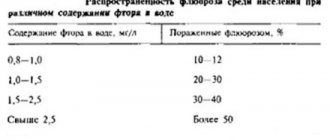
Symptoms
When patients experience pain in the temporomandibular joint, clicking sounds are heard and the mobility of the joint system is limited. The discomfort seems to be in nearby areas rather than internally. In this case, headaches are observed, they are difficult to eliminate with medication. The clinical picture is complemented by:
- Stiffness in the cervical vertebrae, pain in the arms, ears, dizziness, sleep disturbances.
- Tension on the sides of the face, compression of the masticatory organs, impaired night breathing, apnea.
- Patients feel pain in the jaw joint when opening the mouth. The jaw may deviate, making it difficult to open the mouth completely.
- Disc misalignment, causing a popping sound. There is no click if the patient has internal joint disorders that are associated with disc dislocations without reposition.
- Sensation of friction in arthritis, hardening of bone tissue in osteoarthritis, swelling in rheumatism, inflammation in infectious arthritis.
- Limitation of movements with ankylosis.
- High degree of mobility during dislocations.
It happens that the jaw jams, pain appears in the temples, crowns, and eye sockets, vision is impaired, there is ringing in the ears, and anxiety appears.
Bruxism: 3 steps to successful treatment
As a rule, the patient notices that he has clenched his jaw tightly only at the moment of awakening. Relatives may report a quiet grinding sound from clenched teeth, but sometimes attacks of bruxism are not heard.
“The symptom does not cause any particular inconvenience, and many do not see a doctor for years. Meanwhile, the teeth are gradually rubbing against each other,” comments orthopedic dentist Denis Vladimirovich Ovchinnikov.
What is bruxism? This is a spasm of the masticatory muscles. The problem is very common: chronic bruxism occurs in 5-10% of the adult population.
Night cramps are caused by nervous tension and aggravated by pathology of the dental system. That is, the main reason is stress. Overwork, chronic lack of sleep, and information overload lead to an increase in cases of bruxism among city residents, including young people.
The second group of reasons is associated with improper closure of teeth.
Neurological and osteopathic causes of teeth grinding are also less common. Bruxism can be caused by poor nutrition: lack of calcium or magnesium.
Consequences:
- The teeth are severely worn out, the bite decreases;
- Fillings and crowns chip and break;
- Teeth become sensitive and mobile;
- Facial aesthetics deteriorate: a fold appears near the lips, a sloping chin;
- Headaches and muscle pains (neck, shoulders, back), pain in the jaw joints, and insomnia occur.
Which doctor should I contact?
Contact your orthopedic dentist to find dental causes or catalysts for bruxism:
- Bite disorders
- Incorrectly installed crown or filling
- Missing 1 or more teeth
Most likely, you will need to visit a therapist (not a dental therapist, but a local doctor). He will identify the cause of the disease and refer you to a specialized specialist: a neurologist, osteopath or psychotherapist, or help you adjust your diet.
Using a facebow
and articulator before installing crowns reduces the risk of bruxism
The doctor in the photo -
orthopedic dentist Denis Vladimirovich Ovchinnikov
Completing T-scan diagnostics
On the monitor, tall bars indicate supercontact points.
Treatment of bruxism. Step 1 – Protecting Your Teeth
To prevent teeth from being worn down by high loads, it is recommended to wear a special protective mouthguard at night. They are made in dental laboratories from soft plastic or rubber, and strictly according to the shape of the patient’s jaw. This makes them comfortable and discreet to wear. There are self-adjusting bite trays made from water pads, this is also an effective method.
What does a mouth guard do:
- Does not allow teeth to wear out;
- Protects teeth from displacement;
- Reduces the load on the facial muscles;
- DOES NOT eliminate the cause of the disease, DOES NOT treat the consequences of tooth wear.
“Wearing a mouthguard relieves the symptoms of bruxism and the headaches it causes. But the mouthguard does not remove the cause and should be used in combination with other treatment methods ,” warns orthopedic dentist D.V. Ovchinnikov.
Step 2 - eliminating the cause
You will not be able to cope with bruxism on your own. A doctor's help is needed.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the cause. Most often, an integrated approach is used: a combination of psychotherapeutic, medicinal, and dental methods.
- Correcting the bite with braces or aligners.
- Dental prosthetics: in some cases, remaking a low-quality prosthesis eliminates the problem completely.
- Consultation with a psychotherapist or psychologist: to learn ways to unload the nervous system.
- Drug treatment: taking antidepressants, sedatives, B vitamins, ascorbic acid, calcium, magnesium. Sometimes anti-inflammatory drugs are required.
“Patients 30-40 years old come in with worn-out teeth and a reduced bite like a 60-year-old. They spend money on a facelift to avoid sagging cheeks, and bruxism aggravates the problem every year ,” says Denis Vladimirovich.
A quick and mandatory method of helping with bruxism is the elimination of supercontacts, that is, points of increased stress. There the teeth close first and begin to press on each other before the rest close. If a tooth has shifted, tilted towards its lost neighbor, or an uncomfortable filling or denture has been placed, a supercontact point appears.
The body unconsciously tries to get rid of supercontact, to erase this bump. But while this happens, other teeth and the jaw joint will suffer.
An orthopedic dentist can identify problem areas using special sensory equipment, if the clinic is equipped with one. With an ultra-sensitive sensor, it finds supercontacts smaller than the thickness of a human hair. So the doctor determines not only their location, but also the degree of load on each.
