Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis is a disease that affects the oral mucosa and is infectious in nature. It is caused by the complex action of spirochetes and fusobacteria. Painful ulcers appear in the patient's mouth, the temperature rises and general health deteriorates significantly. The patient feels muscle aches, headaches and constant mild nausea.
Clinical manifestations of the disease are necrotic and destructive processes affecting the oral mucosa. Most patients suffering from this pathology are men aged between twenty and forty years. The disease has a seasonal pattern - according to statistics, it is most often diagnosed between October and December.
Dentistry is also aware of cases of ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis of a secondary nature - for example, in blood diseases.
Description of ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
This disease refers to infection with a spindle-shaped rod or spirochete, which is called Vincent. World medical dictionaries describe the disease under terms such as trench mouth, sore throat and stomatitis with the presence of various types of ulcers. If the bacterium affects the gums, then doctors interpret the diagnosis as Vincent gingivitis. In practice, there are situations when the infection affects several parts of the human body. For example, the palatine tonsils may be affected, and then this disease is called Vincent's angina.
Causes of infection
The main cause of the disease is resident flora. It is this that causes Vincent’s stomatitis in most people. Microorganisms are found in the oral cavity of every person, but there is a maximum permissible limit. Exceeding the optimal number of bacteria is observed when the rules of caring for teeth and gums are violated. Unsanitary conditions contribute to the proliferation of infectious microbes, which cause necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis. We have looked at the most common cause of painful symptoms, however, there are also the following pathogens:
- Borrelia or Fusobacterium infection
— these microorganisms appear when a person’s immunity and ability to resist infections decrease. You can get stomatitis if you are frozen, have a cold, or are regularly overworked and in stressful situations. As you can see, this type of bacteria can multiply for many reasons;
- damage to the oral cavity, trauma, improper hygiene care
— if the integrity of the mucous membrane is compromised, then optimal microflora conditions are created for bacterial invasion. Very often observed in patients who have experienced periodontitis. The second reason for the manifestation of Vincent symptoms can be careless oral hygiene. So, if there are wounds or cracks, they become clogged, which leads to the development of infectious bacteria;
- complications of viral infection
— if stomatitis is not treated in time, treatment in adults or children may result in serious health complications. As a final result, the disease will move to a new level of danger, for example, leukemia, scorbuta, syphilide and others will form.
Classification of osteomyelitis
In most cases, osteomyelitis of the jaw is a consequence of caries, as well as a complication after periodontal disease.
This group of osteomyelitis is usually called odontogenic (stomatogenous). The infection enters the bone structures through caries-affected molars. In areas of inflammation there is a variety of microflora. These include streptococcus, staphylococcus (white and golden), pneumococcus and other bacteria.
Contact osteomyelitis is a pathology that occurs due to infection of the skin or mucous membrane (for example, with a facial boil). Here are specific osteomyelitis:
- tuberculosis,
- syphilitic,
- actinomycotic.
Sometimes damage to the bone marrow of the jaw occurs due to bacteria entering the bloodstream. This condition is classified as hematogenous osteomyelitis, which occurs after infections such as influenza, typhoid fever, scarlet fever, and measles.
A separate group consists of osteomyelitis resulting from trauma (fracture, severe bruise). Vincent's symptom in fractures, when sensitivity in the area of the mental nerve is impaired and patients note numbness of the lower lip, occurs due to compression of the lower alveolar nerve, formed due to inflammation with exudate.
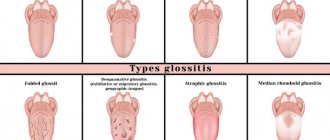
Types of stomatitis for treatment
There are four levels of classification of the disease, each of which has its own subtypes. To determine treatment methods, you must know the correct diagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the types of Vincent’s infectious disease:
- In the division regarding the nature of the course of the disease, acute, subacute, chronic ulcerative-necrotic degrees and relapse are distinguished.
- Regarding the complexity of the disease, stomatitis is mild, moderate and severe.
Each type manifests itself in different symptoms, so in the next section we will look at what the patient feels at each stage of the disease.
The main symptoms of stomatitis in adults
The main symptoms should be considered at different stages of the disease. It is worth noting that the disease progresses and becomes more pronounced over time. When affected by an infection, a person begins to feel weak, he regularly has headaches, there is an increase in temperature and brittleness in the joints. The patient may notice blood on the gums, feel burning and drying of the oral mucosa. Such symptoms torment a person for several hours, and sometimes for several days.
When examined by a doctor, the stage of stomatitis, symptoms and treatment are described. In this case, the optimal course for the stage of the disease is selected. The disease progresses and gradually all its manifestations intensify. The person’s general condition becomes weaker, headaches become more frequent and severe, which affects performance. Over time, the patient feels a sharp pain even with slight contact with the tongue. Brush your teeth
and it becomes more and more difficult to eat, as sharp convulsive bursts of pain occur. At the same time, the patient notices increased secretion of saliva, and also an unpleasant smell of rot from the oral cavity. If a wisdom tooth becomes infected, the ability to open the mouth decreases. This phenomenon in medicine is called trismus.
