What is rinsing the tonsils with the Tonsillor device?
This method combines three types of effects on the tonsils:
- Mechanical. Vacuum pressure helps expel purulent plugs from lacunae.
- Physiotherapeutic. Ultrasonic treatment of the affected lymphoid tissue disinfects, suppresses the activity of bacteria and other possible pathogenic microorganisms, and stops the inflammatory process. Ultrasound also improves blood flow to the ENT organs and microcirculation, which ensures deep penetration of the medicine into the tonsils.
- Medication. The use of saline solution or anesthetic serves to wash out purulent plugs. An antibiotic or glucocorticosteroid drug is then administered to combat local inflammation and infectious agents.
This combination of therapeutic effects, especially against the background of parallel drug therapy to strengthen the immune system, usually gives quick and long-term results.
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
Practically not used in modern otorhinolaryngology. For acute bacterial sinusitis, systemic broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are indicated, which successfully cope with the bacterial process without punctures and “cuckoos”.
Punctures for a bacterial process in the maxillary sinuses are mainly indicated if culture of the sinus contents is needed - usually when 1-2 courses of antibacterial therapy are ineffective.
Very rarely, such punctures are performed for diagnostic purposes, when it is not possible to perform radiography or computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses. Another indication is severe pain associated with the pressure of the contents on the walls of the sinus. The puncture is done once during the main treatment. Several punctures are indicated only in the case of a persistent bacterial process with two or more courses of antibiotics, and there is no possibility of performing endoscopic surgery on the sinuses.
It has been proven that puncture of the maxillary sinus does not speed up the healing process.
It is important to know : puncture, like any invasive method, can have complications, including trauma to the medial wall of the orbit, nasolacrimal duct, soft tissues of the cheek, and nosebleeds.
How is the tonsils washed with the Tonsillor device?
This method is distinguished by its gentle effect on the palatine tonsils, compared to surgery and even rinsing with a syringe. And yet, some patients are afraid of hardware treatment, assuming that it is painful. Such fears are unfounded.
Unpleasant sensations are relieved by first applying an anesthetic solution to the affected area, which weakens sensitivity and prevents the occurrence of a gag reflex.
Then, using a nozzle operating in vacuum cleaning mode, the purulent contents are drawn out from the lacunae. Then comes the turn of ultrasonic treatment in combination with washing with saline solution or an antiseptic (furatsilin, miramistin, etc.) and administration of drugs.
A session of washing the lacunae of the tonsils with the Tonzillor apparatus lasts no more than 10 minutes. Patients usually feel relief after the first time. For most patients, 5–10 sessions are enough to forget about the disease for a long time. If necessary, the course can be repeated after six months.
What should you be prepared for when undergoing hardware treatment for tonsils? Firstly, after each session for 3-4 hours, slight soreness may be felt in the throat due to the cessation of the anesthetic effect. It is better not to drink or eat for at least an hour. By the way, for the entire period of therapy you should avoid foods and drinks that irritate the mucous membranes. Spicy, rough, too hot or cold food is not advisable. Secondly, plugs often come off not only during the cleaning process, but also in the intervals between procedures; there is no need to be afraid of this.
How to rinse tonsils at home with an irrigator
It is better to rinse the tonsils on an empty stomach in the morning, since a stream of water entering the larynx can cause vomiting. Such reflexes cease to bother you after regular procedures. The duration of rinsing the tonsils is 2-3 minutes, but you can start from 30-40 seconds until slight discomfort appears in the throat. Washing is performed according to the following algorithm:
- stand in front of the mirror and take the irrigator handle;
- set the jet pressure to the minimum level;
- insert the tip of the device into your mouth and turn on the device;
- When changing the position of the device, turn it off each time.
Before washing, make sure the device is in working order. Fill the reservoir with a suitable solution.
Do not use decoctions and infusions. The smallest plant particles included in them can become clogged in the device’s filter and damage it.
Effects of hardware washing of tonsils
In most cases, a course of rinsing the tonsils with the Tonsillor apparatus is effective in several ways:
- powerful antibacterial effect, expulsion of pathogenic bacteria and toxic waste from the ENT organs being sanitized, normalization of the microflora of the oral cavity;
- intensification of the process of penetration of drugs deep into the tonsils;
- activation of local blood circulation, metabolism, nutrition and restoration of lymphoid tissue of the tonsils at the cellular level;
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- inclusion of local immunity.
