Clinic “No Hurt!”
Enlarge
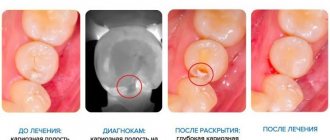
A patient comes to the doctor with caries. Or, during an examination, the doctor discovers caries. Treatment is prescribed. Dental tissue damaged by infection is removed and the tooth geometry is restored using a filling. The nerve of the tooth is not affected during caries treatment and the tooth remains alive. The patient goes home, but the tooth does not allow itself to be forgotten. It hurts to bite. It hurts to chew. Pain occurs when biting, pressing, or pressing on a tooth.
We addressed this topic in the article Tooth hurts after filling. In this publication we will reveal the causes of toothache under a filling after caries treatment.
Complications of pericoronitis
Purulent pericoronitis:
- Constant pain that intensifies when chewing;
- Pain radiating to the ear and temporal region;
- Increased body temperature up to 37.2 - 37.5°C;
- Mouth opening is limited and painful, which intensifies with the development of inflammation;
- The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful when pressed;
- When pressing on the hood, purulent contents are released from under it, causing sharp pain.
Acute pericoronitis can become chronic, when the inflammatory phenomena do not completely subside and exacerbations periodically occur.
Retromolar periostitis.
Occurs as a complication of purulent pericoronitis. The disease is characterized by clinical symptoms of purulent pericoronitis, but more pronounced.
- The pain intensifies;
- The general condition is disturbed, weakness and weakness appear;
- Body temperature rises to 38-38.5°C;
- Chewing food becomes impossible;
- Sleep is disturbed;
- The patient is pale, there is pronounced tissue swelling in the posterior part of the submandibular and lower part of the buccal region;
- The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful;
- When you press on the hood and surrounding tissues, a sharp pain occurs.
source site. www.dentalmir.ru
The best dentists in Sarov, where to treat teeth in Sarov
Ways to treat and reduce tooth pain when chewing
If you experience pain while chewing food, you should immediately seek help, without waiting for the pain to go away on its own or for additional unpleasant symptoms to appear, such as temperature and swelling, which indicate the presence of a significant inflammatory process in the body. However, if it is not possible to go to the dentist in the near future, you can independently relieve the pain and stop the development of inflammation with the help of a few simple procedures.
Ways to reduce pain when chewing:
- rinse the mouth with herbal tinctures or soda solution;
- make tooth lotions from mint, cloves or sea buckthorn oil;
- After each meal, use dental floss and rinse your mouth to get rid of food debris;
- to disinfect the oral cavity, keep onion peel tincture in your mouth for 20 minutes;
- for acute pain, you can take a painkiller, for example spasmolgon, analgin, nurofen, etc.
These methods will help reduce pain before visiting a doctor. However, it is impossible to cure the cause of toothache with their help, so it is necessary to seek qualified help as soon as possible in order not to aggravate the situation and prevent the development of other oral diseases.
A tooth hurts under a temporary filling: treatment
After the filling is installed, you may experience some pain that goes away on its own within a few days. If there is significant discomfort, dentists recommend rinsing with a warm solution of furatsilin or chlorhexidine. A warm saline solution will also relieve pain. After eating, do not forget to rinse your mouth with warm water and 0.5 tsp. soda and a couple of drops of iodine. You can also apply a cooling gel or place a piece of ice on the tooth area. Painkillers can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
In this case, it is highly not recommended to use traditional methods to relieve toothache under a temporary filling. Home remedies provide only temporary relief and do not eliminate the cause of the pain.
The occurrence of acute toothache after a visit to the dentist
If you have a toothache immediately after a visit to the dentist, do not despair. The most likely consequence of toothache is interference with the nerve endings of the tooth, which cannot pass without leaving a trace.
If a filled tooth hurts when pressed, this indicates that the dentist performed a high-quality canal filling. Such unpleasant sensations may accompany you for 1-2 days after treatment.
If toothache persists for a long period of time, it is likely that the tooth filling was performed poorly and the doctor made mistakes.