Some facts about the symptoms of the disease at different stages:
- the first manifestations of the disease are pain in areas of damaged teeth and damaged gums;
- Mild stomatitis is characterized by a limited spread process. At an early stage, only certain types of teeth are affected. The general condition of a person does not undergo significant changes, so performance does not suffer either;
- Severe stomatitis occurs with a body temperature of up to 40 degrees. At the same time, the person feels very bad. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is especially severely affected. In some situations, the infection affects muscle mass and bones. If you do not seek help from a hospital in time, complications of the disease can lead to melting of the jaw bones. You can easily see the image of stomatitis in the photo, the treatment that was started;
- if the infection gets to the site of the palate or tonsil, then this disease belongs to the category of angina ailments;
- in the acute form of stomatitis, the disease can progress to the chronic stage.
- Males are most often susceptible to infection at a young age, namely from 17 to 30 years. The season of exacerbation of the disease is observed in the autumn.
Symptoms
One of the most unpleasant signs of ulcerative stomatitis, in addition to severe pain, is a terrible smell from the mouth, which is formed due to rotting of the soft tissues. In some cases, ulcerative stomatitis is not limited to the oral mucosa and spreads deep inside, affecting many vital organs. In this case, the following symptoms appear on the face:
- sudden increase in body temperature, chills, fever;
- loss of strength, apathy, aches in muscles and joints;
- gums swell, become loose and red;
- severe pain when eating, drinking liquids and when trying to speak, which is why the patient is often silent and sometimes completely refuses to eat;
- Enlargement and tenderness of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes;
- migraine type headaches;
- increased salivation;
- an increase in leukocytes in the blood according to test results;
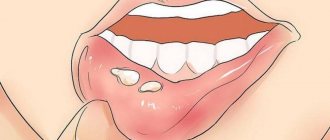
- the number of ulcers is constantly increasing, the older ones are covered with a gray film, when removed, a deep bleeding wound that does not heal for a long time is exposed;
- there is constant bleeding of the gums;
- in rare cases, if left untreated, necrosis can affect not only soft tissues, but also the alveolar process, as a result of which teeth can be severely damaged and even fall out;
- if treatment is neglected, the causative bacteria can spread to the palatine tonsils, which can result in Simanovsky-Vincent angina in both adults and children.
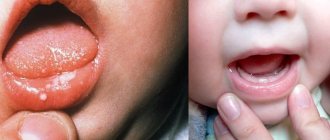
Diagnosis of stomatitis in children for treatment
As we said earlier, young men and young children under 3 years of age are most often affected by the disease. Diagnosing the disease is only possible in a clinical setting. When analyzing, they try to find symbiotic organisms. If their presence is detected, then a course of treatment is prescribed. It is especially important to timely diagnose the presence of infection in young children, since their bodies are still weak to resist infection.
If stomatitis turns into a sore throat, then it is necessary to take an analysis of a sample from the surface of the necrosis or a deeper layer, in case of a complicated form. It is worth noting that Vincent’s illness very often accompanies other dangerous diseases, including HIV, leukemia, syphilis, gingivitis, scorbuta and others. It is for this reason that the examination often includes procedures to screen out the above diseases. When stomatitis is detected in children, treatment is prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment methods for stomatitis
In order to successfully get rid of the disease, it is best to perform sanitation of the oral cavity. After eliminating the pain, doctors can begin to remove ulcers and unwanted deposits. In practice, a course of antibiotics is most often prescribed. So, an adult should drink about 4-5 tablets a day; for a child this norm is reduced to one. Also effective methods of treating the disease include:
- antiseptic substances
- it is recommended to rinse your mouth with them at least 4 times a day; - trichopolum
- for optimal treatment, it is enough to take half a gram per day; - antihistamine therapy
- this method helps to suppress microbial sensitization; - in the vitamin complex
- to maintain the tone of the body, as well as strengthen it, it is recommended to consume vitamin C at least one and a half grams per day; - keratoplastic ointment
- it is used to lyse infectious plaque.
How to treat ulcerative stomatitis with diet?
Diet alone will not be enough to completely cure the disease, but it is mandatory to speed up the recovery process. With such a diagnosis, it is very important to devote time to proper nutrition.
For stomatitis, the following products are recommended: vegetables, fruits, viscous porridges, greens, milk and dairy products, cheese, soups, herbal infusions, green tea, steamed meat without salt, low-fat fish, natural vegetable juices.
Patients with this disease are not recommended to eat: sour fruits and vegetables, citrus fruits, pickled and peppered foods. Also not recommended are foods that provoke allergies, too sweet foods, dry foods and those foods that can cause mechanical damage to the mucous membrane (nuts, crackers, dried fruits, etc.).