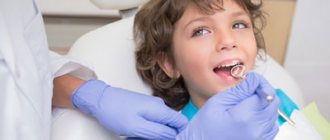
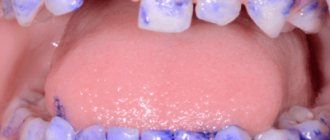
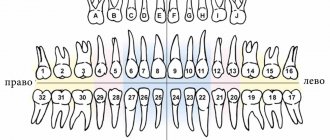
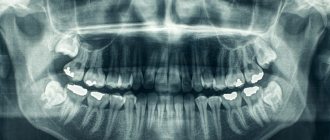
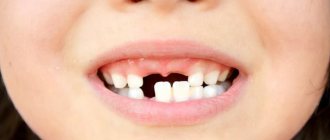
PHOTO: The result of early removal of anterior milk teeth in children. The central primary incisors of the upper jaw were removed at the age of 3 years for emergency reasons.
Early tooth extraction is defined as the removal of a baby tooth 2 years or more before it naturally falls out and is replaced by a permanent tooth. So, for example, the removal of the 4th milk tooth at the age of 6 is early, since this tooth should normally be in the dentition until the age of 9-10.
The main reason for the early removal of baby teeth is the inability to cure the tooth due to severe destruction, fracture of the baby tooth or the spread of the inflammatory process to surrounding tissues (which creates a risk of damage to the permanent tooth germ).
Early removal of chewing baby teeth in children creates conditions for the displacement of adjacent baby teeth into the resulting space. Thus, space is lost where the corresponding permanent tooth will have to erupt. There is a malocclusion of the teeth. For example, the removal of the 4th milk tooth at the age of 3-5 years will lead to the displacement of the 5th milk tooth into the area of the removed 4th milk tooth. When the time comes, there will be nowhere for the 5th permanent tooth to erupt, since its place is occupied and it will begin to push nearby teeth apart. As a result, crowding of teeth will form in the area of the chewing permanent teeth. It also creates inconvenience when chewing food.
PHOTO: Children's orthodontic plate for the upper jaw with artificial teeth. The plate is fixed on the upper jaw using metal clasps, which are not visible from the outside.
Previous removal of the primary incisors on the upper jaw leads to the formation of an aesthetic defect and a lisp in the child, incorrect pronunciation of whistling sounds (“z”, “s”, “ts”) and hissing sounds (“zh”, “ch”, “sh”, “shch”) ") sounds.
When do baby teeth start falling out?
During the first three years of life, a child grows 20 baby teeth. At this time, a temporary bite is formed: it is distinguished by a pronounced anatomical shape, thin enamel, and susceptibility to caries. After the first three years, the roots of baby teeth slowly dissolve, making room for a permanent bite. From the age of 4-5 years, baby teeth begin to fall out, and this continues until the fifth or sixth grade of school.
In most cases, the process occurs calmly and does not require third-party intervention, including medical attention. Dentists strongly advise against rushing things.
Contraindications
Tooth extraction is not recommended in the following cases:
- Acute inflammatory process in the mouth: gingivitis, stomatitis, sore throat;
- Acute infectious diseases of the body: chicken pox, scarlet fever, whooping cough, influenza, ARVI;
- For serious diseases of the body: epilepsy, oncology, heart defects, heart failure;
- For blood diseases that are accompanied by clotting disorders;
- If possible, treat the tooth therapeutically.
Why shouldn't you remove baby teeth yourself?
Removal of a baby tooth is considered premature if more than a year remains before a new one appears. This period is difficult to predict accurately, but you can roughly estimate it using a graph with average indicators.
Premature removal of a baby tooth is dangerous because its neighbors will try to take the vacant space. The roots of permanent teeth that are about to emerge will become crowded. The bite will change, which will take a long time to correct. Moreover, there are several strict contraindications for extracting baby teeth:
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Inflammatory diseases of the throat (ARVI, sore throat, etc.).
- It is not recommended to remove teeth for pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, central nervous system, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency and nutritional dystrophy.
So when your child's first baby teeth start to loosen, don't disturb them and let them fall out naturally. The child's body knows its business.
When a tooth is already loose, it needs to be cleaned very carefully so as not to rush things. If your child is still in kindergarten and his motor skills are not well developed, help him: take ASEPTA® Baby dental wet wipes and wipe the tooth (as well as its neighbors) from the top and sides.
Recommendations after removal
Immediately after removal, the wound formed at the site of the tooth may bleed; the doctor will definitely warn you about this. To avoid additional infection, as well as to stop bleeding as quickly as possible, you should refrain from eating food, carbonated, sweet, hot and cold drinks for a couple of hours. It is best to quench your thirst with plain water and drink it through a straw.
Also, the dentist, if necessary, may suggest installing a space retainer to maintain an even dentition or make modern plates with artificial teeth. This will allow you not to disturb the aesthetics and functionality of the dentition.
