Teething in children is an exciting and responsible period for parents.
A particularly hectic time is when a baby's teeth are cutting through. Unlike other teeth, the eruption of canine teeth is accompanied by more severe symptoms and is particularly distressing for the child. The fact is that the roots of the fangs are longer and pass in close proximity to the facial nerves. Which leads to severe pain, increased temperature, lacrimation, runny nose and other unpleasant consequences.
The time of teething in a child often coincides with a period of weakened immunity. Therefore, it is important not to confuse viral diseases, which often occur at this time, and the symptoms of teething. It is worth closely monitoring the slightest changes in the child’s condition.
How to Reduce Teething Pain
Fever and pain can be reduced by:
- massage the gums where tooth eruption is expected;
- the gums can be lubricated with an anesthetic;
- give the child a vasoconstrictor if the child has a runny nose;
- if the temperature rises above +38C, then the child should be given an antipyretic in the form of a sweet syrup.
Usually, the eruption of baby teeth occurs without complications. In some cases, a complication may occur that is caused by:
- Presence of a dental cyst.
- When the baby tooth has not yet come out, but it is supported by a permanent tooth.
- When a fang erupts, it is out of place in the dentition.
Teething
According to the tradition of many peoples of the world, there is a custom of giving gifts to a child on the occasion of the appearance of the first tooth. This ritual symbolizes wishes to the baby for health, happiness and long life. The appearance of a baby’s first tooth is a solemn moment for relatives and parents, but at the same time, teething can also be a “restless” period for parents and the baby. I would like to reassure parents and orient them to the fact that teething is a physiological process and must be approached philosophically. As if it were inevitable. And timely and correct teething is a guarantee of a healthy future child.
What is teething?
Teething is the process of vertical movement of a tooth from its origin and development within the jaw until a crown appears in the oral cavity. The process of teething begins after the crown has finally formed and is accompanied by its further development and growth of the jaw bones. Signs of physiological teething are: timeliness, sequence of eruption of certain groups of teeth and pairing.
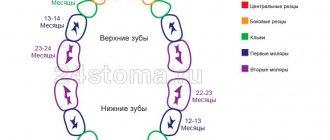
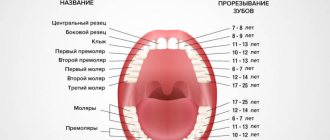
There are temporary teeth (more often called milk teeth) and permanent teeth. According to the number of teeth, the primary teeth are 20, the permanent bite is 32 teeth. According to modern data, the period for the eruption of the first temporary teeth is usually considered to be from 4 months. The end of eruption is 3-3.5 years. Most often, the first teeth appear at the age of 6 months, and as a rule, the teeth on the lower jaw erupt first - the central incisors, then the lateral incisors, canines and molars. The timing of teething can vary from 4 months to 2 years (early teething) or from 8-10 months to 3.5-4 years (late teething).
Average time for eruption of primary teeth according to (R. Illingworth, 1997)
| tooth | Timing of eruption (month of life) | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | |
| Central incisor | 6 | 7,5 |
| Side cutter | 7 | 9 |
| First molar (chewing group of teeth) | 12 | 14 |
| Fang | 16 | 18 |
| Second molar (chewing group of teeth) | 20 | 24 |
It should be noted that the quality of nutrition, sanitary and hygienic conditions and pathological conditions of the child (rickets, hypovitaminosis, intoxication, states of oxygen starvation, the nature of feeding, etc.) significantly affect the process of teething. For example, disordered teething with disruption of the time intervals between groups of teeth, delayed eruption may be a manifestation of a pathology such as rickets.
Adverse effects during teething
Temporary teeth are not permanent, that’s why they are called that. As the child grows and develops, after a certain period of time, all 20 primary teeth will be replaced. As an exception, in individuals, milk teeth do not change, remaining in adulthood (most often this occurs due to the absence of the rudiments of permanent teeth).
