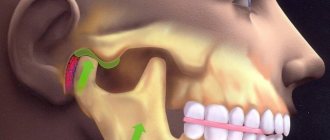
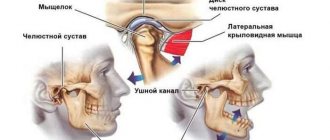
The human jaw joint is quite complex, because we can move the jaw back and forth, left and right, and even in a circle. This process involves not only the articular fossa and the head of the lower jaw, but also the meniscus, capsule and ligaments of the joint. Therefore, arthrosis of the jaw joint leads to a whole complex of disorders associated with degeneration and destruction of articular cartilage. These include digestive diseases (due to insufficient production of saliva and poor quality of chewing food), accelerated tooth wear, problems with vision and hearing, frequent migraines, slurred speech, as well as psychological problems (depression and others).
Let's figure out what arthrosis of the jaw joint is, whether it can be avoided and how to treat it correctly.
The most likely causes of arthrosis of the jaw joint
Before trying to determine the causes of arthrosis of the jaw joint, it is necessary to understand that the pathology is primarily multifactorial, which makes it likely that several prerequisites for its development exist at once.
The group of common causes of arthrosis of the jaw joint usually includes genetic factors and various diseases. Among the local ones there are:
- the presence of a chronic form of arthritis;
- partial absence of molars;
- pathologies of dental tissues (abrasion, etc.);
- violation of prosthetic technology/placement of fillings, especially on chewing surfaces;
- injuries and surgical interventions.
In addition, it is worth noting that among women, the risks of the causes of arthrosis of the jaw joint include a natural decrease and instability of hormonal levels, on which the effectiveness of metabolic processes occurring in tissues largely depends.
A combination of factors provokes difficulties in treatment.
How dangerous is the disease?
Often, arthrosis of the jaw in the first stages is asymptomatic, which leads to prolonged inactivity in the treatment of the pathology. However, ignoring the disease is dangerous. If you notice at least one of the symptoms, you should visit a doctor. In advanced forms of pathology, medications, orthopedics and even surgery are used.
The risk group includes persons:
- over 50 years old;
- females who have reached menopause;
- those who have had injuries and surgeries of the jaw;
- with malocclusion, diseases in the jaw area;
- with damaged or missing teeth;
- with chronic inflammatory diseases;
- with arthrosis of other joints;
- whose family members suffer from jaw joint dysfunction.
Pathogenesis
The study of the mechanisms of development of pathology allowed us to come to conclusions about their progression associated with a lack of physiological endurance of the joint.
The resulting injuries and the appearance of inflammation lead to improper distribution or excessive load on the tissue, which causes disruption of the synchronization of the joints, causing loss of functionality of the muscular system. The result of the development of such unpleasant processes is a disruption of the nutrition of cartilage tissue, as well as a gradual loss of their elasticity, which inevitably leads to destruction.
Simultaneously with all of the above, serious transformations of bone tissue develop, which provokes the formation of growths that modify the elements of the joint: the head of the lower jaw changes shape, and signs of osteoporosis are visible.
As a result of the uncontrolled course of pathological processes, severe deformation and serious disruption of the tissue structure occur.
Treatment of pathology of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
The temporomandibular joint is a complex, paired joint on the skull that is responsible for the closure of the dentition and movement of the lower jaw.
Manifestations of TMJ pathology:
- Violations of facial symmetry, facial shape.
- Extraneous sounds when opening and closing the mouth (crunching, grinding, clicking).
- Inability to open mouth wide.
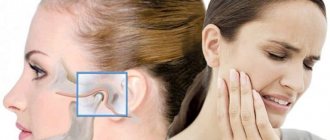
- Painful and unpleasant sensations in the temporomandibular joint when chewing or opening the mouth. The pain may spread to the masticatory muscles and to the head.
- severe headache
, dizziness, pain in the ears and neck. - Noise and feeling of fullness in the ears.
- Reactive enlargement of nearby lymph nodes.
- Pain in teeth when chewing food.
Why do TMJ diseases occur?
- Various injuries in the lower jaw.
- Long-term absence of chewing teeth.