Errors caused by the doctor's actions when filling a tooth may include:
- unfinished grinding of a new filling
. If the bite line protrudes beyond the boundaries of the closure of the tooth, then when pressure is applied, the patient may experience noticeable discomfort. Both teeth will experience increased stress, which can often lead to tooth or filling breakage;
- violation of seal tightness
. The most common case when the seal's tightness is broken is the use of expired or poor-quality materials. As a result, cracks appear, the filling shrinks, thereby contributing to the leakage of the seal;
- If surgery has been performed on the gum, then there is a high probability of a persistent infection getting into this area
. In this case, the inflammatory process proceeds slowly, and the pain is “blurred” in nature.
The first group includes:
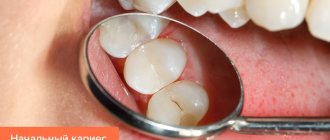
Caries
A carious cavity is a depression in the hard tissues of the tooth that appears as a result of their destruction. Food or drinks (most often cold) enter the cavity and cause short-term (several seconds) pain. If food is retained in the carious cavity (especially sweet food), the pain may last longer.
Seal defect
If part of the filling (or part of the hard tooth tissue around the filling) placed previously breaks off under the influence of chewing load, a part of the tooth that is more sensitive to the effects of food is exposed.
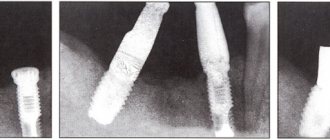
Chronic apical periodontitis in the acute stage
It sounds scary...and in reality it is no less terrible. The mechanism of pain in this case is quite simple. Around the apex of the root, surrounded by a dense bone plate, the inflammatory process is activated. Inflammation in all parts of our body proceeds along approximately the same path and is characterized by an increase in the volume of inflamed tissue (due to blood flow to the affected area). And if this happens, for example, when a hand is bruised, then we will see swelling, that is, an increase in volume. Now let’s imagine the formation of a “swelling” in the area of the root apex surrounded by a dense bone plate... there is no room for the incoming fluid, the nerve endings are compressed, and here you are also trying to chew a delicious steak!
Periodontitis
One of the causes of tooth pain is periodontitis.
The thing is very unpleasant (like most dental diseases). It is characterized by a long-term, most often sluggish inflammatory process of all tissues surrounding the tooth (gums, ligaments, bone surrounding the tooth), leading to their atrophy (reduction). As a result, the tooth becomes mobile and cannot withstand the chewing load, which is indicated by pain.
Functional overload
Each of our teeth, depending on the function it performs, is designed for certain chewing loads. However, if for some reason the number of teeth decreases (extraction, injury, etc.), the remaining ones begin to experience increased chewing pressure (for themselves and for the lost ones). Such excessive load leads to loosening of the tooth and the appearance of the symptom we are discussing. Only high-quality prosthetics will help solve this problem.
Injury to the gingival papilla by hard food
The reasons for this phenomenon may be:
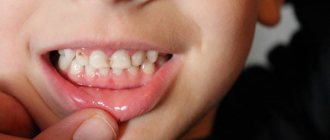
Large distances between teeth (diastema and trema). They can be either physiological in nature (features of the anatomical structure) or pathological (for example, “divergence” of teeth during periodontitis);
Poorly restored contact point
A contact point is a point or area through which adjacent teeth contact each other and through which chewing pressure is distributed. If the carious cavity was located on the side surface of the tooth and after filling it, the contact point was not properly restored, then food will get clogged between the teeth when chewing, injuring the gingival papilla. Hence the pain. This reason relates more to the second group, so let’s move on to it.
Systemic reasons
- Hormonal imbalances. Often observed with improper use of hormones, pregnancy or menopause;
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Products must contain magnesium (Mg), phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca);
- Stress. Depression, psychological fears, and increased anxiety can provoke hyperesthesia;
- Regular contact with chemicals (for example, when performing professional activities in production).
Initially, high sensitivity manifests itself to cold and hot drinks, while the pain lasts no more than 30 seconds. Later (in the absence of professional treatment!) discomfort becomes the norm when eating sweet, spicy and salty foods.
What diseases provoke the development of hyperesthesia?
Did you bite into a cold apple, take a sip of hot coffee, eat some ice cream and feel pain? This means that you have a high sensitivity to hot and cold foods (drinks), which can be caused by certain diseases.
