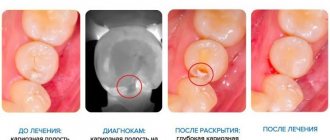
Rules for the treatment of baby teeth
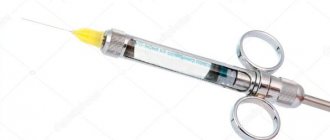
- Anesthesia takes place in 2 stages. This is necessary so that the baby does not feel anything and is not afraid. First, a gel or spray and lidocaine are applied to the gums. Only then is the injection given. For this, the finest needles are used.
- Tissues affected by caries are carefully removed using a special hand tool.
- A safe concentration of anesthetic in the drug is maintained. For Lidocaine it is 2%, for Articaine – 4%. The amount of the drug is selected depending on the weight of the child. Apply from ½ to 1/6 of the standard adult dose. Anesthetics containing adrenaline should not be used for children under 4 years of age.
- Treatment of caries is carried out in sessions. Each should last no more than 30 minutes. Otherwise, the baby will get tired and become capricious.
- Filling materials are used that can be applied in one go. They contain fluoride and other minerals to strengthen teeth.
“Permanent 6th teeth erupt in children aged 5-6 years and, as a rule, are affected by caries first. Teach children how to use toothbrushes and toothpastes correctly, which will prevent plaque from accumulating in deep fissures.”
Rita Martikovna Meliksetyan, Dentist therapist, orthodontist, pediatric dentist, 19 years of work experience
Photos before and after
InformationAge, diagnosis, treatment methodMale, 47 years old
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Treatment: All on 4 dental prosthetics in the upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Woman, 45 years old
Diagnosis: partial loss of teeth
Treatment: All-on-4 implantation of the upper and lower jaws, followed by immediate loading.
All on 4 prosthetics: photos “ before” and “after” the procedure.
Woman, 64 years old
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Treatment: prosthetics according to the All on 4 protocol for the lower and upper jaws, followed by loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Male, 53 years old
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Dental prosthetics: in the photo, the All on 4 method of the upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Female, age 45 years.
Diagnosis: partial loss of teeth
Treatment: All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Male, age 62 years.
Diagnosis: partial edentia
Treatment: one-stage dental prosthetics (pictured) All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate load on the dentures.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Male, age 61 years.
Diagnosis: partial edentia, crowded teeth
Treatment: All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
Female, age 59 years.
Diagnosis: partial absence of teeth, periodontitis
Dental prosthetics: All on 4 upper and lower jaws, with immediate loading.
are presented “before” and “after” prosthetics .
How is childhood caries diagnosed?
Tooth decay occurs much faster in children. This process takes several months. All due to weak enamel of baby teeth. They are permeated with many micropores through which bacteria penetrate. Therefore, you need to undergo a dental examination at least once every 3-4 months.
At different stages of caries, its symptoms differ:
- Initial stage. White spots appear on the tooth enamel, which then turn yellow and become rough. There is no pain, although the tooth may react to hot and cold. To eliminate initial damage, you do not need to drill the tooth. In such cases, it is possible to restore the enamel without filling.
- Middle stage. A “hole” is formed at the site of damage to the enamel. Food debris and softened dectin accumulate in it. In such cases, a cavity is formed and a filling is placed to prevent further decay.
- Deep stage. Not only the enamel is destroyed, but also the bone tissue of the tooth. The damage is noticeable to the naked eye. Deep caries can be cured with fillings, but sometimes even this does not help. In some cases, it is necessary to remove a baby tooth.
Diagnosis of carious lesions is carried out visually or using a special probe. If the “hole” is located in a remote place, an oral camera or x-ray is used. In the initial stages of caries, a special composition is used, which is applied to all teeth. It turns the affected areas pink or blue. This method has no side effects.
Prevention of dental diseases
Some people are not even aware of what dental diseases with inflammatory processes and pathologies are provoked in other vital organs. For those who are not in the know, we inform you: these are gastritis, ulcers, tonsillitis, thrombosis, heart attack and stroke! And the pathogenic bacteria are to blame for everything, which, multiplying in the oral cavity, enter the throat, stomach, blood vessels and even the heart.
To prevent dental diseases, follow simple rules that will help significantly improve your oral health and overall well-being.
- Stop smoking.
A bad habit provokes vasoconstriction and deterioration of blood supply to the mucous membrane, which results in a lack of nutrients necessary for teeth and gums. - Eat a balanced diet.
