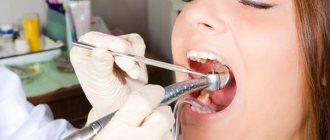
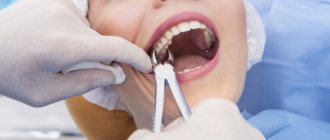
Despite tooth-preserving trends in world dentistry, in some cases only tooth extraction can resolve the situation. In this case, removal is considered a surgical intervention. Even the simplest procedure, when a tooth is loosened and practically falls out on its own, still cannot be done without blood and the formation of an open wound. Such organ removal is classified as simple, and all other cases when it is necessary to use special tools and difficulties arise during removal are regarded by specialists as complex tooth extraction.
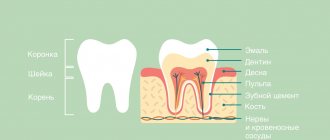
The complexity of this procedure depends on the anatomical structure of the organ and its location in the tissues. The socket in which the organ is located is equipped with alveolar processes or ligaments that are attached to the root. This ligamentous apparatus holds the organ quite rigidly, attaching it to the bone tissue. If a tooth has three or even four root processes, then pulling it out of the tissues of the hole becomes really difficult. When the organ is strong and the crown is preserved, the task is simplified, but in practice the opposite is true, and there are many factors that create difficulties out of the blue. Such complications may be:
- complete or partial destruction of the dental crown;
- a pulpless organ (with a removed nerve), which has a fragile tissue structure;
- acute or chronic inflammatory process;
- the presence of altered tissues (cysts, granulomas);
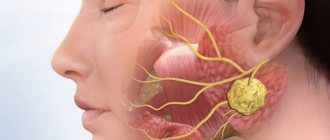
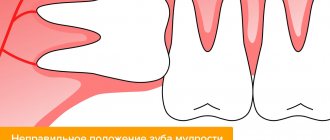
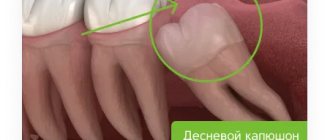
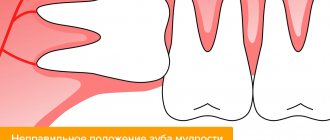
- wisdom teeth, which are located in a hard-to-reach place and have a strong ligamentous apparatus;
- impacted wisdom teeth, which have not yet erupted, but are already growing crookedly, squeezing neighboring organs.
Prices for services
Simple permanent tooth extraction from RUB 2,000.
Complex permanent tooth extraction from RUB 3,000.
Tooth extraction with detachment of the mucoperiosteal flap from RUB 3,500.
Inspection after removal 0
Removal of 1st supernumerary tooth from RUB 3,000.
Removal of a dystopic tooth from RUB 4,500.
Removal of impacted and dystopic teeth from RUB 5,000.
Removal of a tooth fragment from RUB 1,000.
Removal of a baby tooth from 700 rubles.
Initial doctor's appointment 0 rub.
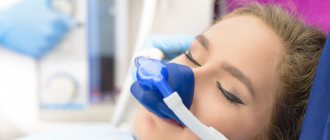
What anesthesia is used
Removal of “eights” is painless for the patient, because before extraction an effective anesthetic is injected into the gum area. The dose is calculated based on the severity of the clinical case and individual tolerance to the drug.
For simple removal, infiltration anesthesia is used (an injection is given into the gum). For complex ones – conduction (several injections of anesthetic along the facial nerve).
Anesthesia lasts throughout the entire operation. After the end of the drug's effect, painful sensations are possible. This is natural, because during intervention mechanical damage to soft (sometimes hard) tissues occurs. In such a situation, experts recommend taking painkillers.
Doctor's advice: before administering anesthesia, the surgeon asks the patient if he has any allergic reactions to any honey. drugs. If you have never had your teeth treated or removed under anesthesia, be sure to tell your doctor about it. He will monitor your condition more closely after he gives the anesthetic injection.
In what cases is complex tooth extraction required?
- Inability to cure one of the molars.
- Growth of wisdom teeth at an angle.
- Uncut "eights".
- Curved and severely damaged roots.
- Fusion of roots with jaw bones.