- Adverse habits such as one-sided chewing, onychophagia (nail biting).
- Broken bite.
- Bruxism is the clenching of teeth, grinding or knocking of teeth. Occurs most often against the background of stress, mental or physical stress, or improper closure of teeth. As a result, the activity of the masticatory muscles increases, teeth wear down, joint damage occurs, and pain appears in the ears and masticatory muscles. If this process is not stopped, movement in the jaw becomes limited, and overstrain of the muscle corset of the neck and back occurs, leading to osteochondrosis of the spine, severe headaches, and
sleep disturbances. - Endocrine and infectious diseases.
- Other reasons.
The most common types of TMJ diseases:
Subluxation and dislocation of the TMJ occurs due to displacement of the articular surfaces relative to each other. It manifests itself as the inability to open the mouth strongly, pain, and extraneous sounds during movement in the joint (clicking).
Arthritis
temporomandibular
joint
. Arthritis is inflammation of a joint; there is acute and chronic arthritis. The acute course is characterized by fever, swelling, redness, pain and impaired mobility. In a chronic course, crunching in the TMJ and pain come to the fore; restrictions in the movement of the joint do not appear immediately, approximately by the third week of the disease. In advanced cases, TMJ deformity may appear.
Arthrosis is a progressive degenerative disease that leads to the gradual destruction of the cartilage tissue of the joint. Causes of occurrence: inflammatory phenomena in the TMJ, injuries, metabolic disorders. Arthrosis is manifested by characteristic movement disorders in the TMJ (zigzag movement of the jaw at the moment of opening the mouth), pain, and extraneous sounds when the joint works (clicking, crunching).
Ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint is immobility in the joint, resulting from infectious diseases and injuries. In severe cases, it can manifest as a violation of facial symmetry, malocclusion, multiple caries and lead to complete immobility of the TMJ.
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is usually called various disorders in the system of the joint itself and the structures associated with it. This pathology is associated with various mental and endocrine disorders. TMJ dysfunction is characterized by facial asymmetry, pain and clicking in the joint itself, as well as in the temple and ear area on the affected side, and blocking of the lower jaw. If left untreated for a long time, it can lead to the development of arthrosis.
Diagnosis of pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
There is a test for self-diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction:
| № | Question | Yes | No |
| 1 | Do you have any extraneous sounds in the joint when you move your jaw? | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | Do you notice yourself clenching your jaw during the day or at night? | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | Can you open your mouth completely? | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | Do you have correct posture? | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | Do you experience pain in the TMJ? | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | Do you experience pain in your facial muscles? | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | Have you ever had fillings or crowns chipped? | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | Do you have problems with tooth sensitivity? | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | Are you bothered by ringing or noise in your ears? | 1 | 0 |
| 10 | Do you have worn teeth? | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | Have you noticed changes in the shape of your face? | 1 | 0 |
| 12 | Have you noticed changes in the position of your lower jaw? | 1 | 0 |
| 13 | Do you have fatigue in your masticatory muscles? | 1 | 0 |
If you score 2 or more points, you need to seek help from a specialist.
When examined by a doctor, the patient's breathing, swallowing, chewing, and posture are assessed. The specialist studies how the teeth close in different positions of the jaw and the condition of the masticatory muscles.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing TMJ pathology:
- Various options for radiographic examination (obtaining intraoral and extraoral images, orthopantomography, multislice computed tomography, teleradiography followed by cephalometry and other methods).
- Production of diagnostic jaw models.
- Manual functional analysis of the problematic joint.
- Electromyography, which determines the force of compression of the masticatory muscles.
Treatment of pathology of the temporomandibular joint
- Reducing the range of movements in the TMJ, a special diet, a set of exercises to relax the masticatory muscles.
- Drug treatment, this includes different options for anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
- Correction of the bite, restoration of the number of teeth, correct closure of the jaws.
- If necessary, intra-articular injections are prescribed.
- Washing the temporomandibular joint.
- Physiotherapy: electrophoresis, diadynamic currents and other methods, massage.
