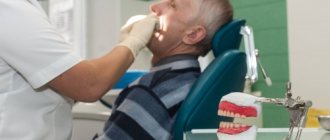
A beautiful smile is the key to the health and success of a modern person. If people smile widely and openly, then those around them are more inclined to like them. Any deficiencies and health problems immediately affect the quality of life, so the problem of cosmetic dental restoration worries many today.
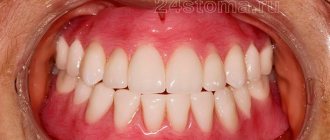
With the help of dental treatment and restoration, you can put in order and restore teeth damaged by caries and other dental diseases. Correctly selected material, shape and color will help to hide any imperfections of the teeth as much as possible and restore them to their original appearance.
Restored teeth after such restoration cannot be distinguished from healthy neighboring teeth. It is prescribed in case of irregularly shaped teeth, chips, cracks and spaces between teeth, as well as after dental trauma. The restoration easily changes the length or width and aligns the dentition. Pigment spots or stains from coffee and smoking can also be removed with cosmetic restoration.
Dangers of toothless life
Which of us is unfamiliar with the expression “eats so much that it’s cracking behind the ears”? But a person with partial or complete loss of teeth can hardly boast of “crackling sounds behind the ears” while eating. He has to exclude hard food from his diet, or swallow it after barely chewing it. And as you know, food, when crushed, begins to be digested in the mouth, but with large pieces the stomach will have to cope with triple strength. The already mentioned “crackling behind the ears” is due to the fact that the salivary glands are located in the parotid region. It is they who produce the production of a very important hormone that is involved in the regulation of calcium metabolism; in addition, it affects the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems, the metabolic processes of the liver, stomach and other vital organs. With partial or complete absence of teeth, chewing movements of the lower jaw are limited, which invariably leads to dysfunction of the salivary glands. This is where changes in the composition of the blood and sudden gastric and liver dysfunctions appear. And a violation of calcium metabolism in the body, among other things, will undoubtedly have a negative “echo” on the remaining teeth. In addition, a person who is missing one or more teeth suffers from the inability to smile broadly, laugh, or conduct a normal conversation, which can negatively affect his communication with others and lead to stress. If this happens, the conclusion is clear - dental prosthetics is simply necessary for a person to continue a normal life.
Don't be afraid to “put your teeth on the shelf”
Removable prosthetics
- Cost: 33,000 rub.
More details
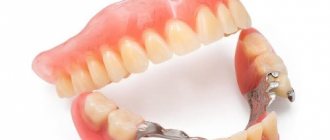
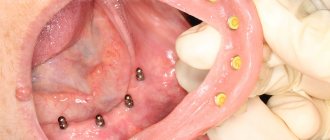
Dental prosthetics makes it possible to restore teeth that have been removed or lost as a result of illness or injury. Modern dentistry and new technologies for dental prosthetics make it possible to quickly and accurately select the required size, shape and color of new teeth to achieve a high cosmetic effect. Nowadays, dental prosthetics is no longer a long and painful process. Modern removable dentures are fundamentally different from the old ones that our grandparents used. The differences between modern prostheses are new, durable, flexible and safe materials, as well as high technologies that allow us to produce the most suitable prosthesis with maximum precision. There are several methods for restoring lost teeth and normalizing chewing function, that is, normal chewing of food. In this article we will talk about one of the types of dental prosthetics - removable dentures. Such dentures are divided into complete removable and partially removable. They can be lamellar or clasp. Despite the prejudices of many people, removable dentures remain the most common type of prosthetics today, since this method is accessible to most and has the fewest contraindications.
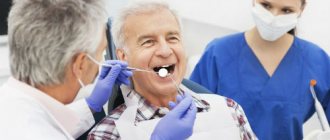
Cosmetic dental restoration. Latest technologies and modern techniques
Dental restoration is of great importance in modern dentistry. It can be performed for medical or cosmetic reasons and can improve a person’s appearance.
Essence of the procedure
The process of restoring the structure of teeth and improving their appearance is called restoration. To carry out the procedure, the doctor uses special preparations, equipment and filling materials.
To reconstruct teeth, one of three methods is used:
- cosmetic polishing and contouring,
- direct adhesive restoration,
- indirect adhesion.
During cosmetic restoration, the patient’s teeth are preserved, which eliminates complications and pain. During the procedure, the doctor changes the shape of the tooth, grinds down uneven edges and polishes the enamel surface. Grinding and polishing is carried out using diamond attachments of different grain sizes. Restoration is aimed at eliminating cosmetic defects: cracks and chips, darkening of the enamel, curvature of the tooth.
