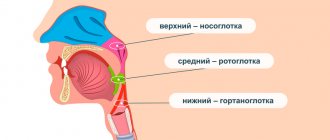
A lump in the throat can be described as a non-painful sensation of the presence of a voluminous foreign body in the throat, usually in the area of the jugular fossa, this is a “hollow” between the collarbones.
This may feel like a “tickling” in the throat, a “stuck pill” feeling. This symptom differs from the symptom of dysphagia by the free passage of food through the esophagus without choking or choking.
Essentially this is a neurosis of the pharynx. But to understand this, you need to understand the criteria. According to medical parameters, the symptom of “coma in the throat” is set according to the following Rome III recommendations (provided that the symptoms have been present for at least 3 months, this is not a “one-time action”.
- constant or periodically occurring non-painful sensation of the presence of a voluminous foreign body in the throat;
- the appearance of a lump in the throat between meals;
- lack of evidence that this symptom is caused by gastroesophageal reflux;
- absence of histopathological changes (according to FGDS) that could affect the motility of the esophagus.
“Lump in the throat” is a functional condition (usually associated with stress of the globus hystericus type, and not a disease. To prove this, it is imperative to exclude diseases that are masked under it. And this is:
- esophageal motility disorder;
- head and neck tumors;
- diseases of the thyroid gland with goiter;
- cervical lymphadenoaptia;
- GERD;
- hiatal hernia;
- chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis or laryngitis;
- esophageal stenosis;
- spondylosis of the cervical spine;
- psychological disorders;
- increased tone of the upper esophageal sphincter.
To diagnose these conditions you need to undergo:
- ENT doctor, sometimes with video endoscopy of the larynx
- FGDS with determination of stomach acidity (ph-metry) followed by consultation with a gastroenterologist
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and blood tests for hormones
- consultation with a neurologist
- psychotherapist.
Actually, globus hystericus can be supplemented by other complaints that confirm its psychogenic nature, and these are:
- cardiopalmus
- increased sweating
- loss of appetite
- insomnia
- increased excitability
- irritability.
The concept of dysphagia is qualitatively different from the “coma in the throat” symptom. These are different concepts. Dysphagia is a feeling of stuck solid or liquid food, delay or disruption of its passage through the esophagus. And there are many more reasons that cause this condition and they are more severe. I will give just a few examples. Dysphagia occurs with strokes, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, butulism (mushroom poisoning), amyloidosis, esophageal diverticula, etc.
These are different concepts. Dysphagia is a feeling of stuck solid or liquid food, delay or disruption of its passage through the esophagus. And there are many more reasons that cause this condition and they are more severe. I will give just a few examples. Dysphagia occurs with strokes, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, butulism (mushroom poisoning), amyloidosis, esophageal diverticula, etc.
Therefore, dysphagia is divided according to the level of occurrence, which facilitates diagnosis:
- oropharyngeal: cerebral, neuromuscular, mechanical obstruction of food passage and esophageal.
For diagnostic purposes, the doctor can interview the patient using a special medical “Mayo Clinic Dysphagia Questionnaire . On the basis of which it is decided which diagnostic measures to apply in a particular case.
Dysphagia, unlike “a lump in the throat,” is always based on a specific disease.
Treatment depends on the identified cause.
Sore throat and gastritis: an unobvious connection
This will probably seem “strange,” but a sore throat can actually be a consequence of gastritis, or more precisely, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Pain in this case appears “on its own”, without other traditional signs of acute respiratory infections. But rinsing, inhaling or taking antibiotics obviously doesn’t make it better. So how not to confuse acute respiratory infections and GERD? And what else does pathology threaten?
What is GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a chronic pathology with a relapsing course, characterized by periodic spontaneous reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus and larynx, and the development of lesions resembling chemical burns.
This type of reflux is felt as heartburn or a sour taste after a burp, and most often appears after eating, during sleep, or when bending the body forward.
At the same time, it also occurs in a healthy body, after eating. True only if it is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations and extra-esophageal symptoms.
These symptoms include:
- pain behind the sternum, radiating to the neck, lower jaw, interscapular area and left half of the chest, which can simulate angina pectoris;
- sore and sore throat, hoarseness, laryngitis;
- as well as cough, shortness of breath and severe bronchospasm, reminiscent of asthma.
