Mouth pain is most often caused by infection, allergies, or injury. A sore throat can easily be confused with pain in the mouth.
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
Contact your doctor if your child:
- refuses to drink for a long time due to pain in the mouth
- he has a mouth ulcer that has not healed for more than a week
- swelling of the gums, lips, palate
ATTENTION!
Pain in the mouth can lead to a child refusing to drink for a long time, and this is dangerous due to the risk of dehydration.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| Is your baby breastfed and has small sores on your tongue? | Incorrect attachment during breastfeeding | Ulcers are formed from pressure from the nipple when the baby is not latched onto the breast incorrectly and go away when proper latching is established. Try changing your feeding position. You can contact a lactation consultant for help in establishing proper feeding. If inflammation or other symptoms occur, contact your child's doctor . |
| Has your child's drooling increased? Does he keep his finger(s) in his mouth all the time? Is he 4-8 months old? | Teeth cutting | If these symptoms are accompanied by signs of illness (fever, loss of appetite, etc.), call your child's doctor for an examination. The appearance of teeth alone cannot cause a high temperature. Some children find it easier if they are given special rubber rings to chew on; others like to live cool objects (see Toothache) |
| Is your baby hungry but refusing to nurse? Are there white spots on the tongue and inside of the cheeks? Did he take antibiotics? | Thrush | This is a fungal disease and can be caused by taking antibiotics. Consult your child's doctor . A good remedy is to treat your mouth with a soda solution. Sometimes it is necessary to take antifungal agents. |
| Is your older child complaining of pain when swallowing? | Viral or bacterial (streptococcal) infection | Take your child to the pediatrician . He will prescribe the necessary treatment |
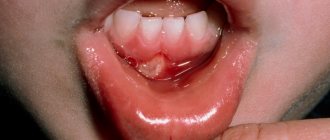
| Do you have small, painful sores on your tongue and inside your cheeks? | Ulcerative stomatitis | Take your child to the pediatrician. He will prescribe the necessary treatment |
| Painful yellowish spots or blisters on the tongue, gums, inner cheeks, swelling and redness of the oral mucosa? Enlarged cervical lymph nodes, “cold” on the lip? Are your lips bright red, swollen, painful? Temperature 37.5-39 C? Loss of appetite, headache, drooling? | Herpetic or other viral infection | Call a doctor and follow all his instructions. A sick child should have separate dishes; isolation is required. Paracetamol will help with pain and fever. Give non-carbonated, non-acidic drinks (water, milk, milkshakes); broths |
| Are your lips dry and bright red? Are there peeling and cracks in the corners of your mouth? | Seizures (cheilitis); may be caused by B vitamin deficiency or food allergies | Talk to your child's doctor . Use hygienic lipstick, baby cream, especially in cold weather |
| Does your child have a constant sore on the tip or edge of his tongue or one sore on the inside of his cheek? | Biting with a tooth | Contact your dentist |
| Does your child have sores on his tongue or on the inside of his cheek? Is he taking any medication, such as an anticonvulsant or an antibiotic? | Possible side effects of the medication | Show your child to the pediatrician - he will recommend what to do |
FOR INFORMATION
"Geographical" language
A healthy tongue is pink in color, its upper surface is covered with papillae surrounded by taste endings. Sometimes parents notice with concern that the child’s tongue is covered with bright red spots with white borders and resembles a map. The spots are painful and appear and disappear. This inflammation of the tongue is the so-called harmless migratory glossitis. It does not require treatment. The reason is not known for certain.
Causes depending on the location of pain
Pediatric dentistry in St. Petersburg will understand every problem, find out the causes of the disease, and prescribe therapy. Provoking factors include:
- Organ damage in chronic and acute form. This could be inflammation or the negative effects of medications.
- Fungal and infectious diseases of internal organs, vitamin deficiency, dysbacteriosis.
- Poor hygiene, alcohol consumption, smoking.
- Glossitis is inflammation of the outer layers of the mucous membrane. The disease occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the capillaries. It is provoked by a burn, cut, or injury. The disease goes away quickly, as saliva disinfects the wounds.
- Streptococci, staphylococci, viruses act pathogenically.
Main forms of pathological processes:
- Galvanic stomatitis;
- Geographical language;
The first disease develops against the background of staples, braces, and occlusion. A white coating and spots with pimples appear. If the form of the disease is severe, burning, erosion, irritation, and tooth marks on the lateral planes occur.
Geographic tongue is a disease of mucous tissue of a dystrophic and inflammatory nature. Desquamations appear on the surface of the organ, that is, areas with scaly peeling. In such areas the epithelium becomes red. They are surrounded by a rim of white epithelium, which peels off. The disease appears against the background of improper tissue nutrition, gastrointestinal diseases, and during the eruption of incisors, fangs, and molars.