What are the benefits of washing the tonsils with the Tonzillor device?
Treatment of tonsillitis and other ENT diseases with the help of Tonsillor has a number of advantages compared to the “old-fashioned” method of washing out pus from lacunae with a syringe.
- There is no risk of injury to lymphoid tissue. Hardware attachments with soft edges are attached to the tonsils extremely delicately. In addition, during the process of pulling out plugs using a vacuum, the doctor adjusts the pressure, depending on the area being treated.
- The spread of infection to neighboring areas is excluded. All pus removed from the patient immediately enters the appropriate reservoir, without contacting the surrounding tissues.
- Maximum deep cleaning of gaps. Tonsillor is able to free even very small and narrow depressions in the lymphoid tissue from “clogging,” which cannot be accomplished by other methods.
- Painless.
And, undoubtedly, rinsing the tonsils with a vacuum method compared to removing them is a preferable choice. After all, the body’s immune defense and hematopoietic processes depend on the integrity and functional suitability of this organ.
Syringe method
This is the most common and accessible method of performing the procedure. And most likely, when you go to the district clinic, you will be offered exactly this.
To carry out the procedure, a needle-free syringe with a curved cannula attached to it is used. An antiseptic solution, for example, a furatsilin solution, is drawn into the syringe. The syringe directs a stream of solution directly into the lacuna. The jet “breaks” the tonsillitis plug. Purulent masses, washed out of the lacunae by the solution, enter the mouth. At this moment, the patient must spit the washing solution into a special tray along with the washed purulent contents. As soon as the manipulation is completed, the surface of the tonsils is lubricated with Lugol's solution.
This method is referred to as the old, “grandfather” methods. Yes, this method is inexpensive, but it cannot be called very effective either. With this technique it is impossible to completely rinse the tonsils and remove deeply located caseous masses. Also, such sanitation requires good professional training from the otolaryngologist. An inexperienced ENT doctor can injure the surface of the tonsils with a syringe, which will lead to the spread of infection to healthy tissue, which will only worsen the situation.
The apparent simplicity of performing such a flush convinces patients to buy a syringe at a pharmacy and try to carry out the procedure at home. But only a few manage to cope. Firstly, we should not forget about the traumatic nature of the method, and secondly, it is not possible to maintain the proper level of sterility at home.
Sanitation with a syringe is an inexpensive and accessible method. But it is much more effective to carry out vacuum rinsing using the Tonzillor apparatus.
Who is recommended to wash the tonsils with the Tonsillor device?
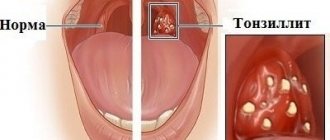
The main indication for ENT procedures is tonsillitis . This is an acute or chronic disease of the tonsils of an infectious nature.
The developmental features and difficulties of treating this pathology are due to the structural specificity of the tonsils. The presence in them of a large number of depressions (crypts, or lacunae) actually serves the good purpose of increasing the surface of this paired organ - a barrier to infections entering the body. But it is precisely this property of the tonsils that causes the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria in them. The warm and humid climate of lymphoid “gorges” that are difficult to rinse is simply ideal for the growth of colonies of cocci, staphylococci and streptococci.
That is why acute tonsillitis easily turns into chronic, when the source of infection in the depths of the tonsils becomes permanent. The chronic form of the pathology is characterized by:
- frequent exacerbations (at the slightest cooling), tendency to sore throats;
- bad breath, periodic release of lumps of pus;
- soreness and increased size of the tonsils themselves and often visible whitish-yellowish deposits on their surface;
- intoxication of the body, since harmful waste products of pyogenic bacteria are carried by the bloodstream throughout the body, which can cause complications in the heart, kidneys, joints, provoking the development of myocarditis, pyelonephritis, arthritis, etc.
Attempts to treat tonsillitis by taking antibiotics, rinsing, and treating with antibacterial drugs are usually ineffective due to the hidden source of infection deep in the lymphoid tissue. Therefore, ENT rinsing of the tonsils is prescribed as the most productive method.
In addition, vacuum washing of the tonsils can be prescribed for ENT pathologies such as tonsillitis, rhinitis, adenoiditis, pharyngitis . Sanitation of the tonsils using the vacuum method is also carried out after removal of various tumors in the mouth and throat, including papillomas.
Who is contraindicated for washing the tonsils with the Tonzillor device?
