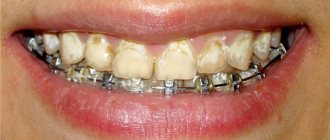
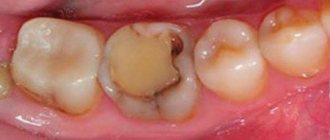
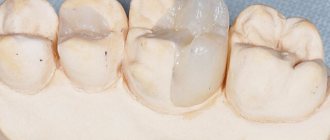
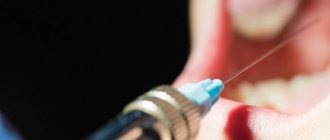
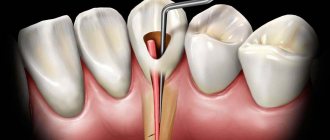
To detect caries, dentists use indicators, special substances that stain colonies of carious bacteria - Str. mutans, and the tissues affected by them. In this way, the doctor can understand how damaged the tooth is and what the boundaries of the caries are, as well as whether the defect is a carious lesion. The action of caries markers is to color areas affected by caries. From healthy tissue, the indicator is easily washed off with water without lingering.
Colored indicators of carious diseases
A caries indicator is a special substance that, when applied to the affected area of a tooth, allows the doctor to see the area of carious formation due to the appearance of bright coloring.
Healthy teeth are not colored; a minimal amount of coloring matter is easily washed off with water. After applying the marker to the tooth surface, the doctor can begin to remove the stained areas with a drill. The procedure is repeated until the paint in the mouth is completely eliminated. A caries marker is an excellent tool for showing patients the affected areas of their teeth. The indicator is not intended for use at home. This should only be done by a professional. If you strictly follow the instructions, the caries marker allows you to completely get rid of infected tissue.
Types of detectors
In modern dentistry, three main caries detectors are used to determine the extent of the disease and recognize the affected areas:
- Chemical. The most common type of indicator due to its ease of use and budget cost. The bright liquid colors damaged areas without affecting healthy tissue. Fuchsin is most often used as a dye; it is a common indicator in biology and medicine and has a bright pink color. Sometimes it can be replaced with a solution of methylene blue. The principle of action for both substances is the same.
- Optic. The dentist directs a light beam with a specific wavelength to the teeth. The program calculates the degree of refraction of the beam in different parts of the tooth and displays an image on the screen in which the damaged areas are painted in a different color. They were the ones who were exposed to the destructive effects of caries.
- Laser. The operating principle of this detector is the same as that of an optical one, only in this case a laser beam acts as an indicator.
In the vast majority of cases, doctors use chemical caries markers. Non-contact indicators are quite expensive, and this leads to an increase in the cost of dental services. In addition, it is not so convenient to control the process of cleaning damaged areas.
When are colored markers used?
The use of caries markers occurs in the following cases:
- to identify areas affected by caries after the removal procedure;
- to control the result of removing hard tooth tissue;
- to identify affected tissues in areas inaccessible to visual inspection;
- to demonstrate to the patient the extent of his caries;
- to find mechanical damage to teeth;
- to determine the nature of tooth enamel defects.
A colored marker helps to detect caries at the very initial stage of its inception. Using an indicator, the dentist cleans out the stained areas of the tissue. When the staining disappears, this will indicate that the lesion has been completely eliminated.
Causes of caries
There are more than 400 theories explaining the causes and mechanism of caries. Currently, dentists mainly adhere to the following concept.
Plaque
, which inevitably occurs in the oral cavity, accumulates in those places where it is not naturally removed by chewing. If oral hygiene is not carried out properly, plaque accumulates and, thanks to the activity of its constituent bacteria, hardens over time. A so-called dental plaque is formed. Bacteria concentrated in such a plaque release lactic acid, which begins to destroy tooth enamel.
In the structure of dental plaque, a significant proportion is formed by dextran, produced by bacteria from sucrose. This is why sugary foods increase the likelihood of tooth decay.
However, susceptibility to tooth decay varies from person to person. This is largely due to the properties of enamel - with a decrease in the amount of calcium in the surface layer of enamel (or rather, a decrease in the calcium/phosphorus ratio), the vulnerability of teeth increases. How well the immune system works is also important. Our saliva contains immunoglobulin A. Normally, its amount is sufficient to prevent microbes from attaching to tooth enamel, preventing the formation of plaque. If the immune system is not healthy or the composition of tooth enamel is compromised, tooth decay can affect the teeth at a young age or even in childhood. Over the years, the activity of the immune system decreases, metabolic processes change, which means the likelihood of developing caries increases.
