At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza you can:
- quickly and efficiently examine the condition of the tonsils (perform pharyngoscopy, laboratory tests - bacteriological, immunological, etc.);
- decide on the choice of effective treatment for tonsillitis (inflammation of the palatine and pharyngeal tonsils): conservative - general and local, surgical.
We use the following methods of low-traumatic surgical treatment:
- tonsillotomy - partial removal of tonsils (tonsils) in children while maintaining their protective functions (all operations are performed under anesthesia);
- tonsillectomy - a low-traumatic operation to remove the tonsils;
- suturing wounds and using a bipolar coagulator to prevent blood loss;
- the use of innovations that accelerate and facilitate the healing process.
Timely diagnosed tonsillitis has a positive prognosis with conservative treatment without transition to the chronic stage. Radical treatment of chronic tonsillitis - tonsillectomy - prevents the development of systemic complications, often leading to disability.
Indications
The main indication for tonsil removal is chronic tonsillitis. This is an inflammation of the tonsils with frequent relapses - 5-7 exacerbations of the disease over 1.5-2 years.
There are other indications that in most cases accompany chronic tonsillitis. This:
- decompensation of the disease – absence of periods of remission, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- purulent complications - peritonsillar abscess, phlegmon of the neck;
- the risk of developing pathologies of other organs and systems (joints, kidneys, cardiovascular system);
- swallowing disorders;
- breathing problems during the daytime;
- Night apnea is a syndrome that stops breathing during sleep.
Conservative therapy
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor draws up an individual treatment plan. Acute tonsillitis is treated by a therapist on an outpatient basis using conservative methods, using antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets, rinsing, washing, and irrigation of tonsil lacunae.
Therapy of chronic tonsillitis is the responsibility of an otolaryngologist, who acts together with an immunologist.
A good result in the treatment of the disease is achieved by affecting the tonsils themselves. The hospital's otolaryngologists conduct courses of medical manipulations, during which:
- caseous plugs are removed;
- The folds of the tonsils (lacunae), which hide foci of infection, are cleaned.
During the treatment process - washing, lubricating and irrigating the tonsils with medicinal solutions, inflammation is stopped, the compensatory stage of the disease is prolonged, which makes it possible to delay or avoid tonsillectomy. Additionally, complex treatment at home is prescribed.
Contraindications to tonsillectomy
The operation is not performed during exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, other diseases of the ENT organs, during acute respiratory viral infections, caries, and for women during menstruation. These are temporary contraindications, after elimination of which tonsil removal can be performed. There are also permanent contraindications. These include:
- blood diseases, especially those associated with a high risk of bleeding;
- pathologies of the vessels of the pharynx;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- active pulmonary tuberculosis.
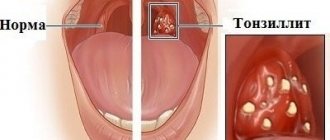
Symptoms of acute and chronic tonsillitis
Signs of acute tonsillitis, or tonsillitis, are characteristic and pronounced:
- sore throat when swallowing;
- redness and enlargement of the tonsils;
- enlargement of the submandibular and/or cervical lymph nodes;
- temperature rise above 38 degrees;
- the appearance of plaque on the tonsils, the accumulation of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils;
- headache;
- general weakness.
A characteristic sign of chronic tonsillitis is a constant low-grade body temperature (37.1-38.0 °C) with an increase in the evening. Sometimes small ulcers appear on the tonsils and spread to the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
The need for tonsillectomy is determined by an ENT doctor after a conversation with the patient, a visual and instrumental examination, and obtaining the results of diagnostic studies. Laboratory tests and instrumental examinations not only indicate the presence of chronic tonsillitis, but also reflect the degree of influence of the inflammatory process on the body. Some of the tests and examinations are necessary to ensure that there are no contraindications to surgery.
Before removing tonsils, the following is prescribed:
- general blood test with leukocyte formula;
- blood chemistry;
- blood clotting test;
- blood for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis;
- rheumatic tests;
- general urine analysis;
- ECG;
- FLG;
- culture from tonsils.
