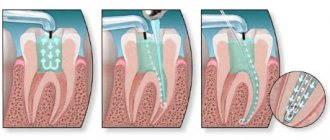
Remineralization of teeth is a dental procedure that involves saturating tooth enamel with compounds of phosphorus, calcium, fluorine and other mineral components.
Regular implementation of this procedure helps restore and maintain the structure of the enamel layer in normal condition, prevent the development of caries and other dental diseases, and also reduce the sensitivity of teeth to the effects of chemical and temperature irritants.
Why is tooth remineralization performed?
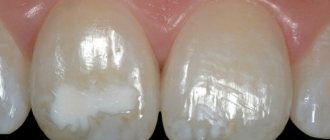
Tooth enamel is a network consisting of microscopic prisms of hydroxyapatite. This mesh has a porous structure that allows acids to penetrate into the enamel layer and remove minerals from it. Gradual demineralization of dental tissues is a factor contributing to the development of caries and other pathological processes that destroy teeth. In such a situation, the dental remineralization procedure comes to the rescue, allowing you to restore the content of useful substances in the affected areas and prevent the occurrence of dental pathologies.
It should be noted that in the body of a healthy person, natural remineralization of teeth occurs constantly, just like demineralization.
In this case, the leading role in restoring the mineral content of enamel tissues is played by saliva, which contains all the microelements necessary for this. When malfunctions occur in the body, saliva changes its composition and ceases to function as a reducing agent, so the patient may be faced with the need for artificial remineralization of teeth in the dental office.
Complete set of CALASEPT dental kit
The standard kit consists of: 5 carpules (syringe cartridges) filled with sterile calcium hydroxide in an amount of 2.5 g and 30 sterile needles with Flexi-tip cannulas. Syringes with paste are sterilized by ionizing radiation in packaged
Special notes.
CALASEPT paste is quite a caustic material, so when:
- contact with eyes and mucous membranes - they must be rinsed with plenty of water and consult a specialist;
- In case of contact with the skin, rinse the skin that came into contact with the substance with water;
- If it gets into the respiratory tract or esophagus, you should consult a doctor.
Individual intolerance to the components of the drug and the occurrence of allergic reactions are possible.
Indications for remineralization
Indications for restoration procedures are:
- enamel damage that occurs after teeth whitening, professional dental cleaning or orthodontic treatment;
- excessive tooth sensitivity;
- the presence of non-carious dental damage;
- increased need for minerals in adolescence, childhood or pregnancy;
- there is an urgent need to protect dental tissues from the harmful effects of acids.
It is worth noting that the remineralization procedure can be carried out not only to eliminate existing pathologies, but also to prevent their development.
Calasept's analogs
There are products for treating dental tissue that are similar in properties and composition to Calasept.
- Metapex - includes 2 syringes of 2.2 g each, cost - 1010 rubles.
- Calsept - 2 syringes of 2.5 g, cost - 580 rubles.
Pastes containing calcium hydroxide are a reliable material that is used to restore damaged dental tissue.
Metapex
The drug is made in Korea. Contains calcium hydroxide as the main active ingredient, supplemented with iodoform . Qualitative and performance characteristics are similar to the drug Calasept.
The Metapex kit contains the following:
- syringe filled with material, volume 2.2 g - 1 pc.;
- sterile disposable tips – 20 pcs.;
- rotating ring for changing the direction of the tip - 1 pc.
Prices for this drug are in the range of 500 – 1000 rubles per set.
Calcept
Russian material, similar in composition and quality characteristics to Metapex. Most often, the consumer is offered a drug with iodoform (but there are composition options without it).
Contents of the Calpex set with iodoform:
- refilled syringe (2.5 ml) – 2 pcs.;
- sterile disposable tips – 20 pcs.
The cost of the drug varies from 1000 rubles and above.
Attention! All prices shown are indicative only. They are subject to adjustment depending on the region and place of sale. More accurate figures can be found on the seller's website.
Types of dental remineralization
In modern medical practice, two main methods are used to saturate dental tissues with essential minerals:
- natural;
- artificial.
Natural method
Natural remineralization is usually called the enrichment of enamel with minerals by eating certain foods or using special hygiene products.
The main methods to start this process are:
- use of toothpastes with increased calcium and fluoride content;
- the use of special rinses;
- correction of the diet, inclusion of dairy products, fatty fish, meat, pork and beef liver, eggs in the daily menu;
- taking vitamin complexes.