Factors contributing to the development of caries
Factors contributing to the development of caries are:
- weak immunity;
- poor nutrition (in addition to excess sweets, a lack of vitamins is also important, as is the lack of fruits and vegetables in food);
- drinking water with insufficient calcium, fluorine and phosphorus;
- diseases suffered in childhood that can affect the formation of dental tissue (rickets, tuberculosis, etc.);
- hereditary predisposition.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of using special colored markers:
- accurate indicators of healthy teeth and teeth affected by carious diseases;
- the natural composition of the markers makes the procedure safe;
- the opportunity to demonstrate to the patient the condition of his teeth;
- using a marker not only for the treatment of caries, but also for examining dental canals;
Disadvantages of using special colored markers:
- staining occurs even in areas with a minimal level of infection, which can be treated with remineralizing drugs;
- When grinding down stained areas, a smeared color may appear, making it difficult to examine the tissues being cleaned and distinguish them from completely healthy teeth.
Symptoms of caries
Symptoms of caries depend on the stage of development of the disease
There are four stages of caries development: carious spot, superficial, medium and deep caries.
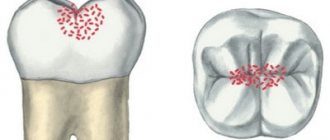
Carious spot
Carious spot
looks like a patch of enamel that has been stripped of its natural shine. Carious spots can be either pigmented or matte (white). The appearance of such a spot means that the process of destruction of the enamel has begun in this place. At this stage, the tooth does not yet respond to stimuli.
Superficial caries
In the stage of superficial caries
the enamel softens. The tooth begins to sense chemical irritants (sweet, sour and salty foods). Sometimes the tooth also reacts to heat or cold. The pain disappears as soon as the irritating factor stops.
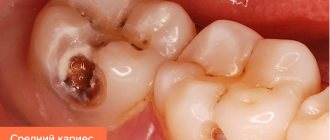
Average caries
For average caries
destruction reaches dentin (dentin is the hard tissue that forms the bulk of the tooth; it is located under the enamel). A carious cavity appears in the tooth. However, the layer of softened dentin does not yet come into contact with the pulp (soft tissues inside the tooth), so the pain caused by physical, chemical and temperature effects on the affected area is not as acute as with deep caries.
Deep caries
Deep caries
characterized by significant destruction of tooth tissue. A deep carious cavity is formed. A layer of softened dentin reaches the pulp. As a result, any food entering the carious cavity causes acute pain.
If the process of tooth decay continues, the exposed pulp may become inflamed and pulpitis will begin. Pulpitis is characterized by attacks of painful toothache, often at night. In advanced cases, tooth loss is likely.
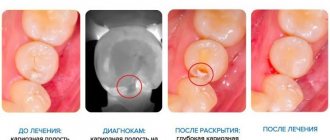
How is the procedure for caries treatment using a marker?
The procedure for eliminating carious diseases using a special colored marker involves several stages:
- Preparatory. The teeth are washed with water and dried thoroughly.
- Applying a marker using a special syringe or applicator to the surface of hard tissue.
- Rinsing tooth enamel with water 10 seconds after staining to remove paint from healthy teeth. The affected areas will remain colored.
- Removing carious formations with a drill.
The appointment with the dentist lasts until the doctor is sure that the tissues are no longer stained. The marker is a safe product based on its composition, however, some patients may experience discomfort if the solution gets on the mucous membrane. This goes away after rinsing the mouth with water.
Method of using caries detectors in practice
The procedure for identifying areas of the dentition affected by caries consists of a number of sequential actions:
- The doctor rinses the teeth and the areas between them with a water jet, then dries the teeth with warm air, which expands the pores and removes remaining water. This point is very important - thoroughly drying the surface of the tooth enamel determines how accurately the caries detector will subsequently color them.
- The doctor treats the teeth with a chemical dye using a syringe or pipette. The indicator is distributed evenly over the entire surface of the dentition.
- After 10 seconds (but no more) after applying the caries marker, the dentist washes off the drug, then dries the teeth again. As a result, only areas with carious lesions remain stained.