In some cases, washing the lacunae of the tonsils with the Tonzillor device may be contraindicated or should be carried out with caution under the especially vigilant supervision of a physician. Contraindications include:
- acute course of an ENT disease, accompanied by fever and severe inflammation;
- acute respiratory viral diseases, including influenza, covid, etc.;
- severe tuberculosis;
- some ophthalmological diseases associated with ruptures and weakness, retinal dystrophy;
- individual intolerance to drugs used during the procedure;
- the presence of malignant tumors, no matter in what part of the body;
- III degree of hypertension;
- problems with blood clotting;
- the first three and last three months of pregnancy;
- children up to three years of age.
Contraindications
It is also necessary to take into account a number of contraindications to such a procedure. These include:
- ENT diseases in the acute stage (including acute tonsillitis);
- influenza, ARVI and other viral diseases;
- acute form of tuberculosis;
- negative reaction of the body to ozone;
- malignant neoplasms of any location;
- hypertension 3 degrees;
- blood clotting disorder;
- first trimester and last month of pregnancy.
Washing the tonsils with the Tonsillor apparatus for children
Before the age of five, hardware lavage of the tonsils is rarely prescribed due to the psychological unpreparedness of children. After all, anesthesia for this procedure is not justified, but it is extremely important that the patient remains motionless. Small children are not capable of this. And even after five years, it is very important to set the child up correctly so that he is not afraid and behaves calmly.
Preparing for vacuum rinsing of tonsils
To prescribe a course of washing the tonsils, you need to consult an otolaryngologist, who will perform an examination and, possibly, give a referral for a number of examinations:
- general blood analysis;
- examination of the microflora of the tonsils for bacterial damage;
- rheumatic tests to determine the intensity of inflammation and the risks of developing complications of tonsillitis in other organs.
In order for the vacuum cleaning session of the tonsils to take place without any excesses from the gastrointestinal tract, doctors strongly advise not to eat 3 hours before the start of the procedure. The fact is that the risk of a gag reflex, although reduced due to the anesthetic, still does not disappear completely. You will receive more detailed recommendations when making an appointment by phone.
Using the Tonsillor device
You can use the device if you have the following examination results:
- examination by a doctor;
- blood test data;
- urine test indicators. The results are necessary to exclude possible pathological conditions of patients during the procedure.
The device operates in two directions:
- Ultrasound radiation “grinds” plugs in gaps;
- The vacuum nozzle carefully sucks out the crushed contents.
The advantages of sessions are painlessness, cleaning efficiency, there are practically no contraindications, minimal time costs.
There can be several procedures using Tonzillor, one per week.
Restoration of the tonsils occurs as follows:
- the tonsils are treated with an anesthetic;
- the vacuum nozzle is installed on the gaps;
- simultaneously with the antiseptic solution supplied to the recesses, an ultrasound effect occurs;
- vacuum removes all contents in them.
Washing of tonsil lacunae: price
One session of hardware washing of tonsil lacunae will cost you only 300 rubles. As a result, even for a 10-day course you will spend the same amount that you regularly leave at the pharmacy, unsuccessfully fighting chronic tonsillitis with medicinal methods. Only now the efficiency will be many times higher!
Remember that chronic tonsillitis is an insidious pathology, fraught with systemic complications from a number of organs and systems. Therefore, it is worth getting rid of it as soon as possible. This will be done by specialists from the Healthy Children MC at st. Sverdlova, 4 and MC “Secrets of Longevity” at Druzhby, 21.
You can make an appointment by phone (Sverdlov St., 4), (Druzhby St., 21).
Chronic tonsillitis
Your child is undergoing surgery. We would like to give you and your child information about the need for this intervention. We make sure that you do not feel helpless in this situation. We would like to acquaint you with the essential aspects of the operation itself, and the risk factors in case of its failure. The written information provided to you serves this purpose. Read it carefully to discuss any unclear points with your doctor.
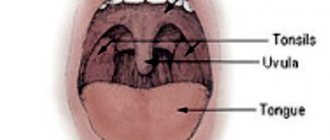
Every healthy child has lymphoid tissue in the pharynx, which is united into the so-called lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring. It includes the palatine tonsils - “tonsils” - they can be seen when examining the mouth - they look like balls protruding on the sides of the tongue, the pharyngeal tonsil - it cannot be seen during a direct examination of the oral cavity, it hides in the nasopharynx, behind the palate, lingual tonsil - located at the root of the tongue, and many lymphoid follicles scattered along the back wall of the pharynx, at the entrance to the larynx (see Fig. 18). These formations help the child defeat pathogenic bacteria that enter the throat during breathing and eating, and contribute to the formation of local immunity - protection against pathogens. By the way, in these organs there are no cells that affect the sexual development of the child, they do not produce sex hormones, therefore their diseases do not affect the sexual development of the child, and if they are removed if necessary (more on this later), sexual development is not disrupted.
