Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity has its own microflora and its own specific diseases arise. Let's talk about one of them - fibrous epulis of the gums: what kind of disease it is, what are the causes of its occurrence, how is the treatment carried out.
Growth on the gum: why it appears and how to treat
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the cause
Infectious diseases
Non-communicable diseases
Types of growth
Gum cancer
Lump after crown installation
Growth on the gum: how to treat
Which doctor should I contact if a growth appears on the gum?
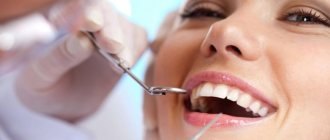
Normally, the gums have a smooth, pale pink texture. Any change, be it a thickening or a growth, signals problems in the body that cannot be ignored, as they pose a health hazard. Why lumps appear on the gums and how to treat them, we will tell you in the article.
Indications and contraindications
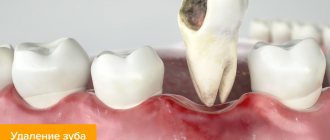
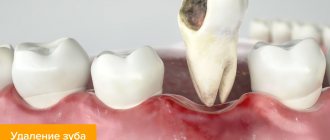
If the formation is large, leads to inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, jaw deformation, or interferes with talking or chewing food, then it is removed. The operation is also prescribed before prosthetics, since even small bumps become an obstacle to the installation of implants.
The patient himself can contact the surgeon if the bone spike spoils the aesthetics of the face. In this case, it is located on the buccal side and the protruding part is visible externally. An aesthetic defect gives a person more psychological discomfort than physical discomfort.
Before the procedure, the surgeon excludes contraindications. The list of restrictions includes infections in the mouth, acute respiratory infections, diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, poor blood clotting, exacerbation of chronic diseases, mental disorders, childhood, pregnancy and a number of other contraindications.
For children, surgery is delayed until they are 18 years old. This is due to the fact that the bones are still growing and the pathology can resolve on its own.
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the reason?
A lump or growth is a compaction on the gum caused by damage to periodontal tissue, which may appear without any previous signs. Growths appear in people of any age, but mainly in young children, as they unknowingly introduce infection into their mouths. The first thing you need to do when you detect formations in your mouth is to determine the nature of their origin (only a doctor can do this). It comes in two types:
- Infectious. The appearance of cones is caused by the activity of bacteria.
- Non-infectious. Bumps and growths as a result of injury, mechanical or chemical damage.
If a lump has formed in your mouth, you should consult a doctor to rule out possible complications. The doctor will help diagnose the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of exostosis of the jaw
At the initial stages of development, the pathology usually goes unnoticed, as it manifests itself asymptomatically. It is often discovered when examining a patient for other dental diseases. The formation is clearly visible on an x-ray.
As the growths increase, characteristic symptoms appear. Their intensity depends on the clinical picture: location, shape, size.
By what signs can pathology be detected?
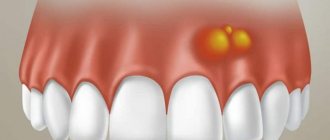
- the appearance of a tubercle or bump on the gums;
- sensation of a foreign object in the mouth, especially if the protrusion is located on the side of the tongue, at the bottom of the mouth;
- pain syndrome of varying intensity (occurs when injured by an acute growth of soft tissue);
- changes in the color of the mucous membranes in the area where the protrusion is located;
- jaw dysfunction if an osteophyte has formed near the jaw joint.
Unlike diseases of an infectious-inflammatory nature, it does not cause an increase in temperature, burning sensation, purulent abscesses, fistulas, and does not affect the tightness of the gums.
Infectious diseases
| Gingivitis and periodontitis Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, often accompanied by the appearance of a red ball-shaped growth near the tooth. The next stage is periodontitis. With it, purulent discharge is observed, and the lump acquires a grayish or beige tint. |
| Granuloma or cyst When pulpitis is advanced, the inflammatory process reaches the apex of the root, where a granuloma forms. Often this process goes unnoticed by the patient, so he is in no hurry to see a doctor. Over time, the pathology can develop into a fistula - a white formation on the gum. |
| Flux Purulent inflammation on the gums occurs against the background of advanced caries or pulpitis, a poorly treated root canal. At the first stage, minor pain appears; on the second - swelling and redness; on the third, the temperature may rise and the cheek may swell; on the fourth – the pain becomes sharp and throbbing, swelling increases. |
Causes
The question of the etiology of osteochondromas remains open to this day. A number of authors do not recognize the tumor nature of osteochondromas, but consider it as a violation of the process of enchondral ossification (as a result of dysembryogenesis ). Many authors are inclined to believe that the appearance and development of osteochondroma is associated with a congenital pathology, the development of which continues throughout the entire period of bone growth (that is, the epiphyseal plate is displaced during the formation of the child’s bones even during the intrauterine formation of the skeleton).