The tip of the tongue hurts
The tip of the muscular organ is rich in taste buds and nerve plexuses. The ducts of the salivary anterior glands exit into this area. Every component can be damaged. If the tip of the tongue hurts, you can assume:
- Damage from trauma;
- Negative influence of physical factors;
- Allergies;
- Development of inflammatory processes;
- Glossalgia;
A child can be injured by hasty eating or inept use of cutlery. An accidental bite may cause bleeding. Damage is caused by salty, spicy foods, low and high temperatures. In such cases, children complain of pain and numbness. With reduced immunity, inflammation often develops. The aphthous form of stomatitis, which is caused by pathogenic agents, is often diagnosed. The disease manifests itself as deep ulcers, at the bottom of which plaque with a white tint accumulates. They heal slowly. Children's temperature rises and they feel unwell.
Viral pathogens cause herpes disease. The mucous membranes of the oral cavity are covered with colorless bubbles. After opening, ulcers form in their place and bleed. The baby may develop a fever.
The frenulum under the tongue hurts
If your child has pain in the frenulum under the tongue, you need to see a doctor to find out the cause of the problem. The main provoking factors are:
- Initial period of stomatitis;
- Incorrectly chosen mouthwash, brush or paste;
- An hysterical cry the day before, active singing;
- Microtraumas;
- Inflammation that appears as a result of an allergic reaction or enlarged lymph nodes;
- Caries, an infection of the gum tissue;
Problems arise due to a short frenulum. Insufficient ligament length can be corrected with conservative therapy or trimming. Specific gymnastics helps recovery: rolling a muscle organ into a ball, folding it into a tube. Exercises help stretch the ligament. Surgery is performed at any age, preferably in preschool. It is optimal to operate the ligament in infancy, since newborn children easily tolerate such manipulations.
Pain at the base of the tongue
Inflammation of the gums in a child is an unpleasant disease. The baby becomes capricious, whiny, his temperature may rise, and his appetite disappears. The sooner the parents show the little one to the doctor, the easier and faster the therapy will be. Children often complain of pain in the root area of the speech organ. This can happen when:
- The area of the base of the tongue is injured: wounds, injections, cuts. Children often suffer from foreign objects entering the oral cavity. If the injuries are serious, they are treated in a hospital.
- A viral or bacterial infection enters the body. The surface of the tongue becomes covered with ulcers and blisters. They interfere with swallowing food and speech. The pathology covers the tonsils, pharynx, and larynx.
- The salivary glands become clogged, which interferes with the swallowing process.
- Medicines are used uncontrollably.
- Neuralgia, allergies, anemia develop, and hormonal disorders appear.
Chronic diseases can be associated with failure to comply with hygiene rules. In any case, parents need to show the child to a doctor for medical care.
Ear inflammation in a child: how to prevent complications
Otitis media is one of the most common diseases in childhood. According to international statistics, 98% of children experience ear inflammation at least once, and 60% experience the disease twice. What is effective prevention and how otitis media is treated, said otorhinolaryngologist of the Morozov Children's Hospital, Candidate of Medical Sciences, holder of the “Moscow Doctor” status Alexander Mikhailovich Ivanenko.
Why does otitis media occur?
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, otitis media can be external, middle or internal. Otitis externa is caused by microbes, most often manifested by damage to the skin of the ear canal and boils in the area of the auricle. Internal otitis in most cases occurs with an advanced form of otitis media.
Acute otitis media is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear cavity. Develops against the background of respiratory infections. Infection of the ear occurs through the auditory tube, when mucus from the nasopharynx enters the middle ear and viruses, bacteria, and fungal flora freely penetrate from the nasopharynx through the mouth of the auditory tube into the tympanic cavity.
Due to anatomical features, the smaller the child, the shorter and wider the auditory tube connecting the ear cavity with the nasopharynx. Therefore, in an infant who spends most of his time lying down, and in a young child who does not know how to clean his nose, mucus may leak at any time. In adolescent children, the auditory tube is a tortuous narrow tube, so the spread of infection from the nasopharynx to the middle ear is less possible.
Adenoid vegetations also contribute to the development of ear inflammation. This is the proliferation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, which is the main focus of bacterial infection in the nasopharynx.
How does the disease manifest?
The main symptom of otitis media is ear pain. Children under one year old, as a rule, refuse to eat, because sucking movements cause pain. Babies often touch their ear, rub it, and cry. You can suspect otitis media by pressing on the tragus of the child's auricle.
The key method for diagnosing otitis media is otoscopy - an examination by a doctor of the external auditory canal and eardrum using a special instrument.
How to treat otitis?
If the inflammatory process is at the initial stage, outpatient treatment is carried out. Therapy is selected by a pediatrician or otolaryngologist depending on the child’s condition. Vasoconstrictor nasal drops must be used.
If medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the inflammatory process develops into acute catarrhal otitis media, and then into acute purulent otitis media, characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge from the ear. In some cases, if the outflow of contents is inadequate or absent, the child undergoes paracentesis in the hospital - an incision of the eardrum. The intervention is performed under anesthesia. Then medical conservative treatment continues.
What prevention measures are most effective?