Artificial method
Unfortunately, the use of such measures is often not enough. Therefore, dentists recommend visiting a doctor regularly (approximately once every six months) and undergoing a professional remineralization procedure.
Artificial enrichment of enamel tissues with minerals can be carried out in two ways:
- fluoridation method (active saturation of dental tissues with fluoride);
- by remineralization using preparations based on calcium and phosphates.
Teeth fluoridation method
Fluoridation can be both superficial and deep. Surface treatment of teeth is performed using the following methods:
- application of special mouth guards filled with fluoride-containing gel;
- coating of enamel with fluorine varnish;
- electrophoresis (introduction of fluoride ions into the bone tissue of the tooth using weak current discharges).
Deep fluoridation of enamel is a complex dental procedure that includes the following steps:
- removal of unwanted deposits on teeth;
- drying the enamel surface and applying the first layer of a preparation containing fluorine, magnesium and copper salts to it;
- re-drying the teeth and applying a second layer of the product;
- treatment of enamel with calcium copper hydroxide.
Remineralization with calcium and phosphates
Remineralization techniques using calcium and phosphates are considered safer, but at the same time, less effective than fluoridation. That is why they are more often used for preventive purposes or in the initial stages of the development of dental pathologies.
It has been proven that remineralization of teeth significantly improves the condition of dental tissues and allows them to be protected from all destructive influences of the external environment. Regularly performing this procedure is one of the easiest and most affordable methods of maintaining a healthy and beautiful smile.
Medical Internet conferences
Relevance. Calcium is one of the main components that make up hydroxyapatite crystals, which represent the mineral basis of hard dental tissues. There are a large number of Ca drugs of different generations on the pharmacological market, however, their price categories are different. Prevention in children should be aimed at creating optimal conditions for increasing tooth resistance and enamel maturation. It follows that for the correct formation of teeth, when the processes of primary mineralization are not yet completed, endogenous prophylaxis with calcium preparations is necessary. [1].
Purpose: to choose the most effective Ca preparation for endogenous caries prevention.
Tasks:
1) study the pharmacological features, indications, contraindications of the drug “Calcium Gluconate” as a representative of monodrugs;
2) study the pharmacological features, indications, contraindications of the drug “Calcium - D3 Nycomed” as a representative of combined calcium preparations;
3) study the pharmacological features, indications, contraindications of the drug “Kalcemin” as a representative of multivitamin preparations.
4) comparative analysis of these drugs.
Materials and methods. In the process of work, the content of dental journals was studied, an analysis of domestic and foreign articles, as well as various websites and brochures was carried out.
Results and discussion. Endogenous prevention of caries is the introduction of Ca, P, F preparations, microelements and vitamins into the child’s body. Its main directions: 1) strengthening the child’s health (treatment of chronic diseases of organs and systems; 2) prescribing drugs P, Ca, F and other macro- and microelements in combination with vitamins in various specific dosages; 3) proper balanced nutrition of a child and a pregnant woman during the formation of mineralization of tooth enamel; Calcium is the most significant macronutrient required for the mineralization of enamel. The daily calcium requirement of a growing organism is 10 – 13 mg/kg. There are: 1) monopreparations that contain only Ca salts (calcium lactate, calcium glycerophosphate, calcium gluconate); 2) combined preparations containing vitamin D or C, Ca salts, and also mineral elements (boron, zinc, magnesium); 3) multivitamin preparations. Ca gluconate is produced in tablet form of 0.25 and 0.5 g. Pharmacological action: eliminates calcium deficiency, exhibits antiallergic, hemostatic, detoxification, anti-inflammatory effects. Pharmacodynamics: eliminates calcium deficiency. Ca ions take part in the propagation of nerve impulses, in the contraction of skeletal and smooth muscles, myocardium, and in blood clotting. Pharmacokinetics: after the drug has been taken, it begins to be rapidly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, penetrating into the blood, where it is available in ionized and bound form. It is removed by the kidneys (20%) and with the contents of the intestines (80%). Indications: 1) hypocalcemia; 2) hypoparathyroidism; 3) rickets; 4) increased need for Ca ions (pregnancy, breastfeeding, increased body growth); 5) a small amount of Ca