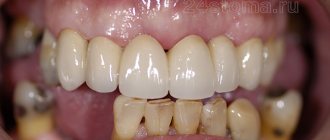
The direct method of art restoration involves performing actions to restore the integrity of the tooth in the patient’s mouth, using fillings and grinding. Indirect restoration involves creating veneers from an impression of the client's teeth and installing them on the teeth.
Teeth on a plate
Complete removable plate dentures
Modern plate prostheses have not changed much structurally, but have stepped far forward in aesthetics.
The base plate is now not just pink, but with introduced capillary vessels, which creates a very natural appearance of the mucous membrane, and artificial teeth, made using modern technologies, have an excellent appearance and high wear resistance. All this contributes to achieving an individual aesthetic effect and reliability of the prosthesis design. A complete plate denture is the only option to replace all lost teeth (if you do not take into account dental implantation). It is held in the mouth by the suction effect and the anatomical features of the jaws. There is one nuance here - the difference between holding the denture on the upper and lower jaw. The large support area, hard palate and structure of the upper jaw contribute to good fixation of the prosthesis. The same cannot be said about the lower jaw. A small support area, a large number of movable and elastic frenulums and folds do not allow the prosthesis to adhere normally. And the very “glib” language makes this task even more difficult to accomplish. For the toothless lower jaw, the patient can be offered a so-called “floating” removable denture, which will float and not sit tightly in place. It takes a long time to get used to it, but to speed up the process, special fixing creams are used. “Pleasure” is, of course, not very pleasant, so you shouldn’t bring it closer. In the lower jaw, you have to fight for every tooth. Fixation of the prosthesis is always better when there is support. A partial plate denture
is used when one or more teeth are missing. It is made entirely of plastic, with the exception of metal clasps (hooks). The prosthesis is light and cheap, it does not take up much space in the mouth, and rests entirely on the gum. It can be simply irreplaceable for temporary prosthetics.
How does the butterfly installation procedure work?
Installing a cosmetic case has many similarities to installing permanent dentures, but will take less time. No more than 2-3 visits to the dental office will be required. The whole process can be divided into several stages:
- Initial dental examination. The specialist will examine the oral cavity, select the shape and type of prosthesis, choose treatment tactics, and give recommendations.
- Taking an impression of the jaw. It is carried out before the tooth is removed. This will allow the specialist to subsequently reproduce the anatomical shape of the tooth being replaced as accurately as possible. If the tooth is missing, you will need to take a picture.
- Creating an immediate construction.
- Removal of problem teeth.
- Trying on the finished product. If the patient does not experience discomfort, then the orthopedist will install the “cosmetic bag” in place.
- Correction. It is carried out if the patient experiences discomfort after installing the product.
Everything will be fine!
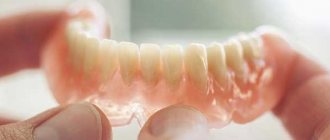
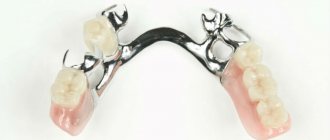
Clasp dentures are radically different from removable plate dentures. The only thing they have in common is that they can be taken off and put on. Bugel means “arc” in German. Instead of a massive plastic base covering almost the entire jaw, clasp dentures have a thin openwork casting, and support-retaining clasps very well fix the prosthesis both by specially prepared (clasp) crowns and simply by living teeth. Clasp dentures are comfortable and elegant, do not interfere with conversation, do not interfere with diction and do not affect the appearance of an undesirable accent. For clasp dentures, it is necessary to have several stable supporting teeth to which the clasps will cling. This allows you to get rid of the massive base, which is designed to perform supporting and suction functions. Teeth intended for support must be selected very carefully so as not to overload them during operation, otherwise the supporting-retaining apparatus may be damaged, and subsequently the teeth may become loose and fall out. Modern technologies and high-precision foundry production have made it possible to produce complex clasp structures in which hidden micro-locks (attachments) are installed - special fastening structures consisting of two jointly working elements. One element is located inside an artificial tooth or prosthesis base, the second is made with a crown or can be fixed in the preserved tooth root. Attachments vary in their design, the complexity of technical manufacturing and the materials from which the lock is made. All this affects the increase in the cost of technical execution and the rise in price of the prosthesis as a whole. Reliable fixation, ease of use, beautiful appearance and complete secrecy from others - these are the main advantages of modern clasp dentures.
UPPER LIMB PROSTHESES
The loss of one or both arms is difficult for the patient not only physically, but also psychologically. However, thanks to the use of modern prostheses, thousands of people lead full lives. With the help of lightweight, easy-to-use and functional orthopedic products, patients can not only perform familiar daily activities, but also complex, precise manipulations.
Depending on the degree of amputation, functionality and purpose, several types of prostheses are distinguished.
COSMETIC PROSTHETICS
Cosmetic prostheses are anatomical copies of the upper limbs that perform the aesthetic function of the amputated arm and serve to improve appearance.