As you can see, GERD successfully disguises itself as several fundamentally different diseases, often leading clinicians down a false diagnostic and therapeutic path.
For example, “provokers” of coughing and choking are often sought among allergens. Chest pain leads to a cardiologist. Laryngitis is treated with antibiotics.
Such treatment, however, will not give any tangible results. After all, the true cause of the pathology lies in excessive acidity of the stomach and insufficiency of the lower esophageal sphincter (“flap” between the esophagus and stomach).
How to check for GERD
The classic way to detect GERD is 24-hour intraesophageal pH-metry.
However, the method cannot be used in a screening format and for self-diagnosis, since it requires the installation of a nasopharyngeal tube and is associated with the psychological experiences of the patient.
Unfortunately, medicine does not yet know another reliable and non-invasive way to assess acidity in the esophagus. However, GERD can be indirectly assumed using the Gastrocomplex blood test.
The complex includes the definition:
- Gastrina-17,
- Pepsinogen (I, II and their ratios)
- and antibodies to H. pylori,
which allows, with a high degree of efficiency, to detect the presence of hyperacid (with high acidity) gastritis and Helicobacter pylori infection, which are the “basis” of GERD.
In addition, the analysis is widely used to identify atrophic gastritis and the risk of gastric oncology.
Treatment
Viral pharyngitis usually resolves within 5-7 days. The child should be provided with:
- peace and the opportunity to sleep as much as he wants;
- Drink plenty of fluids to relieve sore throats and prevent dehydration;
- air humidification;
- a sore throat can be relieved by both warm drinks and cold ice cream, especially popsicles;
- for a sore throat, it helps to gargle with a solution of table salt - a teaspoon per 250 ml of warm water;
- Children over 4 years old can be offered lozenges for sore throats. Do not give candy to small children - they may choke;
- do not smoke when your child is sick, avoid strong odors that irritate the throat;
- A sore throat and fever can be relieved by medications containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. Don't give children aspirin; in rare cases, it can cause deadly Reye's syndrome.
Confirmed bacterial pharyngitis is treated with antibiotics. You should not interrupt or stop the course, because this increases the likelihood of infection spreading to the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs. Continue taking antibiotics even if your symptoms are completely gone.
You can make an appointment by phone: + .
Clinical picture
Along with the feeling of a lump in the throat, the patient also experiences other symptoms that indicate osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Pain in the neck and collar area.
- Crunching when moving in the cervical spine.
- Cerebral symptoms: dizziness, headaches, blood pressure surges.
- Skin sensitivity disorder of the upper extremities.
- Dysfunction of the vestibular system – unsteady gait.
- Peripheral neuropathies - plexitis, radiculopathy with typical pain radiating to the upper limbs and the back of the head.
When laryngopharyngeal syndrome develops, the following symptoms occur:
- feeling of throat constriction;
- difficulty swallowing;
- tingling and burning in the throat;
- attacks of lack of air;
- sore throat;
- pain under the jaw and behind the ears.
Provoking factors that contribute to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms in the throat with osteochondrosis are:
- Prolonged stay in a static position with tension in the muscles of the neck and collar area.
- Sudden turns or tilts of the head.
- Pain in the neck area.
- Sleeping at night in an uncomfortable position with an incorrectly selected pillow.
What does the color of sputum indicate when you cough?
Sputum that is rusty or brown in color
The rusty color of sputum when coughing, as well as its brown shades, is often found in smokers. This happens due to the accumulation of tobacco combustion products.
In other cases, a reddish-red hue of mucus is a sign of blood in the respiratory tract. However, there is no need to panic: this happens when small blood vessels rupture during a strong cough, and the darker the mucus, the more time has passed since the blood loss.
Brown and rust-colored sputum can be caused by:
- inflammation of the bronchi or lungs;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- pneumonia;
- cystic fibrosis;
- lung abscess.
Yellow sputum
Yellow bronchial mucus is common. This is a kind of response of our immune system to the appearance of infection in the respiratory tract.
The yellow tint of mucus is characteristic of:
- flu;
- ARVI;
- bronchitis;
- sinusitis.
If the sputum is yellow when coughing and contains impurities of pus, this may indicate pneumonia. The bright canary color is characteristic of pulmonary aspergillosis, a disease caused by the mold Aspergillus.