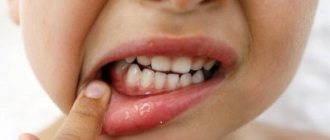
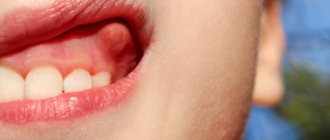
When primary teeth erupt, the child is in a state of “stress” and can often manifest itself with general somatic disorders. The first signs of teething, often the main ones, are the appearance of swelling of the mucous membrane of the gums in the projection of the erupting teeth. Profuse salivation appears, the child may be irritated and tearful. The eruption of central teeth often occurs without any manifestations, except for swelling of the gums and profuse drooling. When the chewing group of teeth erupts and a larger area of the gum mucosa is involved, a secondary infection may occur if the resistance of the child’s body decreases. Symptoms such as increased body temperature, upset bowel movements, redness of the mucous membrane of the gums in the mouth, decreased appetite may appear. To relieve the annoying itch, the child begins to “drag” fingers and various objects into the mouth (toys, sucking the edge of clothing, a blanket) to scratch gums, thereby can damage and infect the mucous membrane. Which can manifest itself as erosive rashes. And aggravate this condition.
How can you help your child when they are teething?
To relieve itching of the gums in a child, it can be recommended to give hard vegetables or fruits (peeled apples, carrots), or a crust of bread to chew. It is good to massage the gums with special “teether” rings or a toothbrush (silicone, or a regular baby brush with soft bristles). Some rings can be pre-cooled, but you should carefully inspect these devices and purchase them in special places in order to avoid counterfeit, uncertified goods and subsequently not harm the baby’s health, so that the child does not get hurt. If the temperature rises, antipyretic drugs can be given. To reduce the sensitivity of the mucous membrane and reduce pain in pharmacies, pharmaceutical manufacturers offer special anesthetic gels for topical use. But we recommend using these drugs only as prescribed by a doctor, so as not to cause allergies in the baby and not miss more severe complications. Contact a pediatric dentist who will conduct an examination and give qualified prescriptions to improve your well-being.
Changing temporary teeth
Permanent teeth most often appear between 5.5 and 7 years of age. Their eruption practically occurs in the same sequence as temporary teeth. The lower central incisors appear first, then the upper central incisors, and in parallel, and sometimes earlier, the first large molars erupt (the first molars, or by their number, they are called “sixths”). Please note: The sixth teeth do not fall out! They should serve your child for life. Parents mistake them for temporary teeth, which is a misconception, especially in the case of absence or poor oral hygiene and damage to this group of teeth. Which can lead to a disastrous result – tooth loss. But this group of teeth - the “First molars” - are fundamental in the formation of a correct bite; they are also called the key of occlusion. The shape of permanent “young” teeth differs from more mature ones. The cusps and cutting edges of the crowns are more pronounced, especially the cutting edges of the central teeth have a scalloped (wavy edge), the size of a permanent tooth differs from a temporary tooth, it is larger. Some parents are alarmed by this fact. To which we answer, there is no reason to worry, literally a year after eruption, the enamel edge will become even and even. And regarding the size of the crowns of the teeth, while the child is small (the appearance of the first permanent teeth is 5.5-6 years old) relative to the facial skeleton, there is a certain disproportion; as the bones of the facial region grow and develop, a harmonious relationship between the face and teeth occurs.
Average time for the eruption of permanent teeth in children (according to Schroder, 1991)
| tooth | Timing of eruption (child's year of life) | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | |
| Central incisor | 6-7 | 7-8 |
| Side cutter | 7-8 | 8-9 |
| Fang | 10-12 | 11-13 |
| First premolar (small molar) | 10-11 | 9-10 |
| Second premolar (small molar) | 11-12 | 10-11 |
| First molar | 5-6 | 6-7 |
| Second molar | 12-13 | 12-14 |
| Third molar (wisdom tooth) | 15 and older | 15-16 and older |
1. In order for the teeth to last a long time and not have to “say goodbye” before the appointed time, they need careful care when they erupt.
2. Go ahead for a consultation with a pediatric dentist, who will select age-appropriate hygiene products (toothbrush and toothpaste) for your child. He will provide training in teeth brushing techniques.
3. Brush your child’s teeth at least 2 times a day (in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed). Helping clean hard-to-reach areas from an early age
4. Limit your child’s consumption of carbohydrate-containing foods (we do not recommend eating sweets for children under 3 years old)
5. If a child drinks liquid drinks before bed or at night, they must be replaced with regular drinking water, without added sugars.
6. The use of toothpastes containing fluoride is very important for children of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug-Ugra
7. Visit the dentist 2 times a year!!!
The article was prepared by: pediatric dentist Malakhova A.A. Head of TOD - Mokrinskaya N.G.
Photos used in the article from satyov:
1. https://ladyspecial.ru
2. https://otvetymamam.ru
Eye teeth in older children
Permanent eye teeth erupt in children aged 9-12 years. Normal eye tooth eruption should occur painlessly. If pain still bothers the child, it may be caused by:
- the presence of infection in the oral cavity;
- periodontal disease;
- development of dental caries.