The abundance of flour and sweet foods in the diet contributes to an excessive increase in microorganisms and inevitably leads to caries and its complications. Take care of strengthening your enamel by taking vitamin complexes. Then the disease when “teeth crumble”, which occurs due to a lack of calcium in the body, will not be scary for you. - Brush your teeth 2 times a day.
Regular hygiene is one of the most effective ways to keep your teeth safe and sound. In addition to the traditional use of brushes and pastes, you should not neglect dental floss. Flosses effectively remove food debris between the teeth, preventing the development of many diseases. - Get preventive examinations once every six months.
It is easier to cure any disease if it is detected at the beginning of its development. Some dental diseases in dentistry have symptoms that cannot be identified on their own. For example, caries at the junction of teeth is visible only on an x-ray.
A person is not able to influence factors that cause various types of dental diseases, such as poor ecology, heredity, and stress. However, with a responsible attitude towards hygiene and prevention, the risk of dental diseases can be significantly reduced or, at least, their treatment can be facilitated.
Treatment of caries in early childhood
- Fluoridation. The second name of this method is remineralization. This is the saturation of the affected areas of enamel with minerals, its restoration. The tooth surface is treated with a special composition containing calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and other elements. The effect of this treatment lasts for about six months. Fluoridation is indicated for children from 6 years of age.
- Silvering. This method is outdated, but is still sometimes used. The surface of the tooth is coated with a 30% solution of silver nitrate, which destroys bacteria that cause caries. The procedure is absolutely painless. But after it the teeth become black, which can cause complexes in the child.
- Infiltration. A special gel is applied to the affected area of the tooth, which softens the tissue. Afterwards they are washed with an abrasive mixture. The area is then dried and covered with Icon Liquid Filling. The material hardens under a curing lamp.
- Ozone therapy. Ozone under pressure in a gaseous state is applied to the area of the tooth affected by caries. This does not cause any pain. The duration of the procedure is 10-20 seconds. Ozone destroys bacteria that cause tooth decay. After ozone therapy, tooth decay stops.
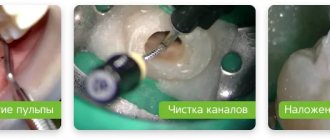
- Filling. The installation of fillings on baby teeth begins with the removal of dead tissue from the cavity. This is done with hand tools or a drill. The cavity is disinfected with a special composition and hermetically sealed. Upon completion, the surface of the filling is ground.
The filling material should be no harder than enamel. Otherwise, protrusions will form along the edges. Therefore, glass ionomer cements are used for children. They wear evenly and naturally together into enamel.
Some clinics use colored fillings for fillings. They are made from compomer and have no side effects.
Treatment or removal during pregnancy
In cases where a wisdom tooth is cut and hurts, causing constant discomfort to the pregnant woman, it can and should be treated regardless of the gestational age. If there is no acute pain and treatment can be postponed, then it is advisable to carry it out in the second trimester of pregnancy or after childbirth.
It is worth remembering that wisdom tooth removal, especially under anesthesia, is definitely contraindicated for pregnant women. Removing third molars is strongly not recommended due to the complexity of such an operation and the risk of developing postoperative complications. As for anesthesia, it cannot be used either for removal or for treatment - during pregnancy, only local anesthesia can be used, and the drugs should be selected very carefully and taking into account the patient’s condition.
Despite their name, wisdom teeth do not bring their owners increased intellectual abilities, but they can cause a number of very unpleasant problems with oral health. Typically, third molars “lead with them” swelling of the gums, purulent inflammation, the development of caries of neighboring teeth, as well as severe pain. Therefore, in modern dentistry they prefer to remove them, without waiting for serious complications to arise and longer and more expensive treatment to be required. In many European countries today, a common practice is to remove the “eights” immediately after their appearance, regardless of their condition and the correctness of eruption.
How is caries of permanent teeth treated in children?
Caries on permanent teeth is treated as in adults. The main method is filling. Photocomposites are the most successful for sealing the affected cavity. These are materials that do not differ in color or texture from teeth. Filling takes place in several stages:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Removing dead tissue using a drill and cleaning the cavity.
- Rinsing the tooth with an antiseptic.
- Air drying.
- Application of phosphate cement insulating gasket.
- Filling with composite materials in several layers, each of which must be dried with a special lamp.
For shallow caries, infiltration, remineralization or ozone therapy can be used. Silver plating is contraindicated.
When is tooth augmentation required?
The following procedure should be followed:
- with congenital anomalies of teeth (underdevelopment, absence of a dental unit, presence of a gap between teeth),
- age-related changes resulting in missing or deformed teeth,
- malocclusion,
- chipped tooth enamel,
- serious damage to the tooth by caries,
- stains or thinning enamel.