Factors that increase the risk of its development include:
- Ionizing radiation.
- Severe bone bruises and fractures.
- Disruptions in the endocrine system.
- Infectious diseases.
Non-communicable diseases
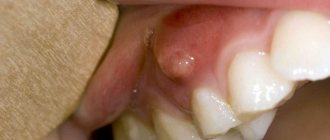
| Epulis This is a benign formation. It has a stem and a cap. Most often it occurs due to malocclusion, improper prosthetics, and hormonal changes. In the absence of adequate treatment, the tumor can develop into a malignant one. |
| Exostosis A bone growth that occurs against the background of a jaw abnormality - the bone extends beyond its usual boundaries, forming a lump. Most often, the reason lies in a genetic predisposition, less often - as a result of injury or complex tooth extraction. |
| Hematoma As a rule, it is formed as a result of an impact and goes away on its own over time. If there is damage to the tissue, then surgical intervention is necessary. |
Tests and diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the patient’s complaints, medical history, results of a physical examination and X-ray data in 2 projections, in which the tumor is visualized as an additional shadow with smooth, clear contours, connecting to the bone with a wide base or pedicle. If the cartilaginous cap does not contain calcifications, then it is not visible on the images. Additional methods of instrumental examination are:
- CT scan, which makes it possible to track the presence of a connection between the central part of the formation, which is filled with bone marrow contents directly with the medullary canal of the maternal bone.
- MRI - allows you to obtain data on the thickness of the cartilage cap, which allows you to determine the nature of the tumor (a thickness of more than 2 cm is a sign of malignant transformation).
- Differential diagnosis is carried out with other types of benign tumors ( chondroma , osteoma , osteoblastoma , chondroblastoma , osteoid osteoma ).
Types of growth
New growths on the gums vary in shape, size, and method of formation.
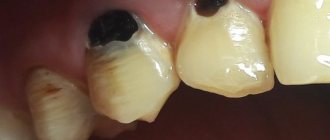
- Angiomatous growth. A soft, bumpy, pink growth that grows very quickly. Often reappears after removal. This growth is diagnosed in children aged 10-12 years; as a rule, it does not occur in adults.
- A fibrous growth is a gum-colored lump. It grows slowly and does not cause pain, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor.
- Giant cell growth. A rapidly growing neoplasm of red-blue color, from which serous fluid is secreted. The lump is easy to injure.
General idea of exostosis in the mouth
New growths on bone tissue are found in different parts of the body. Exostosis in dentistry according to ICD-10 refers to other specified diseases of the jaw K-10.8. The osteochondral formations look like a protrusion, lump, mushroom or ridge, and can branch and be tortuous. When they grow, they injure the mucous membranes of the mouth, which provokes the development of inflammation.
Zkzostoza on the upper jaw are less common than in the mandibular region. Usually formed on the alveolar process on the side of the cheek. When the size increases, they affect the aesthetics of the face, creating asymmetry. In the lower jaw, exostosis often forms on the lingual side. Protrusions can interfere with chewing food and talking.
You can see what exostosis looks like on the gum or bottom of the lower jaw in the photo. If the formation is small, then it is difficult to notice it visually.
Gum cancer
This dangerous neoplasm is worth highlighting separately. Mutation cells begin to divide uncontrollably, which is why a red tumor forms on the gum. The disease progresses quickly and over time can develop into jaw cancer.
What are the symptoms?
- General weakness;
- increased body temperature (37 C°);
- loss of appetite;
- constant drowsiness.
The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis after a detailed examination. As a rule, treatment is long and painstaking. With timely medical intervention, the outcome is favorable.
How is the operation performed?
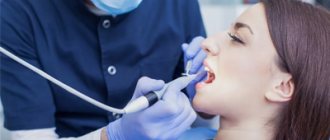
Like the operation to remove exostosis on the leg, there are also 4 main stages in dentistry.
- Pain relief in the mouth using local anesthesia.
- The surgeon makes a careful incision on the gum.
- The build-up is removed using a drill or laser, and the remaining surface is carefully sanded.
- The gum returns to its original place, the specialist applies stitches. To make the removal of exostosis of the lower jaw more effective and the bone to recover faster, it is possible to apply artificial bone.
As a rule, removal of exostosis of the upper jaw, as well as the lower one, takes place without any complications or problems. It is important to follow all the specialist’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period and provide proper care. In particular, limit your diet to soft foods, no alcoholic beverages, taking medication (prescribed by a doctor), treating the oral cavity with antiseptic drugs, etc.
