Causes of bleeding Classification How to stop?
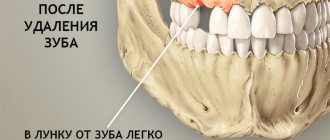
Dentist's help Prevention Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that cannot be performed without damaging tissues and blood vessels. This causes bleeding from the tooth socket. The blood forms a clot that protects the wound from bacteria. Usually, it stops coming out of the wound after a few minutes, but there are cases when bleeding continues for several hours or even days.
Local reasons
- Vascular rupture during traumatic surgery;
- breaking off the root septum or alveoli (socket);
- inflammation in the area of the tooth that was removed;
- the effect of adrenaline (after the narrowing of blood vessels, the second phase begins - their expansion);
- melting of blood clots clogging blood vessels under the influence of purulent secretions;
- local hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels). Occurs from hot food, drinks, rinses or compresses.
Under no circumstances should you apply heat to the wound after extraction!
Thus, the occurrence of bleeding can be provoked not only by a doctor’s error, but also by the patient’s actions.
How to bandage a finger
It is most often necessary to bandage fingers in case of traumatic bleeding. The bandage should fit tightly around the wounded part of the finger, only then will it be useful. Long bandages stay on the finger better.
Before bandaging the finger, the wound must be treated and the bleeding must subside.
First way
Wrap your finger in a sterile gauze bandage and apply a bandage on top. Try to bandage your finger evenly, otherwise the bandage will slip off. The place where the blood oozes the most needs to be additionally wrapped several times.
You can secure the bandage with an adhesive plaster. To do this, you will need two strips of regular adhesive tape. Secure the first strip, about 30 centimeters long, vertically from the base of the bandage to the palm of your hand. Then move it up to the tip of your finger and then along the back of your finger along the back of your hand.
Another piece of adhesive tape will be needed to secure the middle part of the bandage. This plaster should not be tightly secured; its role is to hold the already tightly bandaged bandage and the longitudinal plaster.
Second way
You cannot stick the patch around your finger several times so as to form a ring. This method of securing the bandage will interfere with normal blood circulation. A finger bandage that is too tight will be noticeable - it will begin to pulsate, go numb, and its color will change. The bandage should be loosened immediately.
Wounds heal better and there is less chance of infection if they are bandaged as little as possible. If the bandage is loose or dirty, apply a new layer of bandage on top of the old one.
The bandages should be removed carefully, the last layer should be removed in the direction of the cut. For example, if the cut runs along the arm, the last layer of bandage should be removed along the arm. This will prevent the edges of the wound from moving apart and bleeding will not resume.
The cut or wound may pulsate slightly during the first 24 hours. If the pain gets worse later, the wound may have become infected. You need to remove the bandages and examine the wound. If there is redness, swelling, swelling, you should seek medical help.
Common reasons
The most common of them is a sharp rise in blood pressure as a result of a hypertensive crisis, excessive physical activity, and thermal procedures (bath, sauna, hot bath).
In second place are diseases that affect blood clotting: hemophilia, leukemia, hemorrhagic diseases.
Profuse bleeding occurs with unrecognized vascular tumors (hemangiomas). Therefore, it is important to conduct an X-ray examination, which shows such changes.
Taking anticoagulants can also provoke socket bleeding after removal.
Why might my nose bleed?
Nosebleeds are classified into “anterior” and “posterior.” In the first case, the cause is damage to small blood vessels, this type is usually easy to stop. The second case is considered more dangerous; bleeding occurs due to injury to large vessels located deeper in the nose, so it cannot be dealt with at home. If the blood is “spouting”, this is a reason to urgently call an ambulance.
Causes of nosebleeds include:
- nasal injuries;
- thinning of the mucous membrane;
- inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity;
- fragility of blood vessels, heart and blood diseases;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications (anticoagulants, NSAIDs, vasoconstrictor drops for the common cold).
Classification of bleeding
Bleeding is divided into primary, which begins immediately after surgery, and secondary, when bleeding begins after some time.
The intensity of bleeding is determined depending on how much the hole bleeds after removal:
1st degree
– blood flows
for 20-30 minutes
, saturates the tampons and colors the saliva.
2nd degree
– bleeding continues for more than 40 minutes, blood and saliva mix intensively.