Indications for milk tooth extraction
However, there are several cases when teeth definitely need to be helped to fall out. For example:
- Bottle caries or other caries has damaged more than half of the tooth.
- The tooth has been loose for a long time, but cannot fall out. This makes it uncomfortable for the baby to chew.
- The tooth is broken, the sharp edge scratches the cheek or tongue.
- The root is affected by caries (there is a danger that it will damage the permanent tooth underneath).
- Pulpitis.
- There is inflammation or a cyst on the mucous membrane next to the tooth.
Do not make the decision to remove it yourself: if you see the symptoms listed above, contact your pediatric dentist. He will tell you what treatment is required.
Trying to remove baby teeth yourself at home is dangerous: their thin walls and long roots go too deep into the gums. If you pull out a tooth with a thread or other improvised methods, you can easily disrupt the growth of permanent teeth that are hidden under the milk teeth.
Tooth extraction in children: indications
At the age of five or six years, the process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones begins.
Unfortunately, many parents mistakenly believe that there is no need to treat baby teeth. This often causes the development of pathologies that ultimately lead to the need to completely remove the tooth. Here are some indications for tooth extraction in children:
- Presence of advanced caries. If caries has destroyed a tooth so much that it is not possible to restore it, the doctor, as a rule, recommends removing the tooth;
- Development of a cyst at the base of the tooth. A baby tooth injures surrounding tissues and causes inflammation;
- Difficulty with baby tooth loss;
- The presence of serious damage - chips, microtraumas;
- Referral from an orthodontist;
- The presence of periodontitis, sinusitis or fistula on the gums;
- Additional, super-complex teeth.
Permanent teeth in children are removed quite rarely, usually due to advanced caries and its complications. In addition, their removal is recommended in the following cases:
- The presence of an unerupted molar for which there is no space;
- Severe forms of periodontal disease;
- Serious injuries to permanent teeth.
What to do after removing a baby tooth?
The dentist will provide detailed recommendations based on your child’s jaw development. Below are general tips that will help your gums recover as quickly as possible.
- After a baby tooth is removed, a blood clot appears in its socket, which helps the gum heal faster and protects it from dirt. Therefore, rinsing your mouth is not recommended. The clot may become dislodged.
- The tampon that the doctor left in your mouth should be carefully spat out after 20 minutes.
- Ask your child not to bite his cheek in the area of anesthesia. When it “comes off”, painful sensations may appear.
- For a couple of days it is better to abstain from hot foods and fermented milk products, which create an environment beneficial for bacteria.
- During the first week, you should avoid heavy physical activity (especially swimming and running).
- Do not go to the bathhouse or sauna for a week.
- On the first day, it is better to eat soft, cold food.
- Help your child brush his teeth. Use only a soft brush.
Tooth extraction: complications
Sometimes complications can occur after tooth extraction. What parents should pay attention to:
- if the baby has unbearable and prolonged pain;
- bleeding does not stop, the blood is bright scarlet;
- the child has severe swelling, which makes it difficult to swallow;
- the baby complains of immobility (numbness) of the jaw for more than 2 days;
- temperature above 38ºС.
If you notice that your child feels unwell after tooth extraction, contact a specialist immediately!
Removal of a permanent tooth in a child is always done only for emergency reasons, when other methods of treatment and restoration cannot be performed. Take care of the health of your children's teeth!
How to go to the dentist, remove a baby tooth and not scare your baby?
It is recommended that a child’s baby teeth be removed by pediatric dentists: it will be painless, safe and timely. For everything to go smoothly, a visit to the dentist should be associated with something pleasant and calm. Modern dentistry has a friendly atmosphere, new painkillers have appeared, and instruments (especially in children's offices) do not inspire fear.
Finally, our advice: don’t worry and don’t let your child worry. The calmer you are about going to the dentist, the calmer your baby will behave. Stay nearby in the dentist's office, because parental support is extremely important to him.
Types of pain relief during tooth extraction in children
The painfulness of the tooth extraction procedure in Moscow is the main reason for the fear of visiting the dentist for both children and their parents, who are worried about the well-being of their child and want to carry out the extraction as quickly and easily as possible. Modern dentistry has methods of pain relief in which the child will not feel any pain at all. When it is necessary to remove baby teeth with already resolved roots, the dentist gives preference to topical anesthesia . This method involves applying a special anesthetic gel to the gums. However, it is rarely used - only if the tooth was healthy and did not hurt, but for some reason it failed to fall out.
The most commonly used method to solve this problem is infiltration anesthesia , which involves introducing an anesthetic into the gums by injection. For the injection, special, very thin needles are used. The injection site is numbed with an anesthetic gel, so the young patient will not even feel the injection.
General anesthesia is rarely used to remove baby teeth. It is indicated if the child has serious mental illness, acute and purulent inflammatory processes, or is allergic to drugs used for local anesthesia. As a rule, all substances used for pain relief during the removal of baby teeth are completely safe and easily tolerated by young children.
After the operation is completed, the doctor should inform the parents about how to take care of the oral cavity after visiting the dentist. This is done to avoid complications, speed up wound healing time and relieve stress.