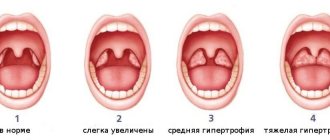
In early childhood - usually from 2 to 5-7 years - the described organs work very hard, as the child expands the scope of contacts with peers by attending kindergarten, and inevitably often becomes infected and develops respiratory diseases. Moreover, if the child’s immune forces are not strong enough due to congenital characteristics, environmental factors and other reasons, the lymphoid organs increase in volume. This enlargement of the palatine tonsils is called “hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils”; they can become inflamed - inflammation of the tonsils is called tonsillitis. Tonsillitis can be acute or chronic. In children, chronic tonsillitis and adenoids - an enlarged pharyngeal tonsil - are often combined.
The tonsils of the pharynx have a significant impact on the state of health and the development of nearby organs. What kind of influence is this? A noticeable obstruction to the passage of air through the nose leads to breathing through the mouth. The consequence is obvious - untreated air enters the respiratory tract - not purified, not warmed and not humidified. A chronic inflammatory process, constantly smoldering in the tissue of the tonsils and adenoids, periodically exacerbating, contributes to protracted, recurrent diseases of the trachea and bronchi (bronchitis, obstructive bronchitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis), can independently cause or aggravate the course of allergies, in severe cases manifested in the form of bronchial asthma , allergic rhinopathy, atopic dermatitis. Adenoids and enlarged palatine tonsils, filling the pharynx, impair the functioning of the auditory tubes, which cannot supply sufficient air to the middle ear, as a result of which secretory otitis media develops, which can lead to hearing loss, and if infection enters the ear, to its acute inflammation – acute purulent otitis media. Poor breathing through the nose contributes to improper development of the maxillofacial area - the bite of the teeth is disrupted, the shape of the face changes (the so-called “adenoid face”).
The causative agents of infectious diseases of the respiratory tract (most often streptococci) after a sore throat remain in the palatine tonsils, and their chronic inflammation develops - chronic tonsillitis. Under unfavorable circumstances (hypothermia, stress, viral infection), the process in the tonsils is activated. This occurs in the form of another sore throat with plaque on the tonsils or purulent plugs. What is very dangerous is that each exacerbation of tonsillitis can cause complications in the form of diseases of other organs and systems of the child’s body, most often rheumatic diseases of the heart and joints, kidney diseases (pyelitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis). In addition, exacerbation of tonsillitis or tonsillitis sometimes causes complications in the form of an abscess (ulcer) in the pharynx. This complication is called peritonsillar abscess. A peritonsillar abscess indicates that the palatine tonsil is unable to cope with its function; it can recur at any time.
What factors contribute to enlargement of the pharyngeal tonsils and the development of chronic tonsillitis?
- Heredity - at least if the parents suffered from adenoids or tonsillitis, the child, to one degree or another, will also face this problem.
- Inflammatory diseases of the nose, throat, pharynx - and respiratory viral infections, and measles, and whooping cough, and scarlet fever, and tonsillitis, etc.
- Eating disorders - especially overfeeding.
- Tendency to allergic reactions, congenital and acquired immunity deficiency.
- Violations of the optimal properties of the air that the child breathes - very warm, very dry, a lot of dust, an admixture of harmful substances (ecological conditions, excess household chemicals).
- Inadequate (incorrect) treatment of acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis). The most common mistakes are an incomplete course of antibiotic treatment, incorrect dosing, violation of the therapeutic and protective regime (early getting out of bed, walking outside before 7-10 days from the start of treatment).
Thus, the actions of parents aimed at preventing chronic tonsillitis come down to correction, and even better, to the initial organization of a lifestyle that promotes the normal functioning of the immune system - feeding according to appetite, physical activity, hardening, limiting contact with dust and household chemicals.
What is the difference between chronic tonsillitis and tonsil hypertrophy?