ions in food, lack of its metabolism; 6) intoxication with Mg salts, hydrofluoric and oxalic acids. Contraindications: 1) hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Children under 1 year are given 0.5 g, 2 – 4 years – 1 year, 5 – 6 years – 1.5 g, 7 – 9 years – 1.5 – 2 years, 10 – 14 years – 3 – 4 g/day. Course – 1 month [2]. Anti-carious effect – remineralizing role to prevent caries and non-carious lesions. Clinically, a child’s reduced calcium intake may not be reflected in anything for a long time. But with a lack of calcium to normalize its content in the blood and create metabolic processes in the body, it begins to be washed out of the bones and teeth. Ultimately, this causes a decrease in the rate of formation of the skeletal system, improper formation of hydroxyapatites, and in acute periods of life (first year, 1-2 years, 6-7 years, 12-14 years) leads to the formation of osteopenic syndrome [3,4] . The child's compensatory capabilities to compensate for calcium deficiency are small. This is confirmed by the results of studies conducted by I.V. Kovach and co-authors, who discovered a special correlation between the mineral density of bone tissue and the intensity of the carious process in children 3-6 years of age, i.e. the lower the mineral density of bone tissue, the higher the intensity of dental caries [5]. Many scientists say that there is a close connection between somatic pathology and calcium metabolism disorders. The main ones are diseases of the kidneys (chronic renal failure, idiopathic hypercalciuria) and gastrointestinal tract (malabsorption syndrome in various diseases, duodenal ulcer), endocrine organs (diabetes mellitus). Inflammatory diseases also have a great influence on calcium metabolism. pain (osteomyelitis ), various toxic substances, radionuclides [6,7]. Of the examined children aged 5-16 years, epidemiological experiments by Russian scientists revealed the presence of osteopenia or osteoporosis in 10-30% (depending on age) [8]. They are manifested by a number of symptoms: general weakness, increased fatigue, decreased academic performance, developing dental diseases (caries, periodontitis), paresthesia and muscle twitching, dry skin, brittle nails and hair, changes in posture [9,10]. Thus, any conditions that involve a low intake of Ca or an increased consumption of Ca lead to the formation of hydroxyapatite crystals of irregular structure and properties in the hard tissues of teeth, which will have a detrimental effect on their resistance to caries. Therefore, there is an obvious need for medicinal endogenous prevention of caries in permanent teeth in children, especially during periods of rapid growth, using new calcium preparations in combination with vitamins and microelements that support its absorption in the development of mineralization of hard tissues. Particularly cheap among them are simple 1st generation calcium preparations (gluconate, lactate, glycerophosphate, citrate), which contain only calcium compounds. Still, synchronous intake of vitamin D is necessary, which was taken into account when creating calcium preparations of the 2nd generation (Calcium-D3 Nycomed, Vitrum Calcium (Unifarm, Inc., USA), Calcevid (Beres)). The bioavailability of calcium increased due to this combination, which affected the increase in the effectiveness of preventive measures [11-14]. "Calcium - D3 Nycomed" is a drug that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. The components are calcium carbonate (500 mg) and vitamin D3 (200 IU). The auxiliary part includes: sorbitol, various flavoring additives, povidone, magnesium stearate and aspartame. It is produced in the form of chewable tablets with mint or orange flavor. Pharmacological action: improves the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body and compensates for the deficiency of the main structural element. The biochemical role of calcium lies in the physiological construction of bone tissue, mineralization of teeth, the processes of coagulation and transmission of nerve impulses, and the implementation of muscle contractions. Pharmacodynamics: reduces resorption and increases bone density, replenishing calcium and vitamin D3 in the body, necessary for the mineralization of teeth. It is produced in the form of chewable tablets with mint or orange flavor. Pharmacokinetics: 1) Ca (absorption – 30% of the dose taken; distribution and metabolism – 99% Ca is concentrated in the rigid structure of bones and teeth, 1% is found in intracellular and extracellular fluids, 50% of the total Ca content in the blood appears physiologically active ionized form, of which approximately 10% is composed of phosphates and other anions, the remaining 40% is associated with proteins, primarily albumin; excretion - Ca is excreted through the intestines, kidneys and sweat glands. 