General recommendations include prohibitions on eating and drinking in the next two hours after surgery, carefully rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions for two to three days, and avoiding injuries from spicy, salty or too hot foods. Parents should explain to their child that it is not recommended to touch the socket with your hands and tongue, and if bleeding or pain occurs at the extraction site, you should immediately inform an adult. In the latter case, you must immediately go to the dentist.
Types of anesthesia
If you need to remove a baby tooth that is already loose, this can often be done without anesthesia. In other cases, pain relief is required. Modern anesthesia drugs do not have a negative effect on the child’s body; their use is recommended by the Ministry of Health and STAR (Russian Dental Association).
In dentistry, several methods of pain relief are most often used:
- local anesthesia;
- general anesthesia (anesthesia);
- sedation
Local anesthesia
Methods of local anesthesia used in dentistry to treat children:
- application - the drug is applied to the surface of the tissue, it anesthetizes the mucous membrane for a short time, is used for anesthesia before an injection or before extracting a loose tooth;
- infiltration – the medicine is administered by injection into the mucous membrane of the gums to anesthetize the tissues surrounding the tooth;
- conductive – allows you to anesthetize and block the trunk of the nerve innervating the neurovascular bundle of a given tooth.;
- intraligamentary - a method of anesthesia in which the medicine is injected into the tissue between the root cement and the socket.
When teeth are removed, children often use two-stage local anesthesia: first, the gums are numbed with “tasty” gels or solutions, and then the medicine is administered by injection. For injections, toy attachments are used so that the child is not afraid of the syringe.
General anesthesia
Immersion in a state of anesthesia occurs through intravenous administration of drugs or through a mask. In this state, the child does not feel pain, his muscular system is completely relaxed. Indications for the use of general anesthesia are:
- the need for dental intervention in a child under 2 years of age;
- difficult removal;
- severe fear in the child;
- removal of several teeth;
- allergies to painkillers;
- large volume of treatment
- neurological diseases.
The decision to use anesthesia is made taking into account all the characteristics of the child’s body.
Sedation
The oxygen-nitrogen sedation technique allows the child to remain conscious and respond to the doctor’s questions. Through a special mask, the child inhales gas (nitrous oxide), with the help of which he relaxes and calms down.
Inhalation sedation does not require preliminary preparation (except for eliminating food 4 hours before).
For tooth extraction, sedation is used in combination with local anesthesia: gas inhaled through a mask calms the patient, and the anesthetic numbs the desired area. The effect occurs within a few minutes and ends when the gas supply is stopped.
Oxygen-nitrogen sedation in pediatric dentistry is a safe sedative. Nitrous oxide does not cause addiction or allergies, does not bind to blood proteins and is completely eliminated from the body through the lungs within a few minutes. Oxygen-nitrogen sedation has been used in world dentistry for more than fifty years.
How does tooth extraction occur under anesthesia?
To prepare for surgery, a preliminary visit to the pediatrician and a comprehensive examination are necessary.
Next, you need to follow these steps:
- Preparation at home. The child should not eat 6 hours before the doctor’s appointment, and drink water 2 hours before the doctor’s appointment.
- Anesthesia. Immersion in a state of medicated sleep by administering the drug occurs under the supervision of an anesthesiologist (a specialist is nearby until the patient is induced).
- Delete. Includes extracting the tooth itself and its roots, checking the complete removal of all roots, and treating the wound.
- Coming out of anesthesia.
After waking up, the child remains under the supervision of specialists for several more hours. Parents receive doctor's recommendations.
Anesthesia
Before tooth extraction, anesthesia must be performed, which can be application, infiltration and general.
Application is the application of an anesthetic gel to the mucous membrane and gums, used for high mobility of baby teeth. Infiltration anesthesia involves performing an injection into the desired area of the jaw. It is used for dental diseases, severe inflammation or lack of tooth mobility. General anesthesia or sedation is rarely used in children; it is indicated for fear of dental procedures, allergies to anesthetics, a large amount of work in the oral cavity, or mental illness.
Anesthesia
Before tooth extraction, anesthesia must be performed, which can be application, infiltration and general.
Application is the application of an anesthetic gel to the mucous membrane and gums, used for high mobility of baby teeth. Infiltration anesthesia involves performing an injection into the desired area of the jaw. It is used for dental diseases, severe inflammation or lack of tooth mobility. General anesthesia or sedation is rarely used in children; it is indicated for fear of dental procedures, allergies to anesthetics, a large amount of work in the oral cavity, or mental illness.
Contraindications
Tooth extraction is not recommended in the following cases:
- Acute inflammatory process in the mouth: gingivitis, stomatitis, sore throat;
- Acute infectious diseases of the body: chicken pox, scarlet fever, whooping cough, influenza, ARVI;
- For serious diseases of the body: epilepsy, oncology, heart defects, heart failure;
- For blood diseases that are accompanied by clotting disorders;
- If possible, treat the tooth therapeutically.