Survey
In the department of otorhinolaryngology (ENT) of the hospital, patients with a chronic form of the disease are examined using:
- pharyngoscopy (visual method);
- PCR diagnostics - a high-precision method of molecular genetic diagnosis of infectious diseases;
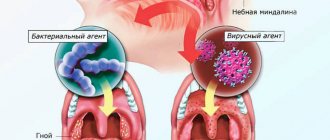
- bacteriological tests - diagnosis of the main agent of infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- antigen tests - diagnosis of immune system activity;
- general blood tests.
Types of tonsillectomy
Classic surgical method
The tonsils are removed using a scalpel, surgical scissors and a special loop. The procedure is quite painful. The disadvantages of this method also include the possibility of bleeding and a long healing period. In some clinics, postoperative bleeding is stopped using electrocoagulation. An advantage of the technique is the ability to remove the entire tonsil, including the capsule, and send it for histological examination.
Laser removal
Under the influence of laser radiation, liquid is evaporated from the tonsil tissue, and the vessels are coagulated, which avoids bleeding. The carbon dioxide laser is most often used; the technique is also called vaporization. The advantages of surgical treatment of tonsillitis with a laser include minimal operating time, painlessness and a quick recovery period. The disadvantages are the possibility of burning surrounding tissues. In addition, using classical laser vaporization, the size of the tonsils is often reduced (partial resection), since a fairly large tonsil is difficult to completely remove by evaporating the tissue.
Thermal welding
A type of laser tonsillectomy. The tonsil tissue is dissected using an infrared laser. The name of the method contains the word “welding”, since the infrared laser is capable of not only cutting tissue, but also connecting them. The thermal welding method allows you to perform virtually bloodless operations, very accurately remove the selected area without affecting the surrounding tissue.
Electrocoagulation
High-frequency electric current with pre-selected parameters is used to excise the tonsils. The advantage of the method is the low probability of bleeding due to vascular coagulation. The disadvantage is the possibility of thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
Radiofrequency ablation
The method is not used for total removal of tonsils, but is indicated for reducing their volume. The tissue of the tonsils is damaged by radio waves and subsequently scars, thereby reducing the volume of the tonsils. In this way, it is possible to preserve the immune function of the organ. Radio wave treatment is used for pathological growths of the tonsils (with full confidence in the absence of a malignant process), but is not suitable for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
Ultrasonic excision
Removal of tonsils is carried out using an ultrasonic scalpel. The advantages of this method of tonsillectomy are minimal damage to surrounding tissues and blood loss.
Coblation
The method is also called cold plasma scalpel. For tonsillectomy using this method, a device is used that converts electric current into low-temperature plasma. Using coblation, you can remove the tonsils completely or partially; the risk of bleeding during surgery is minimal, since the damaged vessels are immediately coagulated.
Microdebrider
For tonsillectomy surgery, a device with rapidly rotating blades is used. The tonsil tissue is cut away and immediately removed using suction. The method is used for partial removal of the tonsils, without excision of the capsule.
Reviews
Andrey
For most of my life I was tormented by constant exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis. Every spring and autumn I consistently lost two weeks for treatment. Surgery to remove tonsils has bothered me since childhood. My wife almost forcibly brought me to the clinic. I didn’t even imagine that new techniques can eliminate the problem absolutely painlessly. I have been living without constant exacerbations for a year now, and I am very grateful to the hospital specialists for this.
Natalia
Not long ago I had to bring my child to have his tonsils removed. From my own experience I remember how unpleasant and painful this procedure is. I was more worried than my son. However, the clinic doctors were able to find an approach to the child and calm him down. The operation was performed without pain or blood. Now I know for sure that your clinic employs super specialists and kind, sympathetic people.
Preparation for the operation and its implementation
No complicated preparation is required before a tonsillectomy. If the patient is taking anticoagulants (blood thinners), they are discontinued several days before surgery. However, this should only be done with the permission of a doctor. The evening before the intervention, you can take a mild sedative. The last meal should be 4-6 hours before the procedure.