There is an opinion among many parents that otitis media can be prevented by “covering the ear with cotton wool on the street” or “putting several hats on the child.” Such recommendations will not protect against otitis media.
Due to the fact that infection of the ear occurs through the auditory tube, which communicates with the nasopharynx, it is necessary to carefully care for the nasal cavity if the child has a runny nose. Otherwise, mucus flows from the nasopharynx into the middle ear, which leads to an inflammatory process in the ear.
If the nasopharyngeal tonsil grows excessively, it is recommended to remove it.
Which doctor should I contact?
Professional oral hygiene is an integral part of dental health. To do this, you need to visit a hygienist regularly. It will remove plaque, hard deposits, and prevent caries. Diagnosis and treatment of oral diseases is carried out by general practitioners - pediatricians, therapists, dentists. When the need arises, the child is examined by gastroenterologists, infectious disease specialists, and neurologists.
During diagnosis, urine and blood tests are taken, and bacterial cultures of deposits from mucous tissues are carried out. Sometimes other tests are recommended. For pain and discomfort, the doctor prescribes painkillers and special baths. To avoid tissue irritation, coarse, hot, and salty foods are removed from the diet. Your child should not be given spicy foods. It is important to promptly treat diseased units and constantly maintain oral health.
Pediatrician appointment prices:
| TYPES OF MEDICAL SERVICES | Cost, rub. |
| Examination of a child by a pediatrician to obtain a certificate + certificate | 1950 |
| Visit of a pediatrician, consultation at home (Moscow) | 5400 |
| Consultation with a pediatrician at home for the second child | 1950 |
| Patronage for a newborn / gymnastics and swimming at home (1 session, pediatrician Kapina A.V.) | 6300 |
A child has a stomach ache: when to sound the alarm
Diagnosing abdominal pain in a child is sometimes a difficult task even for an experienced clinician. After all, children, especially preschool age, are not able to indicate a specific area of pain and note bowel movements. And parents cannot always remember the connection between a symptom and food intake or other provoking factors. So, what do you need to remember if your child complains of abdominal pain? And when should you not postpone a visit to the doctor?
How pain occurs
Most of the digestive system does not have pain receptors as such, and pain “in the abdomen” is caused by irritation of the membrane that covers the organs and separates them from each other (peritoneum).
This irritation may occur due to:
- spasm (in children, more often intestines)
- inflammation (edema),
- or overstretching of the organ, and accordingly, the peritoneum (for example, due to gas formation or obstruction).
And, depending on the cause, it is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms.
Qualitative differences
Thus, a catastrophe in the abdomen also has the name “acute abdomen”, is characterized by high intensity and infertility, has a diffuse (with appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis) or cramping character (with intestinal obstruction, volvulus, strangulated hernia), is accompanied by vomiting (usually multiple), temperature reaction and, unlike food poisoning, retention of stool and gases, and not diarrhea.
Treatment of such pathologies requires the mandatory participation of a pediatric surgeon and urgent research:
- clinical blood test with leukocyte formula (increased leukocytes) (0.D2.202),
- general urine test (differential diagnosis with kidney pathology, the pain in which can “radiate” to the abdomen),
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
- and, if necessary, radiographic examination with contrast.
And to clarify the degree of the inflammatory process, depending on the results of ultrasound and x-ray examination, a blood test may be prescribed for:
- pancreatic amylase and lipase (if acute pancreatitis is suspected),
- total bilirubin, Gamma GT and alkaline phosphatase (for signs of acute cholecystitis).
- By the way, these same tests are also indicated for less pronounced pain, but it occurs regularly and is associated with food intake.
And the main analysis, outside of acute pathology, in this case is a coprogram (general analysis of stool), where you should pay attention to:
- neutral fat (appears with a lack of bile or pancreatic enzymes)
- fatty acids (in case of impaired intestinal absorption function),
- intracellular (a sign of gastric pathology),
- and extracellular starch (lack of pancreatic amylase or too rapid movement of food through the intestines),
- as well as an increase in leukocytes
- and the appearance of red blood cells (blood).
- Intestinal causes of “chronic” abdominal pain include celiac disease (gluten intolerance), lactase intolerance (milk intolerance), as well as ulcerative enterocolitis and Crohn’s disease.
Wherein,
- in the first case, the distinctive feature is the “special” stench of feces and antibodies to transglutaminase and endomysium in the blood;
- in the second, the child’s stool takes on a foamy appearance and a sour smell, and stool containing carbohydrates allows the diagnosis to be confirmed;
- and the last two pathologies are characterized by the appearance of leukocytes, erythrocytes and calprotectin (the most effective marker of “intestinal” inflammation) in the feces.
It should also be remembered that “digestive” pathologies are accompanied by signs of vitamin deficiency, protein deficiency, anemia, calcium metabolism disorders (rickets, enamel destruction, fractures), skin pathologies (especially with celiac disease) and other deficiency conditions. Therefore, timely diagnosis of regular abdominal pain is necessary not only to maintain the health of the digestive system itself, but also the entire body as a whole.