These defects must be eliminated, since damaged teeth are the cause of the development of inflammatory processes. They arise because pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate deep into tissues through chips, cracks and carious cavities and cause infection.
However, extensions have contraindications:
- allergy to the material,
- hilar cysts,
- bite pathologies corrected by braces,
- untreated dental diseases (periodontitis, stomatitis),
- bruxism (involuntary grinding of teeth).
Important! For some patients, age over 60 years may be a contraindication. This applies to people with severe chronic diseases of the heart and circulatory system.
Anesthesia for the treatment of childhood caries
Local anesthesia. Used in the vast majority of cases. There are 2 types: application and injection anesthesia. The first does not involve an injection. The risk here is that the child may swallow saliva containing lidocaine. Injections are safer and more effective.
Anesthesia. Used if the child is restless or simply afraid to have their teeth treated. This method is common in the West. Many parents are afraid of memory impairment due to general anesthesia. However, this happens extremely rarely. In addition, general anesthesia becomes the only option when you need to fill several teeth at once in one trip to the dentist. After all, this can take 2 or more hours. Before general anesthesia is administered, the child must undergo the following tests:
- Blood biochemistry.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Electrocardiography.
- Blood for sugar.
Before the introduction of general anesthesia, you cannot eat for 6 hours, and drink for 4 hours. The child is gently put to sleep using a sedative gas containing sevoflurane. To wake him up, it is enough to increase the oxygen supply. This can be done at any time. After recovery from anesthesia, all reflexes are restored within the first 15 minutes.
Removal of wisdom teeth under general anesthesia
Many patients are afraid to remove problematic “eights” because they fear that the process will be painful. However, you should not postpone the operation because of your own fear: modern methods of anesthesia allow the removal to be performed as painlessly and comfortably as possible for the patient.
Doctors usually recommend performing the intervention under local anesthesia, which will be sufficient to ensure the patient is comfortable during the operation. If for some reason a person is not satisfied with the methods of local anesthesia, there is always the possibility of having a wisdom tooth removed under anesthesia. It should be remembered that this option of pain relief is not available to everyone - there are certain contraindications:
- Decompensated diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases.
- Post-infarction or post-stroke periods for up to 6 months.
- Acute inflammatory diseases of internal organs, including the respiratory system.
- Epilepsy.
- Severe thyroid disease.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Alcohol or drug intoxication.
The presence of at least one of the listed positions makes the removal of wisdom teeth under general anesthesia impossible. Before the operation, the patient must be examined to identify any contraindications to the use of anesthesia. In addition, you need to remember that certain preoperative preparation will be required, and the clinic itself, in which the wisdom tooth will be removed under anesthesia, must have all the necessary equipment, as well as a team of specialists who will treat and monitor the patient’s condition (anesthesiologists, resuscitators, trained nursing staff).
Complications of childhood caries
It is important to treat baby teeth. After all, deep caries can penetrate the tissue so much that it damages the permanent dentition. In addition, the condition of temporary teeth subsequently affects the child’s bite. Removal leads to abnormal growth of the jaw. As a result, permanent teeth may appear out of place. Because of this, the child will have to wear braces.
Deep caries leads to inflammation of the pulp, periodontitis, and the formation of basal cysts. Treating these problems is very difficult and painful. It requires root canal filling.
If periodontitis starts, it can cause an abscess and even osteomyelitis. This is already dangerous for the child's life.
The structure of the human tooth
Each tooth consists of a crown - a part of the tooth protruding above the surface of the gum, a root immersed in the bone socket of the jaw; The crown and root of the tooth are separated by a neck.
The crown of the tooth is covered with enamel, the hardest tissue of the human body. Beneath the enamel is dentin, a bone-like tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth. The root of the tooth is covered with cementum, a thin layer of tissue that resembles bone in structure. Inside the crown and root there is a cavity filled with soft tissue - pulp. The pulp consists of loose connective tissue, vessels, nerves and various cells.
In the jaw, the teeth are held in place by tissues called periodontium.
Our patients
Patient recommendations
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Alekseeva O.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Zolotareva S.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Vera
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Mikhail Ivanovich
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Collapse
Methods of aesthetic dental restoration –
Probably, as you already understood, this article will talk about “direct restorations,” i.e. when tooth restoration is carried out using filling materials. However, there are also so-called “indirect restorations” (see below).
- Direct dental restoration – also known as dental restoration using light-curing composite material (i.e., photopolymers), and is done by dental therapists. It is this type of restoration that we will examine in detail in our article. This method also includes restoration of teeth with composite veneers, more about which you can read in the article at this link.