3rd degree
– the bleeding does not stop for more than an hour, the patient spits blood.
With prolonged bleeding, the patient's general condition worsens. Weakness, dizziness appear, and the skin turns pale. Blood pressure drops, the heart begins to beat less frequently. In case of bleeding, dentists advise not to delay a visit to the doctor so that he can take measures to stop the bleeding and prevent the condition from worsening.
What to do if your nose bleeds?
When bleeding begins, it is important to try not to be nervous, as nervousness causes our heart to beat faster, which leads to more blood loss.
The algorithm for stopping bleeding is as follows:
- Sit up straight, tilt your head forward.
- You should be comfortable: loosen your belt and collar, open the window if necessary.
- Apply a cold, wet towel or ice to your nose and place a warm heating pad on your feet. This will help narrow the blood vessels in your nose and widen them in your legs, which will reduce bleeding.
- Pinch the bleeding vessel: squeeze the wings of the nose with your fingers for 3-5 minutes, the bleeding should stop. Also for this purpose, you can insert a gauze swab pre-moistened in hydrogen peroxide into the nostril.
If you have completed all of the above points and the blood continues to flow, call an ambulance immediately, because even a small loss of blood can lead to fainting.
What should you remember when you have a nosebleed?
- Do not lie down or let your legs be higher than your head - this will increase bleeding;
- Do not throw your head back: a large amount of blood entering the stomach can cause vomiting, in addition, blood can flow into the windpipe and make breathing difficult.
- Once the bleeding has stopped, avoid eating or drinking caffeinated drinks to avoid increased blood pressure and further bleeding.
Preventing nosebleeds
Remember, frequent nosebleeds are a reason to consult a doctor. The specialist will identify the cause of the problem and prescribe treatment, which may include the use of hemostatic agents, as well as medications that improve blood circulation.
To prevent rebleeding, a specialist may recommend:
- Taking medications and vitamins to strengthen blood vessels.
- Proper diet. Adding foods rich in vitamin K and C to the menu. Vitamin K is responsible for blood clotting; parsley, spinach, basil, bananas, avocados, broccoli, bran, etc. are rich in it. Vitamin C strengthens the walls of blood vessels, it is found in large quantities in rose hips, sweet peppers, currants, citrus fruits, etc.
- Activity and moderate physical activity: light exercise in the morning, daily walks in the fresh air, visiting the pool, etc.
Be healthy!
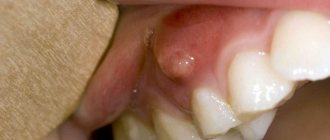
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the dental surgeon cleans the wound and applies a sterile swab. The patient is asked to tightly clamp the tampon with his teeth and hold it for about half an hour. If the tampon quickly becomes saturated with blood, it should be changed.
If the bleeding does not stop after 20-30 minutes
, the dry swab is replaced with one moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
A cold compress can be used to constrict blood vessels. Ice is applied to the cheek, after wrapping it in a towel so as not to freeze the skin. Keep the compress for 10-15 minutes
, then take a break and repeat the procedure.
After surgery, the dentist recommends painkillers. You should follow these recommendations to avoid accidentally taking a product containing aspirin, which thins the blood and can cause bleeding.
If after all the manipulations there is still bleeding from the tooth socket, you need to contact a dental clinic.
First aid for severe bleeding
Severe bleeding must be stopped immediately by applying pressure to the wound. Then you need to make a lining for the wound from the purest material. This could be squares of gauze, several layers of bandages, a clean handkerchief, or a clean piece of clothing.
The pad should be thick enough so that it applies pressure to the wound after dressing. A small pad is sufficient for a finger, but a thick pad is required for the thigh or abdomen.
Press the pad against the wound and hold it tightly until help arrives or the bleeding stops. You cannot remove the original gasket, even if it is soaked through with blood.
The new gasket must be laid on top of the old one. If the bleeding has stopped, you need to tightly bandage the wound with suitable material and take the victim to the hospital. If a tight bandage does not stop the bleeding, you need to press your hand directly on the wound.
Even the most severe bleeding can be stopped by applying direct pressure to the wound. Tourniquet application is rarely required and people who have not applied a tourniquet before should not learn to do so at this critical time. The tourniquet must be loosened every half hour.
What does a dentist do?