Supercontacts are removed by grinding. After this, the patient immediately feels improvement.
Step 3 - correcting the consequences
After eliminating the cause of bruxism, you can move on to restoring your teeth. With low abrasion, procedures to strengthen the enamel are sufficient. In more advanced cases, restoration with photopolymer or dental prosthetics is required.
If you delay the treatment of bruxism for several years, the teeth will be severely worn, the bite will decrease, and total dental prosthetics will be required.
High-quality dentures can not only protect worn teeth from destruction, but also compensate for lost bite height. The shape of your face will become more aesthetic and toned.
“I emphasize. If you manage to catch a patient with bruxism in the early stages, grinding the teeth, remineralization and a course of mild sedative will be enough. If the situation gets worse, it will require expensive complete prosthetics of all teeth, and possibly treatment of problems with the jaw joint and cervical spine.” Ovchinnikov D.V.
The only way to prevent bruxism is to regularly monitor the health of your teeth and nervous system. Get more rest and consult a doctor in a timely manner for preventive examinations and treatment, including orthopedic.
Orthopedic dentist Denis Vladimirovich Ovchinnikov has been dealing with the problems of bruxism, tooth abrasion and occlusion disorders since 1995. The doctor sees patients at the CosmoStom branch on Volochaevskaya street 19/1.
Possible causes of pain
Most often, the joints of the jaw hurt because the muscle fibers are strained and anatomical changes occur in the joint unit. The situation is aggravated by psychological reasons, sleep disorders, and emotional stress. In addition, provoking factors include:
- Bruxism, that is, grinding of crowns;
- Osteopenic disorders of the body;
- Genetic bone pathologies;
- The jaw joint near the ear hurts when an infection develops, the patient has suffered a neck or head injury;
- Muscle pain, internal disorders, tension;
- Ankylosis, arthritis, excessive mobility;
- Lack of chewing organs, unprofessional orthodontic treatment;
- Active conversation load;
- Pain in the jaw joint and radiates to the ear in patients with the habit of biting nails or placing the smartphone close to the hearing organ;
- Problems of the central nervous system, scoliosis and osteochondrosis of the spine;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
In addition, dysfunction occurs with asynchronous movements of the joints on both sides.
Causes
The TMJ connects the lower jaw and the temporal bone of the skull. This is a very mobile joint, actively moving during speech, chewing, swallowing, and if its normal functioning is difficult, then the person’s quality of life suffers significantly. The tissues surrounding the joint have many nerve endings, and even minor disturbances in the functioning of the TMJ lead to discomfort, pain and deterioration in the general condition of a person. A complete clinical and instrumental examination will allow us to find out the exact cause of the pain and differentiate the pathology from other problems in the maxillofacial area.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing TMJ disorders first involves taking a medical history, followed by a physical examination. The doctor applies light pressure on the side of the face where there is discomfort, on the masticatory muscle fibers. At the same time, the patient closes and opens his mouth. Popping or clicking sounds and jaw thrusting are analyzed. If indicated, an MRI may be prescribed. The procedure will show whether there are internal problems with the joint. If osteoarthritis is suspected, x-rays and CT scans can confirm the diagnosis.
Pain in the jaw joint when chewing and opening the mouth often occurs with infectious arthritis. Diagnosis is made by inserting a needle into the joint itself to collect fluid. This research method is called aspiration. The liquid is analyzed for the presence of pathogenic bacteria. Hypermobility and ankylosis are determined by the width of the mouth opening. Sometimes the patient is referred for polysomnography to determine sleep disorders. An orthopantomogram of the jaw plays an important role in the research process.
Which doctor should I go to?
In order to properly treat pain in the jaw joint when opening the mouth, it is necessary to develop an optimal treatment regimen. This can be done by a professional orthodontist.
- If the patient needs to have braces, plates, dentures, or implants installed, impressions of the teeth are taken. Complex therapy for TMJ gives good results.
- In serious cases, surgical technologies are used - bone and muscle grafting. The pathology cannot be neglected so that it does not develop into arthrosis with the proliferation of connective tissue and subsequent immobilization of the joint. It is important to eliminate the root cause of the disease.
- Severe spasms and discomfort are relieved with compresses.
- For stress that leads to tension, the patient is prescribed sedatives.
- Sometimes splinting is required.
- The patient may be recommended physical therapy.
- Patients may be prescribed nonsteroidal drugs, muscle relaxants, and sedatives.
Therapy also includes eliminating defects in the masticatory organs, grinding fillings, correcting prosthetic errors, replacing structures, and correcting bites. The load on the joint must be reduced. To do this, you should include soft foods in your diet, perform relaxation exercises and massage complexes. Ultrasound and laser therapy may be required. It is easier to eliminate the disease at the initial stage so that it does not become chronic. Timely visits to the doctor, correction of posture, elimination of stressful situations, replacement of lost units are effective preventive measures.
Basic information about gnathology
Gnathology is a branch of dentistry devoted to the work of the dentofacial apparatus and all its components - nerves, bones, chewing and facial muscles, periodontal tissues, joints, teeth. It is gnathology that is responsible for the correct structure of the jaw, normal chewing of food, and a beautiful smile.
Every dentist can have minimal knowledge and skills in this area, but when solving more complex and specific problems, you will definitely have to turn to a specialist - a professional gnathologist.