The eye teeth may erupt in a crooked manner. Orthodontic treatment helps correct abnormal tooth growth. If a tooth erupts and grows incorrectly, it is removed on the advice of a dentist. After removing an eye tooth, it must be immediately replaced with a prosthetic so as not to disrupt the integrity of the dentition and not to impair the process of chewing food.
What to do when the temperature rises
Often parents, even with a slight fever, begin to actively treat the child with antiviral, antipyretic and antibacterial drugs. Even if this symptom is due to the appearance of the first teeth. Most pediatricians (including Dr. Komarovsky) are against such radical methods. Why shouldn't you do this?
A temperature of 37 degrees and above is a kind of protective reaction of the body and helps it more actively produce antibodies against viruses and bacteria. Low body temperature does not allow you to effectively fight infection. Therefore, sometimes it is worth not interfering with natural processes and immediately suppressing even minor signs of fever.
But you shouldn’t fall into inaction either. If the fever reaches significant numbers (38 degrees or higher) and is accompanied by a change in the general condition of the child, then prescribing antipyretic drugs for high fever is a primary measure.
If the rise in temperature is not controlled by conventional medications, then it is possible to scrub the child with cool water or an vinegar-alcohol mixture.
If the fever does not subside within 3 days, then you must definitely visit your treating pediatrician to decide on further examination and the possibility of prescribing antibiotics or other medications.
Some parents prefer homeopathy in such cases. Such drugs do not effectively reduce the temperature, but they can alleviate the baby’s general condition and speed up the recovery process. A prerequisite before taking homeopathic medicines is to consult a specialist.
How to reduce pain in an eye tooth using traditional medicine
Dental treatment of the eye tooth can be supplemented with treatment with traditional medicine. Typically, after visiting a dentist in a specialized clinic, they advise the following:
- Dissolve a teaspoon of baking soda or salt in a glass of warm water. Rinse your mouth with this solution several times a day.
- Prepare a decoction of medicinal herbs: chamomile, sage, or make an infusion of oak bark. Rinse your mouth with prepared decoctions and infusions several times a day.
The eruption of eye teeth in children should occur under the supervision of a pediatric dentist. Adults who have problems with their eye teeth should also see a dentist.
How many days does it last
In answering this question, it should again be recalled that all children are different and react differently to the appearance of teeth. On average, fever in babies can last 1-3 days and usually disappears immediately after teething.
But in the experience of many pediatricians, there are children whose high body temperature associated with the appearance of their first teeth lasted up to 4-5 days. Or there are cases when the fever lasts only a few hours and goes away without any intervention. In any case, you should not delay consulting a doctor, since if you have any diseases, identifying them earlier has a more favorable outcome.
How to help your baby during teething
Many of the symptoms that occur when children are teething can be relieved. Home and medical methods will come to the rescue:
Gel teething toys, as in the photo, will relieve itching of the gums, but the baby should not chew on them without a break - such items are periodically washed, cooled in the refrigerator and given to the child again.- Pharmacy anti-inflammatory and analgesic gels for local applications will help relieve inflammation and pain. Dentinox, Kalgel, Baby Doctor, Kamistad are used in pediatric dentistry.
- If a child’s fangs are cutting due to a high fever, antipyretic medications can be used. Paracetamol-based drugs effectively relieve fever and inflammation. Drugs containing ibuprofen are no less well tolerated by infants.
Children's antipyretics are available in several dosage forms. For children of the first year of life, syrups or suppositories are relevant. Potions quickly reduce the temperature, but their effect is short-lived. Candles do not work immediately, but they last a long time. Before using any product, consult a doctor.
Which teeth exactly have such a strange name?
So, the term “eye teeth” is not a medical term. The correct name for these teeth is upper canines. Where did such a strange name come from? The fact is that in the immediate vicinity of the upper fangs there are threads of the facial nerve. When these threads are irritated, very severe pain occurs in the upper part of the face. This pain even extends to the eyes.
When babies' upper canines begin to erupt, pain occurs that makes children cry. Unfortunately, this process takes quite a long time. Removal of eye teeth in adults is also always accompanied by severe pain. In this case, dentists use very strong anesthesia.
From somewhere there are ridiculous rumors that a person can even go blind from the removal of eye teeth. Such cases are unknown to medicine.