A healthy and beautiful smile is simple. Even if this requires manipulation to remove the root of a tooth, exostosis, the hood of a wisdom tooth (or the tooth itself) or anything else, over time you will see that it was worth it in every sense. And the specialists of the Priority clinic are always ready to try their best for you.
Growth on the gum: how to treat
The treatment plan is developed by the doctor based on the nature of the growth, so in no case should you self-medicate. It is important to understand that if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, serious complications can arise.
If the cause is an infection, then it must be removed. In case of periodontal inflammation, professional oral hygiene is performed. If the cause is periodontitis and complicated pulpitis, then first the lump is opened and pus is pumped out of it, and then conservative or surgical treatment is carried out.
If there is no pain, for example, with epulis or ecostosis, then the decision about surgical intervention is made together with the patient.
Rehabilitation after removal of exostosis
The wound heals completely in about 1 week. For better tissue healing and prevention of complications, it is necessary to comply with the doctor’s requirements.
During the recovery period, you should not exercise or overheat the body. It is prohibited to visit the bathhouse, sunbathe on the beach, or take a hot bath. Otherwise, bleeding from the wound may occur.
In order not to injure the damaged mucous membrane, you should not eat rough, spicy or sour foods. Food should be liquid or pureed, at a comfortable temperature. It is undesirable to smoke, as nicotine constricts blood vessels, which prevents rapid healing.
When brushing your teeth, you should avoid the operated area. The toothbrush should be soft. After eating, you should rinse your mouth with warm water. Daily rinsing with antiseptic solutions, for example, chlorhexidine, miramistin, is recommended. For these purposes, you can prepare decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula, and oak bark.
In the first few days, pain and swelling of the tissues persist. To relieve acute pain, you can take analgesics. A cold compress will help relieve swelling. Ice or frozen product is wrapped in plastic wrap, cloth and applied to the cheek several times a day.
If the patient is in poor health or has chronic diseases, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
If you ignore the dentist’s requirements, complications may occur: infection and inflammation of the wound, bleeding, suture dehiscence.
Exostosis of the humerus
The humerus is one of the most common sites of osteochondroma. During its formation, the following may be observed:
- dull pain in the shoulder area that occurs when moving the arm with a large amplitude;
- a feeling of stiffness in movements, present mainly in the morning, until you manage to warm up;
- limited mobility of the upper limb in the shoulder;
- dystrophy of the muscles of the shoulder and forearm, which in difficult cases can be seen with the naked eye.
Exostosis in a child
It is in children that osteochondroma is most often first diagnosed, which is due to its formation from cells of the epiphyseal plate that is present only until the end of the growth period, which is adjacent to the metaphysis. It is also called the bone growth zone, since it is a hyaline cartilage whose cells are in constant miotic division. As a result, new chondrocytes (cartilaginous tissue cells) are formed, forming the epiphyseal plate, and the old ones are shifted to the metaphysis and subsequently replaced by osteoblasts (bone tissue cells).
In infants, violation of the rules for the prevention of rickets, in particular excessive use of vitamin D preparations, increases the likelihood of the formation of exostoses.
After puberty, the growth plates gradually close and are replaced by bone tissue, transforming into a thin epiphyseal line. If hormonal imbalances occur during this period, it is possible that the growth zones may remain open, which creates the preconditions for the formation of osteochondromas.
Usually, until the age of 7-8 years, bone exostosis does not manifest itself in any way in a child and makes itself felt only during the period of intensive growth, i.e., at 8-16 years, since it also begins to grow actively. In young children, such growths are present in the metaphysis area immediately near the epiphyseal plate, but subsequently move away from it and approach the diaphysis. Therefore, by how far the bone exostosis in children is from the epiphysis, the time of its formation is determined.
The growth of the neoplasm continues until the end of the growth period.
Exostoses of the ribs
The formation of growths on the ribs is more often observed with curvatures of the spine, which also lead to deformation of the chest. Their growth causes fixation of the pathological position of the chest and limitation of the vital volume of the lungs. As a result, respiratory function disorders may occur, which provokes the appearance of signs of hypoxia (oxygen starvation). To a greater extent, the lack of oxygen affects the brain, which can be accompanied by dizziness, headaches and other disorders. The heart, liver, spleen, and other internal organs are also sensitive to changes in the gas composition of the blood.
Exostosis of the calcaneus (calcaneal spur)
This is a well-known type of osteochondroma. The growth can take on different shapes, which determines the characteristics of the symptoms that arise. With a spherical or mushroom-shaped neoplasm, after it reaches a size of 3-4 cm, pain appears when walking and the inability to fully step on the foot. Since the growth is located in an area that is constantly subject to friction from shoes, the skin in its projection gradually becomes coarser and thickens. A characteristic symptom is an increase in pain in the morning and a gradual decrease in its severity during the day. In the evening, swelling of the lower extremities is often observed.