- Splinting is used to prevent teeth from closing together during sleep, to relax the masticatory muscles, and to prevent tooth decay during bruxism.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Classification
Based on the results of an X-ray examination, in accordance with the diagnosed changes, it is customary to distinguish between two types of arthrosis:
- sclerosing - changes suggest sclerotic changes in bone surfaces, accompanied by a significant narrowing of the gap between the heads of the bones;
- deforming – there is a significant loss of texture and inherent forms of bone tissue, as well as a significant proliferation of osteophytes.
According to their origin, there are two types of pathology:
- primary – forms independently, without previous diseases/damages, mainly in old age;
- secondary - has a close connection with previous trauma, inflammation or metabolic disorders.
Stages of development of arthrosis of the jaw joint
Regardless of the type/type of disease present, several stages of its development are determined.
Stage I
Diagnosed as joint instability.
Based on the results of the X-ray examination, a moderate and uneven, but clearly noticeable narrowing of the joint space is observed, which is caused by the activation of degenerative-dystrophic changes in cartilage tissue.
Stage II
The clinical aspect assumes full compliance with the general symptomatic picture.
X-ray examination shows that all the changes that occur are characterized by the presence of sclerosis and ossification of the lower jaw.
Stage III
The active progression of pathological processes causes a limitation in the functionality of the jaw.
X-ray examination reveals signs of complete degeneration of cartilage tissue, as well as total sclerosis of the surfaces of articular tissues. In addition, the presence of multiple bone growths, as well as noticeable transformations, is noted.
IV stage
If left untreated, degenerative processes in combination with various types of neoplasms cause fibrous ankylosis of the affected joint.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint
Considering the etiology, it is worth noting that the development of the disease is gradual. Symptomatic signs begin to appear slightly, and therefore the patient cannot always independently notice what is happening.
The initial symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint are clicking, extraneous crunching, and stiffness. Subsequently, during exertion (chewing food or talking), dull pain begins to appear, which can develop into other pathologies (for example, synovitis).
After the first months of symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint, a limitation in the mobility of the lower jaw becomes noticeable. Not only stiffness is observed, but also a displacement of the lower jaw to the affected side with a visually noticeable asymmetry of the face.
It is assumed that symptoms may also include: numbness, tingling of the skin, hearing loss, and even headaches or eye pain.
How to understand what is bothering you with TMJ: 4 obvious signs
If you feel discomfort while talking, chewing, or yawning, look out for these signs:
- Are there any clicks or popping sounds during jaw operation (only 20% of people who notice this symptom complain of pain, however, this is a reason to suspect arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint and go for a diagnosis);
- Is there a feeling of jamming of the joint (if the fossa and the articular head are not in perfect contact, you have to open your mouth as much as possible, trying to find the right point);
- How severe is the pain (can occur when chewing, radiate to the temples, under the tongue, ears, neck, sternoclavicular region);
- Has your general health changed (headache and dizziness, insomnia, hearing impairment, depression and other uncharacteristic manifestations are possible).
With TMJ dysfunction, some patients develop snoring
Diagnostic methods
Medical diagnosis is carried out using x-ray examination, the results of which make it possible to determine the type and stage of changes occurring.
In addition to radiographic diagnostics, in order to make the most accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests of urine and blood, as well as additional instrumental research methods, can be used.
Self-diagnosis reminder
Changes such as:
- the appearance of crunching/clicking sounds when performing various types of movements;
- decreased jaw mobility, manifested when eating, yawning, etc.;
- hearing impairment;
- decreased visual ability;
- pain of a pressing or bursting type, localized mainly in the temporal or parotid-masticatory region of the head;
- periodic convulsions accompanied by painful sensations;
- dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus;
- increased fatigue when chewing food, difficulty eating solid foods;
- partial loss of facial expression;
- numbness of the skin and mucous membranes in the area of the affected joint.
Treatment options
Diagnosis and treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint is carried out by an orthodontist or gnathologist. It is these medical professionals who can determine the primary signs of arthrosis of the jaw and refer the patient to the necessary diagnostic procedures, while establishing the presence of malocclusion or contact between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw.
In rare cases, an additional visit to an orthopedic dentist may be required.