In many cases, yellow mucus appears in the initial stages of colds. As the pathological process progresses, it acquires a greenish tint.
Green sputum
Green mucus is a sign of an active bacterial infection. The causative agents can be staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella.
Diseases that occur with green sputum:
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- purulent bronchitis;
- laryngitis;
- pneumonia;
- cystic fibrosis (sputum is produced in the form of lumps);
- lung abscess (thick green mucus with a distinct unpleasant odor).
Green sputum when coughing gets this color due to white blood cells - neutrophils. This is the most numerous group of leukocytes, and they are the ones “attracted” by the body to fight fungal and bacterial infections. Neutrophils simply absorb pathogenic microorganisms - so they always end up in the place where the pathogen appears.
Pink or red sputum
Pink sputum usually indicates mild bleeding, which is provoked by aggressive coughing attacks. However, if symptoms do not decrease for more than three days, or the sputum becomes more saturated red, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The mucus gets its red color due to the presence of blood impurities. This symptom is typical for:
- tuberculosis;
- abscess;
- pulmonary infarction;
- oncological diseases of the respiratory system;
- pulmonary edema.
In addition, foamy mucus with bloody inclusions is a characteristic sign of anthrax.
But foamy pink sputum when coughing often indicates pulmonary edema, which in turn can be caused by heart failure. The appearance of such mucus during expectoration is a reason to consult a cardiologist.
Bloody sputum often indicates a dangerous condition, so you should never hesitate to see a doctor.
White sputum
White sputum is a signal of an inflammatory process in the respiratory tract.
- It can often be observed in the initial stages of viral bronchitis (in later stages, the mucus becomes yellow or greenish).
- Another reason for the appearance of white sputum is being in an environmentally unsafe place and, as a result, intoxication of the body. It can also be caused by taking certain medications or drugs.
- If white mucus is released in the form of lumps and the consistency resembles curdled, this may be a sign of pneumonia of fungal origin. Antibiotics do not help in this situation: to treat this type of inflammation, special antifungal therapy is required.
White sputum when coughing means that the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is swollen. Because of this, liquid transparent mucus cannot easily move through them, and gradually acquires viscosity and a white color.
Gray or blackish sputum
A light gray tint to sputum is natural for infectious diseases in their initial stages. It could be:
- acute respiratory infections;
- ARVI;
- flu.
Saturated gray or black mucus is quite rare. In particular, miners and representatives of other professions in which they have to inhale air with a large amount of suspended particles: coal dust, iron shavings, etc., suffer from a cough with the release of this kind of sputum.
Coloring substances in products such as Coca-Cola, strong tea, and dark chocolate can also give sputum a dark color.
Smoking can also cause gray and black mucus: this is typical for long-term smokers.
In some cases, the gray color of sputum when coughing indicates an advanced stage of tuberculosis, as well as cancer of the respiratory system.
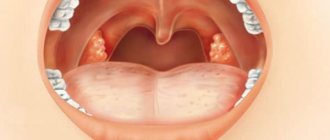
What is pharyngitis?
This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and its lymphoid tissue. With pharyngitis, the throat is sore, sore and irritated. The pain intensifies when swallowing. Pharyngitis usually develops with influenza and ARVI. Viral pharyngitis usually goes away on its own. Some other less common forms of pharyngitis may require treatment.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
Typically, the ENT examines the patient's throat, as well as his nose and ears, carefully palpates the lymph nodes, and listens to breathing using a stethoscope.
The streptococcal test is a simple and accurate way to diagnose bacterial pharyngitis. The doctor takes a scraping from the child's throat, and within 24-48 hours the result is ready. Streptococcal pharyngitis will have to be treated with antibiotics.
We have our own laboratory in the clinic, so you can always take all the necessary tests with us!
Risks and measures to prevent pharyngitis
Pharyngitis most often affects children and adolescents; adults also get sick, but somewhat less frequently. Also, the risks of pharyngitis increase with dry air, throat irritation from tobacco smoke or chemical reagents, allergies, weakened immunity, chronic or frequent infections of the nasopharynx.
You can reduce the likelihood of illness in the same way as in the case of other nasopharyngeal infections: wash your hands, do not drink from the same cup with others, cover your mouth when coughing and sneezing (do not “share” your viruses), wipe the screen and keyboard of phones and other devices etc.