The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia - the mucous membrane of the pharynx and the root of the tongue are irrigated or injected with an anesthetic solution. For young children, general sedation may be used. The duration of the procedure depends on the type of intervention, on average – from 20-30 minutes to 1 hour.
Recovery period
In most cases, after the operation the patient remains under observation in the hospital for no more than a day. This period can be extended with tonsillectomy using the classical surgical method.
Pain is normal during the first 24 hours. To relieve pain, you can use analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor. Adults should not eat on the first day after the intervention; children should not eat for 4-6 hours.
In the first 3-4 days after surgery, physical activity should be minimized. Within 5-6 days, scabs form on the wound surface after removal of the tonsils. They should not be removed by force; the crusts should come off on their own.
For 7-10 days you cannot visit the bathhouse, sauna, or do facial skin steaming procedures. When exposed to high temperatures, blood vessels dilate and bleeding may occur.
During the recovery period, it is important to follow a special diet. In the first week, you need to exclude solid foods, spicy, fried, and sour foods from the menu. Strong tea, coffee, carbonated drinks, and alcohol are also prohibited. You should prefer mushy food, pureed soups, pureed dishes. Drinks allowed are water, fruit drinks, compotes, and rosehip decoction.
Complications
Complications after tonsillectomy can be associated directly with mechanical effects (bleeding) and with the addition of infection.
Bleeding may occur during or immediately after surgery, or several days after surgery. According to various sources, this complication occurs in 2-10% of cases. In the early period, bleeding develops due to incorrectly chosen surgical tactics, concomitant diseases of the patient, and incorrect preparation for surgery. Secondary bleeding occurs during the rehabilitation period, when films and scabs begin to come off, most often due to active interference in this process. To avoid complications, careful preoperative preparation is necessary, compliance with all doctor’s recommendations - abolition of blood thinners before the procedure, a period of rest after surgery.
As a result of bacterial complications, in the first 5-7 days after tonsillectomy, the patient may develop purulent foci at the site of intervention, bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy, and lung abscess. Failure to maintain sterility during surgery carries the risk of developing septicemia - generalized damage to the body as a result of bacteria entering the blood. An important measure to prevent this complication is compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during surgery, medical supervision of the patient in the first few hours after the intervention, and following the doctor’s recommendations during the recovery period.
Syringe rinsing technique
The technique is used in all clinics. Washing is carried out in a treatment room. A syringe is used, on which a special curved metal tube is placed - a cannula.
- An antiseptic solution is drawn into the syringe.
- The free end of the cannula is brought to the lacunar fold filled with pus.
- By pressing the piston, a medicinal solution is supplied into the cavity.
- Together with pus from the tonsil, the liquid is poured into the patient’s oral cavity and then spat into a ditch.
- After washing out the purulent exudate, Collargol or Lugol's solution is applied to the tonsils.
While flushing, you need to inhale through your nose. If the nasal passages are congested, it is recommended to use nasal vasoconstrictor drops to ensure free breathing. To reduce the urge to vomit that appears when the tonsils are irritated, the sound “a” is pronounced.
People suffering from chronic tonsillitis often try to rinse their tonsils on their own during an exacerbation of the disease. Despite the fact that a special syringe with a cannula is sold in pharmacies, and the procedure seems simple, you should not rinse the tonsils yourself. Inept actions can damage the mucous membrane or cause the infection to spread to nearby tissues.
It is allowed to wash the lacunae yourself if it is not possible to see a doctor. The algorithm of actions is similar to that carried out by a doctor:
- spray antiseptic on tonsils for disinfection;
- open your mouth wider and stick out your tongue;
- breathe through your nose, taking shallow breaths;
- direct the stream from the cannula to the purulent accumulation;
- spit out the solution that has leaked out with pus.
However, you must understand that performing the procedure yourself can aggravate the process due to damage to the mucosa. In addition, the effectiveness of self-washing is significantly lower. If possible, it is better to entrust the manipulation to a specialist.