Hypertrophy of the tonsils is an increase in their size in the age of a child up to 9-10 years. With chronic tonsillitis, the tonsils can be of any size; its distinctive feature is the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the tonsils.
What if a child, along with chronic tonsillitis or enlarged tonsils, has adenoids?
The presence of adenoids and difficulty in nasal breathing significantly influence the development of tonsil disease. In this case, otolaryngologists suggest that in the case of a compensated form of tonsillitis, while preserving the palatine tonsils, it is necessary to remove the adenoids, and in the case of a decompensated form, include adenotomy in the scope of the operation to remove the palatine tonsils, which slightly lengthens the operation and is almost imperceptible to the patient, but greatly affects the result of the operation. If this is not done, the child has a high probability of progression of tonsillitis or adenoiditis, which will negate the results of tonsillectomy - difficult nasal breathing will persist, the child will again become ill often, snoring will not go away or will worsen.
When is tonsillitis treated and when is surgery performed?
There are two forms of chronic tonsillitis: compensated and decompensated. In the decompensated form, surgical treatment is not possible - the tonsils must be removed. This diagnosis is made when tonsillitis often worsens (2-3 sore throats per year), the process extends beyond the tonsils, if diseases of distant organs and systems develop, for example, nephritis, rheumatic diseases of the heart and joints. Tonsils must be removed if a peritonsillar abscess develops.
Is it possible and necessary to treat chronic tonsillitis?
Let us emphasize that treatment is not only possible, but also necessary. Until the child develops the changes mentioned earlier, every six months, local treatment should be carried out in the form of irrigation of the pharyngeal mucosa with aqueous solutions that have anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antimicrobial properties, as well as general treatment methods, including vitamin preparations, agents that affect immune system, locally acting vaccine preparations, physiotherapeutic methods (magnetic and laser therapy, inhalations). Otolaryngologists consider it particularly important in the treatment of tonsillitis to conduct a course of washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils (7-10 procedures per course of treatment).
How urgently should the operation be performed?
The operation to remove the tonsils - tonsillectomy - is planned, that is, it is performed when the child is in full health or in remission of chronic diseases. It cannot be performed during acute illnesses (ARI) and 3-4 weeks after recovery. Thus, it is always possible to perform this operation in a period favorable for the child, which will minimize the risk of postoperative complications.
Do palatine tonsils grow again, are relapses possible?
No, completely removed tonsils cannot grow back.
How are tonsils removed?
This operation is performed using local or general anesthesia (narcosis). It lasts 25-30 minutes and, with proper psychological preparation of the child, is tolerated satisfactorily. The simplicity of the operation does not indicate its safety. Complications due to anesthesia, bleeding, and damage to the palate are also possible. But all this does not happen often.
Surgeons have long abandoned the removal of tonsils using ultrasound and laser due to the huge risk of complications.
How long does a child stay in the hospital after surgery?
Due to the high risk of bleeding in the postoperative period, the child is in the hospital for 6 days after surgery.
What should you do after your baby is discharged?
The child is discharged from the hospital under the supervision of an ENT doctor or pediatrician at the clinic at the place of residence. Home treatment is usually recommended for 1-2 weeks. In this case, physical activity should be limited, however, there is no need to keep the child in bed. When eating during the first days, you should not eat hot, spicy foods, sour juices and fruits, carbonated drinks, or ice cream. After 5-7 days, the diet becomes normal. 10-14 days after discharge, if the child’s general condition is satisfactory, there is no elevated body temperature, and the wound in the pharynx is healing smoothly, you can visit the children’s group and go outside. You can’t just do sports or go to the pool. The wound in the pharynx heals completely in 3-4 weeks. A month after the operation, there are no restrictions in lifestyle or diet.
How to remove tonsils at the Children's City ENT Center?
To establish a diagnosis, if there is no ENT doctor in the clinic, you can make an appointment at the city ENT consultation office by calling 2-78-49-00 (inquiry).
Reception is carried out on weekdays, from 8.00. until 20.00.
If the diagnosis of “chronic tonsillitis” has been established and you have made the decision to operate on your child, with a referral for surgical treatment issued at the clinic, you should go to the emergency department of the 3rd Children’s Clinical Hospital at any time convenient for you. Your child will be registered for hospitalization on the day you choose and will be given an examination plan (a list of tests necessary to perform the operation). Hospitalization is carried out on Tuesday and Thursday, from 13.00. until 15.00. and on Sunday from 16.00. until 18.00. The operation is carried out the next day.