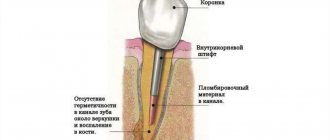
There is also such an operation as complex tooth root removal. Sometimes the tooth is completely destroyed from the outside, but the root remains in the jaw and continues to become inflamed and painful. In this case, the dentist cannot simply pull out the tooth with forceps, since there is nothing for it to grab onto. You have to cut the gum and use special tools.
Objectives of the operation
- sanitization of the body by eliminating foci of infection;
- effective elimination of pre-tumor processes caused by trauma to the tongue by teeth and oral mucosa;
- neutralization of acute odontogenic inflammation by draining the source of infection;
- improvement/regeneration of chewing function by creating optimal conditions for prosthetics and treatment of patients with anomalies of the dentofacial system.
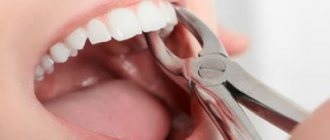
Based on the complexity of the procedure, a distinction is made between simple tooth extraction (simultaneous intervention without breaking the roots using forceps) and complex – with the use of additional tools, equipment and auxiliary manipulations.
What is the difference between complex removal and simple removal?
- The first difference is that complex removal takes much longer. A dentist can simply remove a tooth in 5–10, or maximum 20 minutes. But complex removal sometimes lasts for half an hour or even an hour.
- The second significant difference is the use of special tools. For simple removal, forceps are usually sufficient; for complex removal, elevators and other tools are used. Sometimes they look threatening, but in fact they are designed to cause as little discomfort to the patient as possible and minimal trauma to the tissue.
- The third difference is the need to cut the gum. With a simple extraction, it is usually enough just to pull out the tooth, but with a complex extraction, parts of it are hidden deep under the gums - in the bone, so you have to make incisions and then apply sutures. This, in turn, leads to a more difficult and longer recovery period.
- The last important difference is that after a complex extraction, the gums hurt more, and the risk of complications is higher. Therefore, it is important to take all medications prescribed by your doctor and maintain good hygiene.
Possible complications
Serious complications can be caused by ignoring medical recommendations, the presence of concomitant diseases (periodontal disease, periodontitis, hemorrhagic abnormalities), or violations of surgical technique:
- bleeding
_ Prolonged blood loss worsens the condition - severe weakness, dizziness, pale skin appear, pulse quickens, blood pressure decreases. If the alveolar bleeding cannot be stopped for several days, you need to consult a doctor who will perform coagulation and stitches will be placed on the wound; - alveolitis
. Inflammation of the walls of the socket (alveoli), characterized by aching pain in the soft tissues, aggravated by eating. Alveolitis causes swelling and redness of the gum mucosa, fever, headache, lymphadenitis, abscess, and osteomyelitis of the jaw. Treatment consists of cleansing the socket from necrotic decay products, prescribing local anti-inflammatory drugs; - sharp bone edges
. The occurrence of pain in the postoperative area may be due to the protruding edges of the socket, traumatic to the mucous membrane. Painful sensations manifest themselves 4-5 days after the intervention and intensify when touched with the tongue. The bone edges are removed surgically under local anesthesia; - change in the position of adjacent healthy teeth
. After extraction, adjacent organs may become mobile and begin to tilt in its direction, which can lead to disruption of the chewing process and bite deformation. It is recommended to replace the removed unit and restore the dentition with an artificial analog using implantation, installation of removable/fixed orthopedic restoration.
Progress of the procedure
Before complex removal, the doctor must prescribe an x-ray to the patient. This is necessary in order to understand the configuration of the roots and know where to make the incisions and what to prepare for during the operation. After preparation, the actual removal begins:
- The patient is given anesthesia. Modern powerful anesthetics can completely eliminate pain during surgery. If the patient cannot tolerate anesthesia or is undergoing a very complex procedure, full anesthesia may be given instead of anesthesia. In this condition, sometimes even several teeth are removed at once.
- If the tooth is partially hidden by the gum, that is, it has not fully erupted, the gum is cut to gain access to it. The problematic tooth is removed using a special elevator.
- If the tooth is completely hidden by gum and bone tissue, it is necessary to cut most of the gum, cut the tooth into 2-3 parts and remove them one by one with an elevator.