- Indirect dental restoration - in the manufacture of this type of restoration, an orthopedic dentist (prosthetist) takes part, as well as a dental technician sitting in a dental laboratory.
This includes prosthetics with ceramic veneers, metal-ceramic ceramic crowns, restorative ceramic inlays. In this case, the tooth is first prepared and then an impression is taken of it. Based on this impression, an inlay, veneer or crown is made in a dental laboratory, and then fixed to the teeth using cements. For indirect restoration methods, mainly only ceramics are used - this can be Emax, zirconium dioxide, feldspathic ceramics. If we are talking about aesthetic restoration with metal-ceramic crowns, then for their metal frame they use not an ordinary cobalt-chromium alloy, but alloys of precious metals (for example, gold-palladium). Alloys containing gold give metal-ceramic crowns a more natural shade. Read more about indirect restoration methods in the articles:
→ Restoration with ceramic veneers → Restoration with metal-ceramics → Restoration with ceramic crowns
Methods for diagnosing contact caries
Visual inspection.
It is carried out during an appointment with the dentist. An old, traditional, cost-free method. But less accurate, because In some places, the dentist may not notice the early stages of caries development.
Diagnodent device
. Detection of lesions occurs by emitting special sound waves, which, reflecting from carious areas, are captured by the device. A very accurate diagnostic method.
X-ray diagnostics.
An excellent diagnostic method, because... allows you to identify carious lesions at an early stage at any location.
Main types of caries
How caries is treated in dentistry largely depends on which type of spread is typical for a particular person. There are several classification criteria:
- Spread intensity. This category includes single and systemic caries. The difference is that in the first case, the patient is not diagnosed with any additional symptoms. In the second case, the entire row or most of it is also affected. The constant spread of new lesions not only stimulates damage to the enamel and soft tissues, but also impairs the functioning of the human immune system.
- Complexity of development. Uncomplicated caries is the easiest to treat. In this case, there are no additional disorders that lead to the need for additional surgical intervention. Complicated caries is a situation that is accompanied by periodontitis and pulpitis. In this case, treatment must be much longer and more difficult.
In our clinic, doctors treat caries regardless of the stage of the process. We are ready to deal with a problem when there is one of the following four stages:
- Spot. In this case, only the enamel is affected. At the same time, there are spots on the surface with a dark or pale tint. Some people develop stripes instead of spots that are a different color from the rest of the surface.
- Initial surface position. The spot begins to gradually grow, and a hole develops. Sensitivity also increases.
- Middle stage of caries. Dentin begins to deteriorate and pain worsens.
- Deep defeat. Active necrotic damage to hard and soft tissues begins, nerve endings and blood vessels are affected. Treatment in this case will be much more complex and lengthy.
There is also another classification factor - the location and depth of tooth damage. There are five main classes:
- First. It is characterized by damage to the enamel. At the same time, at the first stage it will be very difficult to understand whether there is a lesion, because visually caries shows little of itself.
- Second. Most often it appears on chewing molars, as well as premolars, regardless of the jaw.
- Third. Found on canines and incisors. Most often, the problem is due to the fact that a person eats a lot of sweets.
- Fourth. Characterized by significant destruction of enamel.
- Fifth. The most severe type of flow option. In this case, caries can affect the entire row of teeth, manifesting itself closer to the gums, near the root - where it is very difficult to cure.
Disadvantages of restorations –
- Restorations darken and lose their shine over time - fillings and restorations made from light-polymer filling materials tend to gradually darken. In addition, they lose the shine characteristic of healthy tooth enamel. If the loss of aesthetics on chewing teeth is not so terrible, then on the front teeth it is very unpleasant. Not very good restorations will have to be replaced every few years, but high-quality restorations should require periodic care (you need to visit the dentist once a year to polish them) - then their aesthetics will last longer.
- Risk of breakage of restorations - if your tooth is destroyed by more than 1/2, and especially if it is also depulped (nerve removed), and you still want to chew meat, then there is a risk of breakage of the restoration.
Depulped teeth are much more fragile than living ones. Particularly often, restored teeth break when the tooth is restored completely from the root. If the chewing load suddenly exceeds the strength limit of the restored structure, the restored part of the tooth breaks off. Sometimes this even causes a fracture of the tooth root (with the need for its subsequent complete removal). What is the best way to restore a tooth if it is destroyed by more than 1/2 - this is where indirect aesthetic restorations will help us, because ceramic crowns, veneers, etc.