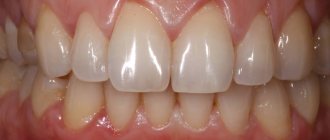
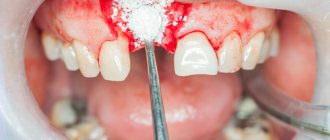
The zygomatic bone is one of the paired elements of the skull structure, consisting of dense spongy-type plates. The fragility of these areas causes a high probability of fracture under active mechanical stress, the consequences of which depend on the complexity of the deformation. Simple cases are characterized by the absence of displacement of the fragments, as well as the preservation of the bone structure against the background of damage to the arch itself. However, any damage of this kind requires medical intervention, excluding negative consequences for the health of patients.
Briefly about the treatment method
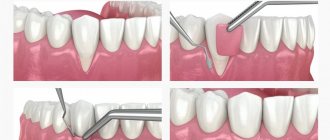
Elimination of skin defects using nearby tissues is called local plastic surgery. Local plastic surgery is used, in particular, in the presence of fresh injuries, cicatricial deformities after traumatic injuries, congenital defects, and also defects after removal of tumors in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. As defined by A.A. Limberg (1963), local plastic surgery is the main method of treating scar deformities or defects, as well as an additional method of plastic surgery after tissue transplantation from distant areas of the body.
Introduction
Epithelial coccygeal tract is a fairly common congenital defect in the development of soft tissues of the sacrococcygeal region, occurring mainly in young people. This nosological form is benign and very rarely leads to serious complications, but it significantly worsens the quality of life and leads to disability in patients of the most active age group [1, 2, 7]. The results of surgical treatment remain not entirely satisfactory, which is due to the relatively large number of postoperative wound complications and frequent relapses of the disease [5, 6].
Many methods have been proposed for the treatment of the coccygeal tract, but none of them has found universal acceptance. The main controversy is caused by the choice of method for completing the surgical intervention, ranging from open wound management after excision of the fistula tracts to the use of complex plastic surgeries to close the wound defect.
The purpose of the work is to analyze the results of using the skin-plastic method of closing a wound defect after tissue excision in common fistulous forms of the coccygeal tract according to Limberg with some modifications.
Indications and contraindications for the treatment method
Indications for plastic surgery using local tissues:
– minor congenital defects and deformities of the maxillofacial area;
– defects that formed after surgical removal of the tumor;
– scars of various etiologies;
– fresh wounds
- firearms, non-firearms, operating rooms
Contraindications to plastic surgery with local tissues:
– the presence of pathological processes (hemangioma, lymphangioma, neurofibromatosis, age spots, scars, etc.);
– insufficient amount of tissue adjacent to the defect or located next to it;
– if plastic surgery with local tissues leads to deformation and disruption of the functions of neighboring organs.
How the treatment method works
When planning local plastic surgery, it is necessary to determine the functional significance of the area of the defect to be closed, its size and relief, as well as the condition and reserves of adjacent tissues. When using methods of local plastic surgery, it is necessary to follow the general rules for this type of plastic surgery:
1) the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue should be dissected at the same level, within healthy tissues, 3-5 mm away from the edge of the defect;
2) when mobilizing the edges of a wound or a displaced flap, subcutaneous fatty tissue must be completely included in the thickness of the mobilized tissue, separating it directly from the fascia;
3) sutures on the edges of the wound must be applied without tension, which can be judged by the color of the skin after applying the sutures. In order to ease the tension of the skin, it is permissible to tighten the tissue by placing sutures on the subcutaneous fatty tissue, and also to apply incisions to the entire thickness of the skin without damaging the underlying tissue;
4) if there is significant tension on the edges of the wound, causing concern for the outcome of the operation, another type of plastic surgery should be used. Simple approximation of the edges of the wound is applicable when closing a defect if the tissue around it is displaced. Good mobility of the skin is observed with prolonged use of prostheses. In this case, the delimited defects of the stump close freely, without tension on the edges of the wound. Approaching the edges of the wound after their mobilization with possible additional incisions is carried out with limited displacement of the skin of the stump surrounding the defect. To mobilize the edges of the wound, the skin with subcutaneous fatty tissue is separated from the fascia itself for a distance of 4-6 cm. Blood circulation and innervation are usually not disturbed. If there is a lack of plastic material, extended, parallel or unloading incisions are additionally made, which allow a more rational distribution of the mobilized tissues or an increase in their area. The shape of the cut depends on the specific conditions. Applying unnecessary incisions or a large number of unloading notches leads to the formation of unwanted additional scars on the skin of the stump.
First aid
In a situation with a serious injury, the people around him must provide first aid to the victim. Medical recommendations exclude independent adjustment of individual parts of the skull or contact with open wounds. The main tasks are to create conditions of complete rest, eliminate re-injury, try to stop the bleeding and call an ambulance team.
In case of acute pain, an injection of an anesthetic is allowed. To stop continuous bleeding, it is necessary to press down the artery. In cases where the wound is small, you can treat the area with hydrogen peroxide, as well as ensure careful application of cold.
Possible complications during treatment
Possible complications:
1. The danger of thrombosis is greatest within 20 minutes after restoration of blood flow through the anastomosed vessels. This time should be waited out, observing the pulsation of the stitched arteries.