- Using a drill, the affected tissue is removed. After this, the doctor again applies the caries marker to the teeth, washes off and cleans the stained areas again.
- This algorithm of actions is repeated over and over again until the tissues stop staining, which indicates the absence of affected enamel.
Of course, the procedure is carried out gradually: as a rule, one or two teeth per session. And although the use of caries detectors somewhat reduces the speed of the therapeutic process, it significantly improves the quality of dental treatment.
Indicators allow for thorough cleaning of the enamel from carious damage and prevent possible complications. For example, if diseased tissue is poorly removed under fillings and crowns, secondary caries may begin to develop.
Possible complications and ways to eliminate them
In some cases, patients after prosthetics complain of severe pain. The reason may be incomplete sealing of the dental canals, due to which an inflammatory process develops. Pain under the prosthesis can also be caused by the formation of a cyst or the presence of a piece of instrument in the canal. To fix the problem you need:
- remove the prosthesis
- open the channels,
- clean them,
- reseal,
- install a crown.
If there is structural damage to the tooth, cracks or holes at the junction of the crown with living tissue, prosthetic stomatitis may develop, which occurs due to strong pressure on the gums. This leads to poor circulation and bedsores. In this case, re-installation of the crown is also required.
Some patients experience allergic reactions to the material from which the prosthesis is made. Galvanic syndrome is observed if crowns made of different materials are installed in the mouth. Such a proximity is fraught with the appearance of a galvanic current, which stimulates the oxidation process. The patient feels a metallic taste in the mouth and weakness. He has a change in the color of the crowns and teeth next to them.
Removing dental crowns is quite difficult, especially if you need to save the structure for later reinstallation. Help to preserve the denture: special tools, which are hooks, with the help of which dentures are cleaned. In addition, modern dentistry allows crowns to be removed using ultrasound. After treatment, the crown can be easily returned to its place.
Stages of disease development
At the initial stage, the manifestations of the disease may be invisible: this is what makes the disease dangerous. When the defect becomes visible to the naked eye, bottle caries is already gaining strength and affects several teeth. Therefore, it is extremely important to know about the first signs in order to stop the development of the disease in time.
- The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of white spots on the teeth. No painful sensations are observed. Many parents think that the stains are the result of an injury (for example, when a child chewed on a toy) and do not consult a doctor.
- The superficial stage begins when the baby begins to experience pain when eating sweet and sour foods. The spots turn yellow or acquire a brownish tint (for this reason they can easily be confused with plaque).
- During the middle stage, depressions with uneven edges appear on the tooth enamel (as a rule, the defect is located near the gums). The pain makes itself felt when eating cold or hot food, and sensitivity to sweets appears.
- If the disease has reached a deep stage, dental changes become visible even to a layman. The affected tooth begins to resemble an apple core, and pain occurs when pressure is applied. If treatment is not started as soon as possible, the child may lose a tooth, which will affect the ease of chewing.
Prevention of bottle caries in children
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later: bottle caries is no exception in this regard.
The disease can be avoided if:
- Brush your teeth immediately after the first tooth erupts. First, a soft toothbrush and a special toothpaste for babies are used for this purpose (there are more than enough of them on store shelves at present); after the child reaches one year of age, you can begin to use dental floss;
- you should not delay giving up bottle feeding - as soon as complementary foods have been introduced, you must immediately teach your child to eat with a spoon;
- You should not leave a bottle with your child’s crib, giving him free access to it;
- there is no need to accustom your baby to sweet drinks - instead of soda and sweet tea, you can give your child plain water and unsweetened tea;
- In no case should you eat with the child with the same spoon - cariogenic bacteria can get from the adult’s body into the baby’s body in this way;
- even if there are no visible changes in the condition of the child’s teeth, you need to visit the dentist for an examination twice a year (since bottle caries develops very quickly, it is better for the doctor to say that the visit was in vain than to announce the need to treat pulpitis).
Get a consultation
We will answer all your questions before visiting the clinic!
+7
Online registration
Content
1 What is a caries detector?
2 Types of caries detectors
3 Intraoral camera VistaCam IX 3.1 Possible applications of the intraoral camera
3.2 Benefits of the VistaCam IX intraoral camera
3.3 Stages of diagnosing teeth with a caries detector
4 Caries marker
5 Cost of diagnosing teeth with a caries detector