Among them:
- Caries. It leads to exposure of the pulp (the “dental nerve”). Externally, this can be determined by a dark-colored hole located on the tooth enamel. Typically, pulpitis causes acute pain when consuming cold foods (drinks), while such a reaction is not observed with hot dishes;
- Bleaching. The use of whitening pastes with large abrasive particles and unskilled mechanical whitening at the dentist provokes a violation of the sensitivity of tooth enamel. It reacts to cold and high temperatures, sweet and sour;
- Filling. After installing a temporary or permanent filling, tooth sensitivity increases, BUT it usually lasts no more than 2-3 days. No special treatment is required, but if hyperesthesia does not go away after some time, seek qualified dental care;
- Periodontitis. Inflammation of the periodontal tissues, accompanied by bleeding of the mucous membranes, exposure of the necks and roots of the incisors, subsidence of the gums, the formation of large pockets, suppuration, leads to increased sensitivity and the formation of a reaction to hot and cold.
If your teeth are absolutely healthy, but begin to hurt under the influence of irritants, then it is recommended to refrain from sweet, sour and spicy foods. Replenish your diet with healthy foods that help restore tooth enamel (fish, milk, cottage cheese, fresh vegetables, fruits and berries).
Formation of hyperesthesia
The high sensitivity of tooth enamel to external irritating factors develops gradually, going through several stages:
- The first pain signals. Occurs when taking cold or hot food or drinks. The pain is “aching” in nature, there is no pulsation.
- Expanding the list of irritants. It includes sweet, salty and spicy foods. The pain lasts longer and makes eating irritating foods impossible.
- Reaction to all stimuli. Even cold air becomes a factor causing acute throbbing pain. Pain syndrome is a constant concern.
Treatment of hyperesthesia
How to restore normal tooth sensitivity so that eating does not bring pain and suffering, but pleasure? Immediately go to the dentist - no one can solve the problem better than him.
Do not delay contacting a specialist and do not hope that hyperesthesia will go away without treatment. Perhaps the pain will subside and not bother you, but it will arise again - it’s only a matter of time, and it will be much stronger and longer lasting.
The dentist will carefully examine the oral cavity and, if abrasion of tooth enamel, cracks, chips, caries or inflammatory processes is detected, he will make a diagnosis and then prescribe the correct treatment using one of the methods:
- medicinal (medicinal),
- hygienic,
- physiotherapy,
- surgical.
Attention! To test the sensitivity of teeth, a stream of water is directed from the tip onto the enamel, the temperature of which is about 30 oC.
If hyperesthesia is accompanied by caries, periodontitis, pulpitis or other diseases, then they are quickly treated (if possible), and then the normal sensitivity of the tooth enamel is restored. For general therapy, use soft brushes and stop smoking.
TOP 3 toothpastes for hyperesthesia
At home, it is recommended to use special toothpastes to reduce the sensitivity of enamel and restore its sensitivity:
- Sensodyne paste. The active elements are zinc and sodium fluoride, which ensure 100% elimination of bacterial plaque and increase the protective properties of teeth. The result of regular use is a decrease in enamel sensitivity.
- Pasta "Lacalut". Contains active fluoride, which promotes rapid restoration of tooth enamel. Additionally, it provides remineralization of tissues (gums and mucous membranes of the oral cavity).
- Pasta "Silca". The active ingredients are fluorides, urea and potassium citrate. They reduce tooth sensitivity and stop calcium leaching. Additionally, the paste eliminates the negative effects of acids.
TOP-3 gels for hyperesthesia
Special gels will help enhance the therapeutic effect of toothpastes. Their regular use helps reduce the reaction of teeth to temperature changes:
- Gel "ROCS". It contains calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, which create a protective film on the enamel and prevent the negative effects of various irritants. The result of use is a decrease in tooth sensitivity and lightening of the enamel.
- Gel "Emofluor". The content of stannous fluoride ensures the effectiveness of the product against bacteria and bacterial plaque. Providing a cariesostatic effect, the gel reduces the sensitivity of the enamel and prevents the development of periodontitis.
- Gel "Fluoridex". Recommended for use together with regular toothpaste. The active element is sodium fluoride, which strengthens the enamel and reduces the sensitivity of teeth to irritants.