- In the most difficult situations, when the lower teeth are close to the mandibular nerve, the operation becomes more complicated, since the roots sometimes completely surround the nerve. In this case, you must first cut down part of the tooth, gain access to the roots, and then divide and extract the roots one by one so as not to damage the nerve.
Indications
Modern medicine adheres to the principles of maximum preservation of permanent dental units and uses every opportunity to cure them, but there are a number of diseases in which a problematic tooth must be removed in order to avoid the development of dangerous somatic conditions/pathologies: endocarditis, arthritis, myocarditis, pyelonephritis:
- active stage of odontogenic osteomyelitis. During the intervention, pathogenic flora and tissue decay products from the infectious focus are eliminated, as a result of which intraosseous pressure stabilizes and the inflammatory process subsides;
- osteomyelitis of the jaws. Organs with “dead pulp” located in the area of inflammation are removed;
- periostitis, peri-maxillary abscesses, phlegmon, lymphadenitis;
- chronic periodontitis;
- periodontitis with damage to the supporting apparatus;
- follicular/perihilar cysts;
- benign/malignant tumors of the jaw;
- root fracture, dystopic/retained row units;
- orthodontic indications, such as removal of an excess unit.
Recommendations after complex tooth extraction
Immediately after surgery, you should neither drink nor eat for the first 2–3 hours. Then for 2-3 days it is better to eat only soft and liquid food, and in the first week, chew only on the opposite side of the jaw.
It is important not to rinse, clean or warm the wound, and not to rinse anything without a doctor’s instructions. In this case, it is necessary to brush your teeth, but you should try not to touch the surgical area with the brush so as not to damage the sutures.
Contraindications
There are local and general diseases that are contraindications to extirpation of the unit. In this case, the tooth is removed after therapy and preparation of the patient; in case of severe concomitant pathologies in the anamnesis, it is better to carry it out in a hospital setting:
- odontogenic periodontitis;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- stomatitis, gingivitis;
- lesions of the mucous membrane due to viruses, syphilis, tuberculosis;
- hypertensive crisis;
- pregnancy;
- blood diseases;
- nervous system;
- psychical deviations;
- chronic heart disease;
- precancerous conditions, benign/malignant tumors.
What to do if you have pain
In the first 5–7 days, the gums will definitely hurt. This is a normal reaction to a serious intervention, so there is no need to panic. To relieve pain, your doctor will prescribe pain medications, possibly even prescription ones. You should not take painkillers without a doctor's prescription - they can cause bleeding and other complications.
Over the course of this week, the pain should gradually subside. If it gets worse and the gums at the extraction site become red and swollen, this may be a sign of inflammation. If the pain is severe, you should visit the dentist.
If the pain does not go away after 7 days, it is better to consult a doctor. This happens when an infection enters a tooth. If you don't see a doctor right away, it can cause inflammation of your jawbone.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Lyubomskaya Olesya Alekseevna
Dental surgeon-implantologist, dental therapist, dentist - orthopedist (K.M.N.) (Candidate of Medical Sciences).
You may also be interested in:
Wisdom tooth removal Tooth extraction Removal of the dental nerve Resection of the apex of the tooth root Removal of an impacted tooth Removal of the tooth root Removal of a dystopic tooth Excision of the hood
Show more
Preparing for surgery
In order for the removal to proceed without complications, you should properly prepare for surgery:
- Before the procedure, you should not refuse medications that are taken for chronic pathologies - epilepsy, hypertension, diabetes. At the appointment, you must inform the dentist about prescribed medications and existing diseases;
- in case of acute inflammatory process, 24 hours before surgery, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs, and anesthetics are indicated. The dosage should be checked with your doctor;
- Before visiting the dental office, it is recommended to eat a hearty meal - the blood of well-fed people clots faster, and the body better resists stress. Alcohol is strictly contraindicated - it can change blood counts, there is a risk of prolonged bleeding and swelling;
- in case of severe anxiety, as a rule, the use of sedatives 30-60 minutes before the procedure is allowed;
- You should be careful about your oral hygiene: brush your teeth thoroughly, use a mouthwash.
Traumatic intervention in a calm period is tolerated more comfortably than in an acute one. If a row unit is subject to extirpation, you should not wait for pain to appear - it is better to visit a doctor and have it removed as planned, rather than in an emergency.