First of all, the doctor will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. In accordance with it, the dentist will carry out treatment.
First aid is to stop blood loss. To do this, local anesthesia is performed, blood clots are removed, the wound is dried and the place where the blood is coming from is determined.
Methods to stop alveolar bleeding depend on its cause and location:
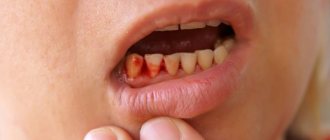
- if there is a rupture of the gums or mucous membrane, they are sutured;
- a ligature (a special thread for ligating blood vessels) is applied to the bleeding vessel;
- If there is bleeding from the alveoli (socket), a tampon of iodoform gauze is placed on it. It is left in the wound for several days.
Tamponation is used as a prophylactic measure if there is a risk of bleeding. The tampon is left in the hole for several days. Then they take it out and see how well the wound has healed.
Removing wisdom teeth is potentially dangerous. Such operations are often difficult. Sometimes you have to cut the gum, saw the roots or the tooth itself and remove it piece by piece. Bleeding after such complex operations occurs more often than after ordinary ones.
Measures taken when a hole bleeds after wisdom tooth removal are the same as after regular removal. If there is a history of blood diseases, preparations are made for such an operation in advance. A blood test is carried out, in some cases calcium chloride injections and vitamin C
and
K.
_
If the cause of alveolar bleeding is systemic diseases, general hemostatic agents are used (calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, aminocaproic acid, dicinone, vikasol).
For hypertension, antihypertensive therapy is prescribed. After the pressure normalizes, the bleeding usually stops.
Symptoms
The main symptom of epistaxis is blood coming out of the nostrils or entering the oral cavity from the upper part of the pharynx. In more severe cases, accompanying symptoms are revealed:
- weakness, nausea, disturbance of spatial orientation;
- feeling of fullness in the ears;
- headache;
- tachycardia;
- hypotension;
- pallor of the skin.
If blood ends up in the stomach, vomiting with blood clots occurs, and the stool becomes dark in color.
Diagnosis and treatment of blood diseases
To establish a diagnosis, various blood tests are performed for diseases:
- general blood test - the cellular composition of the blood is studied;
- myelogram - the cellular composition of a bone marrow puncture is studied;
- immunohistochemistry in severe cases is a high-precision method that allows us to identify the nature of malignant tumors;
- immunohematology analysis to determine the ratio of antibodies to red blood cells in the blood;
- establishing the group and Rh factor; appropriate tests are also used for this.
Each blood disease requires a special approach and a specific treatment system. After carrying out all the necessary tests, the doctor will formulate an individual therapy. The main methods of treating blood diseases are chemotherapy and radiotherapy and bone marrow transplantation (alogenic and autologous).
Treatment
For treatment of this condition to be effective, the causes of the disease must be determined. It is very important to promptly identify and treat the main disorders - liver pathologies or oncological lesions.
Additional therapy methods include:
- injection of vitamin K;
- drugs to improve clotting;
- transfusion of frozen blood plasma;
- Other medications include hydroxyurea and oprelvekin, which help eliminate platelet problems.
The patient's diet should include foods high in calcium, folic acid, vikasol, and amino acids.
These include dairy products: cheese, cottage cheese, kefir. Fish and meat will also help eliminate the symptoms of pathology. It is equally important to eat leafy vegetables - green onions, spinach, cabbage.
What is the main danger of capillary bleeding?
First aid for capillary bleeding should not be called an unnecessary procedure. Compared to arterial and venous bleeding, capillary bleeding is not so dangerous, and in most cases the body copes with it on its own. But there are situations that are life-threatening:
- the skin is extensively damaged;
- the ambient temperature is increased;
- blood clotting is impaired;
- There is blood poisoning, oncology, hepatitis, arterial hypertension and other severe pathologies.
The most dangerous is bleeding as a result of damage to the blood vessels of internal organs. Prolonged bleeding provokes a decrease in blood pressure, oxygen starvation, and disruption of the cardiovascular system. If the blood loss is severe, the person dies without treatment. Hemorrhage in the brain affects important centers and also leads to a fatal outcome. Pleural bleeding disrupts breathing and puts pressure on the lung. In most cases, it is important to react in time to manifestations of capillary bleeding and provide first aid in a timely manner.