Therapeutic physical education (PT)
The use of gymnastic exercises provides the opportunity to maintain facial mobility, and also helps maintain speech intelligibility and helps strengthen the jaw apparatus.
Systematic implementation of a set of exercises, developed taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease, contributes to the correct distribution of loads, which inhibits destruction and reduces the intensity of the manifestation of the symptomatic picture.
Drug treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint
Treatment using medications is carried out mainly in a hospital setting. However, at home it is allowed to take painkillers prescribed by a doctor, as well as use local warming and analgesic medications.
In order to relieve inflammation and improve jaw mobility, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used, which can be administered to the body both intravenously and orally, for example, using the highly effective drug Artradol.
Additionally, painkillers, glucorticosteroids, antibiotics and chondroprotectors are used.
The duration and frequency of drug therapy is determined by the attending physician. In order to achieve the most effective result, taking medications is combined with other methods.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint
Physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out subject to well-chosen drug therapy and various orthodontic measures.
In order to eliminate pain without surgery, techniques such as:
- exposure to ultrasound/laser/microwaves;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- healing mud;
- performing myogymnastics;
- attending a massage course.
All procedures are aimed primarily at improving metabolic processes and contributing to their normalization.
Surgical intervention as a method of radical treatment
Prescription of surgical treatment is used in situations where conservative methods are not effective. Depending on the degree of neglect of the pathology, the following may be used:
- injection of fluid simulating a healthy joint;
- meniscus prosthetics using cartilage tissue of the auricle;
- partial or complete prosthetics.
Diagnosis and treatment of TMJ athrosis in Altufyevo dentistry
After seeking help from a dental clinic, the patient will be sent for an examination, during which he will need to undergo clinical tests to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. In order to identify dysfunction and prescribe treatment for TMJ, it is necessary to obtain the results of an instrumental examination. Therefore, the doctor gives the patient a referral for:
- ultrasonography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- three-dimensional radiography;
- CT.
After receiving the results, specialists can make an accurate diagnosis and select treatment for each specific case of TMJ arthrosis that corresponds to the stage of development of the disease and the degree of the inflammatory process. Of course, when choosing tactics and methods for carrying out therapeutic measures, doctors at the Denta Lex clinic take into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
Therapy is based on eliminating the cause of the disease. First of all, the doctor will take measures to stop the inflammatory process and relieve the patient of severe pain. Once TMJ arthrosis has been diagnosed, treatment is aimed at restoring the basic function of the joint.
The goal of treating TMJ with arthrosis is the need to stop the process of joint destruction, restore mobility and prevent further development of the pathological process. That is why the chosen methods include TMJ treatment:
- non-medicinal.
- medicinal;
Drug therapy involves the prescription of potent analgesics that help a person get rid of severe, excruciating pain. It is necessary to prescribe and use anti-inflammatory drugs and antipyretics. During the treatment of TMJ, patients receive muscle relaxants and sedatives, and in the most difficult cases they receive intra-articular injections.
Prevention
Preventive measures require the fulfillment of such conditions as:
- maintaining proper and at the same time maximally balanced nutrition;
- optimization of the patient’s motor activity;
- rejection of bad habits;
- ensuring the proper level of oral hygiene;
- systematic attendance at preventive medical examinations.
Do not delay the treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint, because in the first stages the disease is treatable, which allows us to talk about the complete restoration of jaw functionality.
Contacting the Denta Lex clinic
In order to find out in detail what products the doctors at the Denta Lex clinic use to treat TMJ, and what price you will need to pay for therapeutic measures, just contact the clinic using the phone numbers listed on the website. During the telephone conversation, the operator will answer all questions that arise. This way you will be able to clarify not only the price, but also the duration of therapy, features of the procedure, find out the level of qualifications of the doctor and take advantage of the opportunity to make an appointment in advance.
The peculiarity of treatment at the Denta Lex clinic is that it is based on an individual approach to solving the existing problem. The most modern equipment is installed here for instrumental examination and other procedures. All therapeutic measures are carried out at the modern level with the prescription of effective medications.
Before the patient undergoes completely safe and painless, but very effective procedures, doctors will accurately determine the essence of the problem, which will allow it to be solved with the highest quality and in the shortest possible time.