Tooth dislocation is a displacement of the tooth position in one direction or another, the direction of which depends on the direction of the impact force (impact). Dislocations of primary teeth are approximately three times more common than similar injuries to permanent teeth; this is due to the lower stability of primary teeth in the jaw bone.
Not all situations can be foreseen; if an injury occurs, you need to remember that the treatment of each type of dislocation has its own characteristics, and seeking dental care as soon as possible increases the percentage of favorable outcomes.
Causes of tooth dislocation
Dislocation occurs due to mechanical stress and is accompanied by damage to the ligamentous apparatus. This disease of the fangs and central teeth is often formed by a fall, impact, and molars - by inaccurate removal of nearby teeth. With dislocation, a fracture of the neurovascular bundle and the alveolar wall may occur.
The following reasons exist:
- biting into hard food;
- injury;
- inaccurate removal;
- bad habits such as opening bottles with teeth;
- foreign body in chewed food.
Prevention
Prevention of tooth dislocation includes:
- Explanatory work with employees of industries associated with increased injuries. Each employee is required to comply with safety regulations, which provide for an algorithm for performing certain actions and the use of protective devices.
- Explaining to parents and children the rules for arranging playgrounds and behavior on them, familiarizing themselves with possible types of injuries and methods of providing first aid if they occur. Parents should supervise young children during play.
- Educational work among the population about the need to comply with traffic rules by drivers and pedestrians, as this is necessary not only to reduce the level of injuries, but also to save lives.
- Compliance by medical personnel with the rules for performing dental procedures.
- Avoiding bad habits: you need to use special tools to open bottles and crack nuts.
- Avoiding situations that could lead to a fight; if it does occur, during it you need to tense your masticatory muscles and keep your teeth closed: this will help avoid not only dislocation of teeth, but also a fracture of the jaw.
- Providing a high level of protection for athletes involved in traumatic sports (hockey, boxing). For this purpose, helmets with full face protection and mouth guards are used (molded, which have a ready-made shape, and molded - after heating in hot water, they take the individual shape of the teeth).
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Symptoms
- Disposition of a dental unit in a row (from slight mobility to loss);
- severe pain in the area of injury;
- violation of chewing and speech functions;
- swelling, redness, increased sensitivity of the gums;
- Difficulty closing the jaws.
Dislocation of a baby tooth is one of the most common injuries in children under 3 years of age. The most threatening is an impacted tooth dislocation, since in this case the bone bottom may be destroyed, which will interfere with the formation of a permanent unit. Signs of tooth dislocation in children are similar to those in adults.
Varieties
This disease is classified into:
- complete;
- incomplete.
In the first case, the disease forms after an absolute rupture of periodontal tissues and the circular ligament of the tooth due to a strong blow to the crown. Often there is damage to the upper jaw of the front teeth.
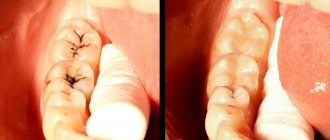
A complete dislocation clinically looks like this: upon examination, you can see that the tooth is missing from the dentition, and its socket is filled with a fresh blood clot and continues to bleed. Often there are concomitant injuries to the soft tissues of the lips - wounds to the mucous membrane, bruises, and so on. In order for the treatment to be complete and effective, the condition is assessed, namely the presence of carious cavities, the integrity of the root and crown, etc.
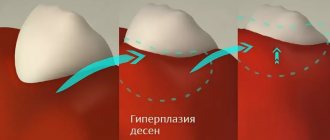
Incomplete luxation changes the position of the tooth in the row. The patient complains of mobility, pain, changes in his position and impaired chewing function. An examination of the oral cavity shows the displacement of the crown of the injured tooth in different positions. It can be highly mobile and very painful upon percussion, however, it is in its place in the dentition.
In this case, the gums are hyperemic and swollen, and ruptures may occur. Due to rupture of periodontal tissue, the circular ligament and damage to the walls of the alveoli, pathological dentogingival pockets can form, as well as bleeding from there. In the case of dislocation and oral displacement, its root is usually displaced vestibularly and vice versa. Often the patient has concomitant injuries - wounds, hemorrhages, bruises.
Questions and answers
If a tooth falls out due to injury, can you put it back in place yourself at home?
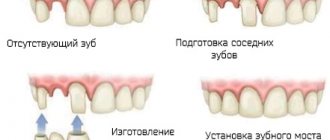
This procedure should not be performed at home. Such attempts will not give the desired result, but will lead to infection. You should contact your dentist immediately. Replantation is possible only in exceptional cases. In other cases, the patient will be offered prosthetics (bridge construction) or implant installation.
What diagnostics are needed for dislocations?
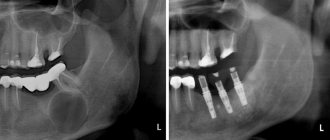
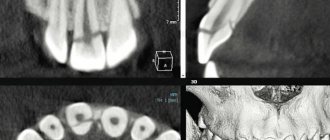
The dentist prescribes a computed tomography scan of the jaws - a three-dimensional image that will show whether there is damage to the alveolar process, roots, or whether there are changes in the periodontium. Computed tomography will help determine an accurate diagnosis and choose the right treatment tactics.