2. A slow capillary reaction of the tissues of the transplanted flap indicates inadequate blood flow; its cyanosis indicates difficulty in venous outflow.
3. If the anastomosis is performed incorrectly, microvascular thrombosis cannot be prevented in any way, including the use of medications.
4. Vascular sutures, especially on vessels less than 5 mm in diameter, should not be attempted by a surgeon who has not been trained in microsurgery.
Prognosis after treatment method
Postoperative monitoring should be as close as operative monitoring. It is necessary to maintain body temperature and fluid balance. Pain relief is extremely important. The patient should not experience anxiety or malaise. A high level of observation and care for the patient is required, which is best achieved in the intensive care unit, where the patient should remain for the first 24-48 hours. In addition to monitoring the patient, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the autograft. The surgeon or nurse on duty must constantly monitor the presence of a capillary reaction. In specialized microsurgery departments, monitoring of the patient and the condition of the autograft is carried out by a team on duty. If thrombosis is suspected, an urgent operation is required - thrombectomy. Complications that arise must be corrected as soon as possible, while the viability of the flap is still preserved. If everything goes smoothly during the flap transplant operation after removing the vascular clamps, the likelihood of complications is low. It increases in cases where there were difficulties in applying vascular anastomoses during surgery. A decrease in flap temperature compared to the patient's body temperature indicates arterial or venous insufficiency, or both complications. Blueness of the skin of the flap and accelerated capillary reaction indicate inadequacy of venous outflow, and vice versa: pallor, slower capillary reaction indicate arterial insufficiency. It is incorrect to assume that the success of a flap transplant depends only on the personal skill of the surgeon and on how skillfully he performed the anastomoses. Success, like failure, depends on the choice of the patient, the skill of the surgeons, anesthesiologist, and the staff of the operating room and recovery rooms.
Diagnostic methods
To determine a fracture of the zygomatic bone, methods such as visual inspection and palpation are used. In difficult cases, an X-ray examination is prescribed to clarify the severity of the damage, as well as determine the optimal recovery tactics. The resulting image reflects a violation of tissue integrity, as well as a likely decrease in the transparency of the axillary areas and the continuity of the outer radius of the orbit near the affected area.
Features of treatment
The treatment plan is determined by the symptoms of the pathology, the results obtained during the X-ray examination, as well as the assessment based on the results of the medical examination. The priority task is to restore the intact bone structure. In situations where the anomaly is characterized by a displacement of the cheekbone, surgical intervention is prescribed, the purpose of which is to correct the position of the separated elements.
If the injury is not associated with displacement, it is possible to limit oneself to conservative therapy, which involves taking medications selected based on the indications of the clinical picture. The agents used include anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antibacterial substances, and neuroprotectors. In situations where there is a possibility of contact between the wound and a dirty surface, administration of tetanus serum is also recommended. Standard conservative treatment tactics include:
- Ensuring a calm state for a period of 10-14 days, with partial fixation of the jaw;
- Use of low-temperature compresses in the first 48 hours;
- Eating liquid foods and prescribing physiotherapeutic procedures.
In case of severe pain, analgesics are also prescribed. In the future, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and UHF, as well as other procedural measures, can be used to relieve swelling and pain.
Surgical intervention involves the use of one of the author’s techniques, which include the Keene, Duchant, Dubov and Limberg protocols. Within each operation, the preparatory stage is important, during which the risk to the patient’s health is assessed, the appropriate type of anesthesia is determined, and an action plan is drawn up. The rehabilitation period involves the use of painkillers and antibiotics, as well as a course of physical therapy.
Observation program after treatment method
Rehabilitation after plastic surgery usually includes a set of measures aimed at reducing swelling, eliminating hemorrhages, increasing muscle tone, and improving the quality of the skin. Rehabilitation programs should be aimed at improving the health of the body as a whole - its detoxification, improving microcirculation, increasing the intensity of metabolic processes, moisturizing and lifting the skin. On the other hand, they should be aimed at restoring the skin in the surgical area. When drawing up a rehabilitation plan, many factors are taken into account, including the patient’s health and age, the presence of chronic diseases, bad habits and other individual characteristics.
A comment
The article is undoubtedly of scientific interest and is devoted to a topic that is relevant for coloproctologists and surgeons - surgical treatment of complex recurrent forms of the epithelial coccygeal tract.
The author used a modified method of plasty of a wound defect with a diamond-shaped skin-subcutaneous flap according to Limberg. The described technique is quite popular abroad, but is extremely rarely used by domestic surgeons, which further increases interest in the results obtained in the study. To select patients, the author developed and used a special classification of fistulous forms of the coccygeal tract, with the help of which it is quite clearly possible to identify a group of patients for whom surgery using Limberg plastic surgery is indicated. This is undoubtedly important, since the rhomboid flap method should be used only according to strict indications, in the presence of a widespread scar-inflammatory process in the sacrococcygeal region. As a result of the work, the author obtained impressive results - recovery of patients in 97.3% of cases. For practical purposes, the article provides a number of recommendations aimed at reducing the incidence of complications and relapse of the disease, which significantly increases the practical significance of the work. Thus, the article is of scientific and practical interest and shows the possibilities of plastic closure of extensive wound defects after excision of complex recurrent forms of the epithelial coccygeal tract.
Prof.
Yu.A. Shelygin