They are made using safe materials that do not cause allergies - high-quality silicone, the color of which is matched to the patient’s skin color. Today you can choose prosthetics that are as close as possible to real hands with acrylic nails, hair, images of moles, veins and palm lines.
WORKING PROSTHETICS
Working prostheses have a special adapter instead of an artificial hand - it is attached to the prosthetic socket. Such products are equipped with many different working attachments that allow you to actively use the prosthesis in everyday life.
ACTIVE or TRACTION PROSTHETICS
Active, or as they are also called, traction prostheses allow the artificial hand to be compressed due to special cables and hold various objects. The mechanism of operation of such prostheses is based on a traction action - in order to compress or unclench the artificial hand, you need to make a special movement with your healthy shoulder.
PROSTHESES WITH AN EXTERNAL ENERGY SOURCE, or BIOELECTRIC
The most modern and functional prostheses of the upper limbs are bioelectric. They are made of polymer composite materials and equipped with an electronic brush made of light and durable metals. Such prostheses can be used for any level of amputation.
The principle of operation of bioelectric prostheses is based on the fact that after amputation, the stump of the hand retains groups of flexor and extensor muscles. Special sensors are located in the prosthetic sleeve - they are able to recognize bioelectric impulses in the preserved muscles. The resulting impulse, using an electronic amplification system, turns on a small but powerful electric motor that controls the fingers, raising or lowering the artificial hand.
With the help of a bioelectric prosthesis, the patient can perform many precise movements with an artificial hand.
Some of the bionic prostheses are controlled using an application that is installed on a smartphone or tablet.
PRODUCTION STEPS OF PROSTHETICS
The first step in the production of any type of prosthesis is the production of a prosthetic socket. To do this, the prosthetist technician makes a plaster cast, the so-called positive, based on individual measurements. Then the sleeve is made. After the socket is ready, prosthetists begin assembling the product according to the parameters recommended for the patient.
PROSTHETIC CARE
It is necessary to keep the product clean and remove dirt regularly. For some types of prostheses, sudden temperature changes are contraindicated. It is worth remembering that even minor mechanical damage can lead to serious damage.
HOW TO GET A PROSTHESIS?
By contacting the Territorial Centers for Social Protection of the Population at your place of residence, you can issue a referral for the manufacture of prosthetic and orthopedic products (and in the absence of contracts, issue a notice of further provision), as well as receive information and advice on existing government contracts with companies producing prosthetic devices -orthopedic products and the procedure for obtaining compensation in case of their independent purchase.
You can also contact the Moscow State Budgetary Institution “Resource Center for Disabled Persons” of the Department of Labor and Social Protection of the Population of Moscow by phone or at the address: Moscow, Novoostapovskaya Street, Building 6.
Your new smile is our concern
For prosthetics, specialists from the CELT Dentistry Department use ultra-thin imported ceramics, which allows for maximum preservation of tooth tissue, as well as removable dentures with invisible micro-locks. In case of complete or partial absence of teeth, frameless ceramic, metal-ceramic and solid-cast crowns are made. Fixed (bridge) and removable (clasp and plate) prostheses are performed. We can prepare for prosthetics, remove the nerve and fill the canal. If necessary, X-rays can be taken in our Center, in the radiology department, which will allow you to significantly save time. All crowns are selected exactly to match the color of real teeth, for which we have a special color shade scale at our disposal. The department also has its own dental laboratory, equipped with the latest equipment (6 highly qualified dental technicians on staff), which allows us to produce crowns or dentures in a fairly short time, thereby saving your time. Come! You will leave us smiling broadly!
Indications and contraindications for the installation of a cosmetic prosthesis
It’s worth mentioning right away that the “cosmetic bag” is not intended for long-term wear. It is used for a short period of time, usually before the installation of a permanent prosthesis or implant. "Butterfly" is irreplaceable:
- During the recovery period after tooth extraction, it is not yet possible to install a permanent prosthesis.
- At the stage of rehabilitation after surgery for implantation of dental implants.
- During the retention period after completion of orthodontic treatment.
- During the period of restoration of bone tissue, which has become thinner due to the prolonged absence of a tooth.
- In childhood and adolescence. Until the formation of the dental system is completed, the installation of permanent orthopedic structures does not make sense. They will still move and will need to be replaced.
A “cosmetic bag” can be installed for a patient for a longer period if for some reason he does not want to resort to permanent prosthetics using bridges or dental implants.
Despite the fact that installing a cosmetic prosthesis is a simple procedure that does not involve surgical intervention, there are a number of contraindications. These include:
- deformation, congenital or acquired, of the jaw;
- inflammatory process in the oral cavity;
- increased mobility, damage to neighboring teeth, which should serve as support for the prosthesis;
- abnormal jaw structure.