What are the complications of a dislocation?
If you do not consult a dentist in time, serious consequences of this injury will occur. Among the complications are inflammatory ones: pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis, abscess. Children often experience a stop in the development of the permanent tooth germ. To avoid these complications, you should immediately contact your dentist.
How to protect yourself from dislocations when playing sports?
For this purpose, sports protective mouth guards are manufactured. You should contact an orthopedic dentist. Mouthguards are made individually for each patient based on casts of the jaws. Therefore, they are conveniently fixed on the jaws, do not create discomfort and reliably perform their protective function.
Treatment of tooth luxation
First of all, during treatment, the dentist determines the need to preserve the tooth that is injured. He decides this issue based on the clinical picture as a whole, the degree of change in position in the alveolus and the severity of the injury. It is also important whether nearby teeth are affected. A tooth can be saved if the bone tissue remains intact at the root for at least half the length of the root.
An x-ray is taken before treatment. With its help, the condition of the pulp is determined and the consequences that occur when a tooth is dislocated are identified.
If damage to the soft tissue inside or damage to the pulp is diagnosed, the dentist cleans the affected root canal and fills it. After these procedures are completed, the immediate treatment of the dislocation begins. In case of incomplete dislocation, after all necessary measures have been taken with the pulp, splinting is carried out. The purpose of this procedure is to return the tooth to its original position in the socket and dentition, strengthen it and preserve it.
A completely dislocated tooth requires urgent treatment. Under local anesthesia, a specialist performs replantation, that is, returns the tooth to its place in the socket. First, he opens the tooth cavity, eliminates the pulp and fills the root canal.
After this, the tooth returns to its place and splinting is performed - strengthening it in the tooth socket. This is done with the help of a wire splint, which attaches the tooth to its neighbors in its row. This special splint is kept in the mouth, as a rule, for no more than 1.5 months.
When replantation is impossible for one reason or another, prosthetics are used. The effectiveness of replantation largely depends on the timeliness of the measures. It should be carried out immediately after injury. The most optimal time for surgery is within the first half hour.
Author:
Additional treatments
Drug therapy
- When carrying out manipulations to reposition a tooth after dislocation, local anesthesia is used, for this purpose Ultracaine D-S, Ultracaine D-S Forte, Cytokartin, Septanest, Bupivacaine are used. But the effect of the anesthetic stops after some time, so painkillers from the NSAID group are prescribed: ibuprofen, nimesulide, ketorolac, dexketoprofen. Children are prescribed ibuprofen and paracetamol.
- To improve the condition of the gums after injury, use: Dentol Gel - has a local anesthetic effect.
- Gel Metrogyl Denta - contains two antibacterial components, eliminates inflammation.
- Kamistad gel is a combined drug: lidocaine has a local anesthetic effect, chamomile flower tincture produces antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects, thymol has an antiseptic effect.
- Solcoseryl dental paste - stimulates regeneration processes in tissues, thereby shortening the healing period of wounds of the mucous membrane. The composition also includes polidocanol, a local anesthetic.
Physiotherapy
After acute phenomena have subsided, the following are used to stimulate healing processes and eliminate tissue swelling:
- UHF therapy is the effect on the body of an alternating electric field with ultra-high frequency.
- Microwave therapy – uses alternating electromagnetic oscillations of ultra-high frequencies of various ranges (centimeter, decimeter and millimeter).
- Magnetotherapy is the effect of a low-frequency magnetic field on the injured area.
- Magneto-laser therapy is a complex effect of magnetic and laser radiation.
Diagnostics
Only a dentist can differentiate a root dislocation from a fracture. Not only the incisor is damaged, but also the periodontal tissues. A crack may form in the jaw bone. Comprehensive diagnostics includes:
- Orthopantomogram;
- sighting shot of the incisor;
- CT;
- three-dimensional scanning of the maxillofacial area.
The dentist makes a diagnosis based on examination, complaints, and X-ray results. The doctor analyzes the clinical picture and assesses the condition of the jaw bone in the injured area.
INJURY OF MILK TEETH. What to do?
Baby teeth can be injured just like permanent teeth, but first aid and treatment tactics are different.
An important feature that determines “what to do” is the proximity of the roots of baby teeth to the rudiments of permanent teeth. Therefore, in case of injury, the main concern is the preservation of future (permanent) teeth.
Nevertheless, if it is possible to preserve baby teeth without harm to permanent teeth, the dentist will act this way. The goal of treatment is to organize the healing process of the periodontium (tissues surrounding the tooth) and the pulp of the baby tooth, provided that this does not harm the formation of permanent teeth.
TOOTH FRACTURE. What to do?
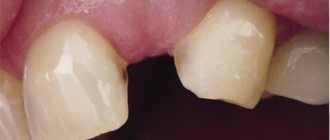
As we wrote above, the following injuries include tooth fractures:
- chipped piece of enamel
- chipping of the crown within the dentin without damage to the dental pulp
- fracture of the tooth crown with damage to the pulp (blood is visible at the fracture site)
- tooth root fracture
Root fractures can be of more complex types:
In all these cases the recommendation is the same:
- If possible, find all the broken tooth fragments and place them in water
- No emergency visit to the dentist is required; make an appointment this day or the next .