2) Vitamin D3 (absorption - about 80% of the dose taken in the small intestine; distribution and metabolism - circulates in the blood in a bound state with a special globulin, metabolized in the liver, then accumulates in adipose and muscle tissue; removed through the intestines and kidneys. Indications: 1) prevention and treatment of calcium deficiency and vitamin D3; 2) prevention and complex therapy of osteoporosis and its complications. Contraindications: 1) hypercalcemia; 2) hypercalciuria; 3) hypervitaminosis D3; 4) severe renal failure; 5) hypersensitivity to the drug. Directions for use and dosage: adults and children over 12 years old - 1 tablet 2 - 3 times a day, children from 5 to 12 years old - 1 - 2 tablets per day, children from 3 to 5 - as recommended by a doctor. Anti-carious effect - for the prevention and treatment of carious and non-carious lesions, periodontal diseases, well suited for people with normal bone mineral density. Calcium-D3 Nycomed prevents a decrease in the number of chalk spots and an increase in enamel remineralization, activation of bone tissue remodeling processes and inhibition of its resorption [15-19]. Nowadays, the most effective are calcium preparations of the 3rd generation, which contain, in addition to calcium and vitamin D compounds, a number of vitamins and microelements that affect mineral metabolism (Kaltsinova (KRKA), Kalcemin (Sagmel), Biocalcevit). “Calcemin”, each tablet contains 842 mg of calcium citrate and 202 mg of calcium carbonate (250 mg of elemental calcium), 50 IU of vitamin D, 2 mg of zinc, 0.5 mg of manganese, 50 mcg of boron. The citrate and carbonate present in Kalcemin belong to the group of salts with a high content of simple Ca. At the same time, calcium citrate reduces the risk of stone accumulation in the urinary tract, hence it reduces the activity of parathyroid hormone and is absorbed by itself. Pharmacological action: replenishes calcium deficiency, regulates calcium-phosphorus metabolism, replenishes the deficiency of vitamin D, macro- and microelements. Pharmacodynamics: combination drug. Increases the resistance of hard dental tissues, prevents diseases of the musculoskeletal system. There are no data on pharmacokinetics. Indications: 1) prevention and treatment of osteoporosis; 2) replenishment of the deficiency of Ca and microelements in children, pregnant women and during breastfeeding. Contraindications: 1) urolithiasis; 2) hypercalcemia; 3) hypercalciuria; 4) hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. The anticarious effect is due to its ability to increase the resistance of tooth enamel, as well as its effect on mineral metabolism and on the body as a whole. There is no data on the effectiveness of using Calcemin for the prevention and treatment of lesions of hard dental tissues in pregnant women and children under 6 years of age in scientific literature. At the same time, it should be noted that the combination of microelements in one Calcemin tablet is not entirely justified. Magnesium and calcium have a common transport system in the intestines, so they are absorbed 2 times less. The use of the mineral-vitamin complex “Kalcemina” has a beneficial effect on the acid-base balance of the oral cavity, normalizes the processes of de- and remineralization in the enamel-saliva system, thereby reducing the intensity of caries development in adolescents [20-25].
Conclusions:
1) A special feature of the drug “Calcium Gluconate” is its low cost and the possibility of use in children under 1 year of age. The disadvantage was an overdose, with the development of hypercalcemia with deposition of Ca salts
2) A special feature of the drug “Calcium – D3 Nycomed” is the rapid absorption of the drug in the oral cavity and its pleasant taste. The downside was the presence of aspartame, which is not recommended for pregnant women.
3) A special feature of the drug “Kalcemin” was the content of vitamins and minerals necessary for humans, intended for use during pregnancy. Disadvantage: possible development of an allergic reaction.
4) The largest number of positive criteria is noted for the drug “Kalcemin”: it contains a complex of vitamins and minerals, a minimum of side effects, and contraindications. The most effective drug for endogenous prevention is Kalcemin.
Properties of copper-calcium hydroxide:
The water-containing paste contains highly dispersed calcium hydroxide, which is produced from exclusively pure calcium using the author's method. The positive effect of calcium hydroxide is due to its high alkalinity (pH ~ 13), which kills any microorganisms and their non-vegetative forms. When the drug is applied to bleeding tissue after initial surface cauterization, proteolysis occurs, which ensures sterility in the area of contact and promotes the rapid formation of a calcium carbonate membrane. The membrane softens the diffusion of dissolved calcium hydroxide, leading to the appearance of an alkaline environment that promotes the formation of dentin and bone tissue. Calcium hydroxide exhibits these properties only in a wet state, so the addition of a water-insoluble hardening agent was fundamentally abandoned.